Aerial cables are commonly used for telecommunication networks and are typically installed on towers, poles, and other elevated structures. These cables are designed to provide fast internet, telephone, and television services, making them well-suited for urban areas where supporting infrastructure already exists. But can aerial cables be used to deploy 5G networks?
The answer is yes! 5G has already been rolled out in some areas with outstanding results. The telecommunications sector is preparing to scale 5G adoption, and traditional copper cables are insufficient for this task. As a result, the transition to fiber optic cables has been made in all deployment regions. But why use aerial cables when burying cables can establish seamless connectivity and data transmission?
The article below provides an in-depth explanation of how aerial cable deployment can be used for 5G networks. So keep reading to gain insight into this fascinating topic.
Contents
What are aerial fibre optic cables?
When optical signal transmission is established, there are certain challenges that the teams need to overcome, one of which is long distance. One of the most prominent solutions to the problem of covering long distances is installing aerial cables.
Aerial cables over the burying technique are faster and more cost-effective. But one point of concern is that the aerial cables are exposed to all of the weather and climate elements, which can cause problems in specific regions.
All aerial optical fibre cables have a lifespan of approximately 25 years. These cables can withstand ice, UV rays, heat, rain, and other climatic variations for more than two decades. But, in some specific regions where the atmospheric temperatures vary drastically, these aerial cables can experience contraction or elongation.
Such adversities affect not just the cables but also the supporting structures, which might also affect the fibres within those cables. Therefore, the deployment of aerial cables for 5G networks is opted for based on an assessment of local conditions, such as maximum and minimum temperatures, humidity, sun exposure, and others.
Read More: Introduction to Aerial Fiber Cables
