With the emergence of the digital era, business houses are registering good growth, and the demand for faster and more secure networks has multiplied tenfold. This increased demand necessitates an immediate move to fiber optic technology to meet the challenges and opportunities that the new-age startups and the prominent players can potentially tap into. Moreover, fiber optics not only supports varied industries but also benefits households. As a result, we can expect significant improvements to our quality of life as we continue to tap and fully unlock the power of 5G in the years to come. A recent market study reveals that the fiber cable market will grow at a rate of 8.5% in the next year, reaching approximately 7 billion dollar value by 2025.
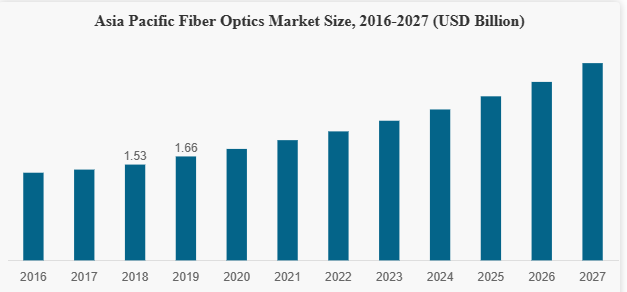
Fig 1: Fiber optics market size for the Asia-Pacific region
Image credit: fortunebusinessinsights.com
Contents
Challenges in deploying a hyper-scale network
With increased demand, the expectation is to ensure the technology continuously performs better and, at the same time, scales to meet the varied needs of any growing economy. These networks will transform the next digital revolution and connect thousands of devices across diverse domains. The most common challenges that we face during any deployment include the following:
- Multiple approvals are required at different stages of the fiber rollout process
- Time and cost overruns that are more often than not unavoidable
- Surveys that provide sub-optimal results and deter good decision making
- Availability of unskilled or partially skilled workforce
- Limited automation with many manual processes for planning and all day-to-day operations
Hence, we must have a seamless design, rollout, and well-planned deployment. There is plenty of scope for improvements like upskilling people with virtual reality technologies, utilizing drones for more comprehensive surveys, having proper workflows for multilevel approvals, and automating planning, operations and executions. Gartner research points out that by the close of 2024, 60% of service providers will commercialize 5G services covering at least all major cities by then.
Fig 2: Growth rate of the fiber optic cable market
Image credit: mordorintelligence.com
Fibre optic deployment strategies
One can use multiple deployment strategies, depending on the environment and demography. What also needs some consideration is the ease of maintenance post-deployment. Most deployment costs primarily account for the plumbing and cable laying works. These costs account for more than 60% of the total project costs. Also, deployments can happen above the ground, under the ground, and beneath the ocean. We will cover each of these in more detail.
Aerial Deployment:
In this deployment mode, environmental factors significantly affect the overall fiber rollout services. The overall pressure that cables are subjected to depends on climatic conditions and wind speeds.. Aerial cables are one of the cost-effective means of deploying to last-drop connections. To understand why this is cost-effective, the operators use existing poles built for electricity or other fixed lines to run the fiber cables. The costs are further saved as there is no purpose in digging up and relaying roads to bury the cables. Considering the different pain points, aerial cables are more often than not fragile and can break under rough weather and temperature variations seen due to global warming. Therefore, it is crucial to determine the length of aerial cabling and the strength tolerance of the poles and cables during the planning and survey phase to identify suitability for aerial deployment. We must have all approvals from regulatory agencies and an existing pole network that is suitable and strong enough to run fiber cables to choose this deployment mode. Cheap labor and materials further reduce costs in such a type of deployment.
Buried Cable Deployment:
The primary advantage of this type of underground fiber deployment is the limited exposure to harsh environmental factors. Also, the reliability of such underground deployments is at least ten times higher than the aerially deployed fiber cables. On the flip side, the deeper you plan to bury, the more your operational expenses. This additional digging will eventually increase the cost of services, although reliability, in this case, would be the unique selling point. However, tree roots can come up as obstacles and further increase costs. Additionally, relaying and maintenance will cost due to the digging effort each time there is any breakdown. Finally, expensive repairs can cause cost overheads for operators.
Ocean Deployment:
A majority of international communications happen through cables running in the sea beds. Telecom carriers and technology giants own up and build these cables. The cables run several feet underwater with an open design and advanced transmission system. Improvements can be seen across the bandwidth, spectrum, and capacity when we choose the ocean deployment mode for rolling out fiber optic services. The only part of the equation is that the costs overshoot and this is a future deployment option when data demand rises significantly. Google has funded multiple submarine cables in the last decade or so. Growth in the cloud and internet of things domain drives such deployments and rollouts under the ocean.
Importance of terrain for deployment and rollout of fiber cables
Amongst the different terrains on this planet, the operators could lay fiber cables alongside mountainous rocky terrain, sandy terrain or clay soil. Each landscape is unique, and the deployment should consider the terrain type before narrowing to one of the deployment modes. For example, an aerial deployment would suit a rocky terrain, given the ease of putting poles here. Meanwhile, when you have sandy soils, you can build trenches for all the fiber cabling needs. If you look at a clay terrain that contains rocky impediments, this could increase digging costs. Also, deeper trenches with fiber cables enclosed in thicker padding are necessary. If the surface has tarmac or asphalt, digging costs are ten times more than digging a shallow trench on sandy soil. The workforce or automated robots can use innovative technologies like slot cutting in trickier environments