Classification of the Aerial Cables
There are two categories of aerial cables that are used for deploying the 5G networks, which include catenary and self-supported. Choosing among the two depends on the location where it will be installed.
If the cable installation is to be on a path where the supporting structures already exist and there’s no concern about the cable’s span, then catenary cables are the right choice. They can be fixed to the messenger wire that already exists.
But if you consider the self-supported aerial cables, then three different sub-categories fit various case scenarios. They are:
ADSS
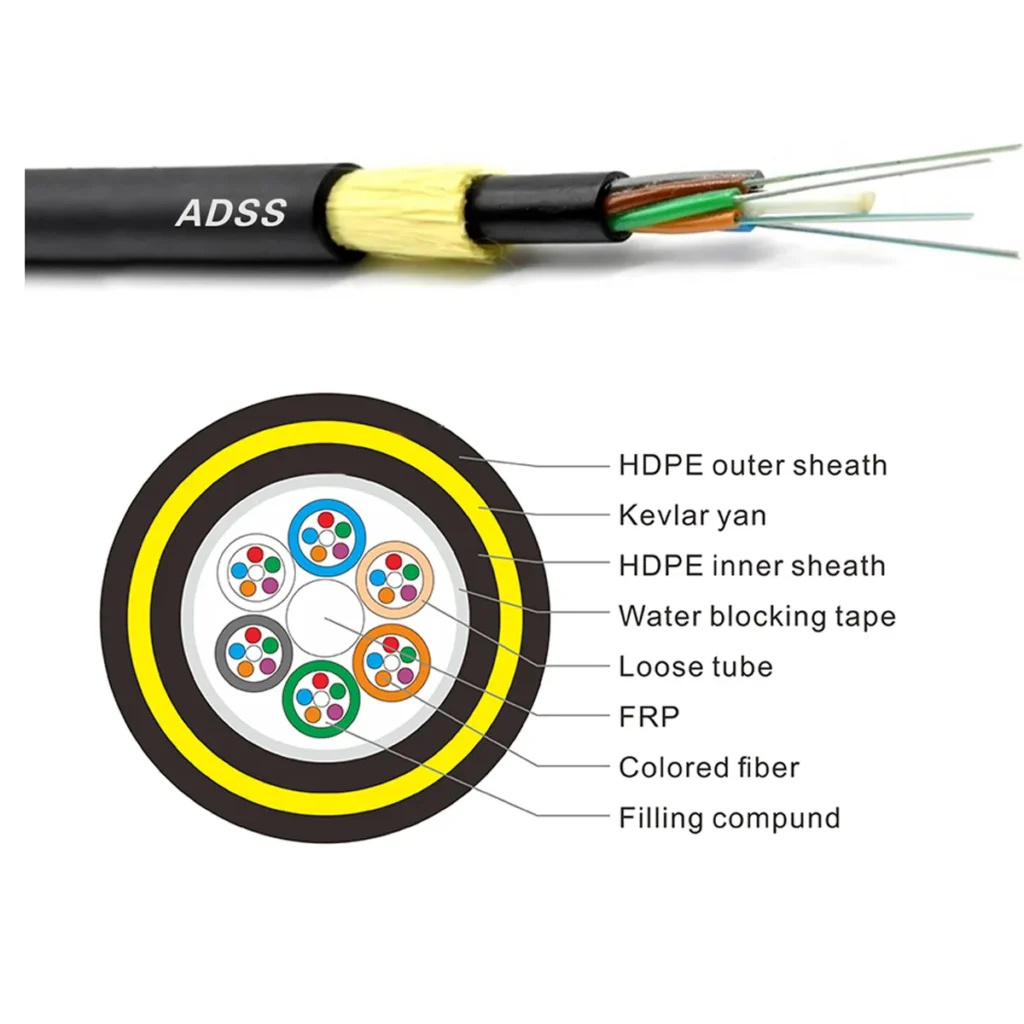
Figure 1: ADSS Cable Components
Image off the Internet
All Dielectric Self-Supporting Cable (ADSS) is a strong aerial cable capable of supporting its weight. While deploying 5G networks, they can be spread for up to 1000 metres on the supporting poles. Hence, it has a very long extending ability, uncommon with standard aerial cables.
Read More: ADSS Fiber Optic Cable: What You Should Know
The fibres installed within these types of aerial cables are kept loose at their core to prevent any form of attenuation due to potential elongation or contraction in them.
- Fig 8
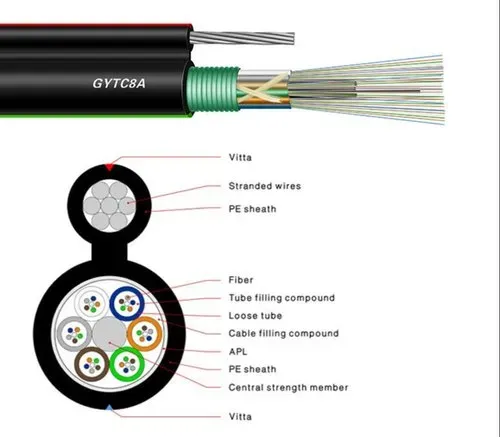
Figure 2: Fig 8 Cable Components
Image off the Internet
The strength element of this self-supported cable is what gives it its name. The vital part of this aerial cable is constructed on its exterior surface, which forms the shape of the number 8 when you cut it. The strength element of this cable is made with either a dielectric material or steel.
These types of aerial cables have the potential to withstand high-tension forces, which support the extension of up to 180 metres. The Fig 8 aerial cables are available in GYTC8S, GYXTC8Y, and GYXTC8S types. And all of them have the same mechanical strength, UV resistance, and water protection capabilities.
OPGW
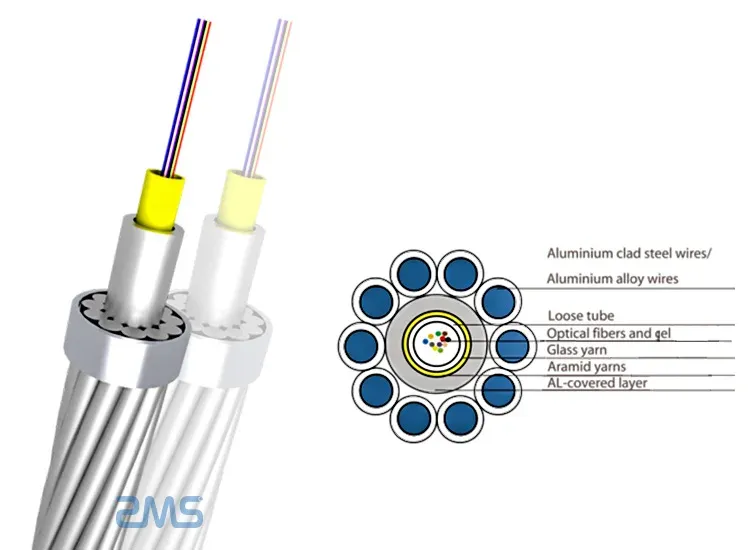
Figure 3: OPGW Cable Components
Image off the Internet
Optical Ground Wire (OPGW) is a fully metallic aerial cable capable of holding large fibre quantities within it. They are standardised for use in power lines and data transmission lines.
They are perfectly fit for deployment to enable 5G networks across regions due to their strength and protective properties. These cables are highly resistant to lightning strikes!
Why are aerial cables being considered for 5G deployment?
Underground fiber optic deployments have been the preferred method for local and government authorities due to their reliability and immunity against weather conditions. However, aerial cables have become a popular alternative for deploying fiber optic connections and 5G networks for various reasons.
The primary reason for using aerial cables is the cost of deploying them compared to burying them underground. Digging deep into the earth to bury fiber optic cables is expensive, and removing obstacles like tree roots and rocks can add to the cost.
Read More: 5G Deployment: For Unmatched Speed and Potential
Additionally, repairing underground cables can be very expensive, and removing them can be difficult or nearly impossible. Aerial cables, on the other hand, are more accessible for maintenance and repair staff and are cheaper to deploy since the supporting structures are already in place in most regions.
The second reason for using aerial cables is their ability to efficiently complete deployment jobs, especially in remote or rural areas where underground deployment can be challenging and time-consuming. Aerial fiber optic cables offer a faster and more efficient solution for expanding 5G networks and FTTH projects. The connectors for aerial cables are also easy to plug in, eliminating the need for on-site splicing, and the components of aerial cables are resistant to various environmental obstacles, such as temperature fluctuations, vibrations, torsions, and external pressure.
In conclusion, while underground deployments of fiber optic cables remain reliable and immune to weather conditions, aerial cables have become a cost-effective and efficient alternative for deploying fiber optic connections and 5G networks, especially in remote or rural areas.
Conclusion
5G is fundamentally going to upgrade the entire telecommunications sector. The demand for faster connectivity is now at its peak across industries and the public. As more and more devices are connected to the internet, fibre optic connections are experiencing high demand due to their capabilities of providing ample bandwidth.
Therefore, industries are contributing their strategies for using the right set of cables, as per varying environments, to support the faster deployment of 5G networks and FTTH projects.
To learn more about it, click here and access the insights offered to you by STL Tech!
Frequently Asked Question
Some of the critical factors that operators consider when deploying aerial fibre cables are:
Verifying and planning the cable trajectory
Assessing the climatic and temperature conditions around the location
Choose the installation method for the cable, whether to go with a stationary reel or a moving reel method.
Plan the distance between the support points of the cable.
Determining the area where you can install the distribution boxes.
Other factors that may also be important include assessing the structural integrity of existing poles or support structures, obtaining necessary permits and approvals from local authorities, ensuring proper grounding and lightning protection, and conducting thorough testing and inspections before and after installation.
Additionally, operators may also need to consider factors such as the capacity and speed requirements of the network, as well as the potential for future expansion and upgrades.
Here are some benefits of using aerial fiber cables for 5G network deployment over other types of cables:
Cost-effective: Aerial fiber cables are often less expensive to install compared to underground cables, as the latter require digging trenches and laying conduits.
Faster deployment: Aerial fiber cables can be deployed faster than underground cables, as they don’t require extensive trenching and excavation work.
Easy maintenance and repair: Aerial fiber cables are easier to access and maintain, as they are visible and can be reached with bucket trucks or other aerial equipment.
Flexibility: Aerial fiber cables can be easily rerouted or modified to accommodate changes in network infrastructure or to avoid obstacles such as trees and buildings.
Compatibility: Aerial fiber cables can be installed over existing utility poles, reducing the need for additional infrastructure and minimizing disruption to the environment.
Scalability: Aerial fiber cables can be used to expand network coverage quickly and efficiently, making them ideal for 5G network deployment in rural or remote areas.
Overall, aerial fiber cables provide a cost-effective, flexible, and scalable solution for 5G network deployment.
5G doesn’t just need fibre optic cables; it also needs a huge number of fibre counts with enhanced density. 5G demands high frequencies to handle the heavy load of data. Thus, traditional copper cables cannot cope with this demand, for which fibre cables are used on a priority basis.
















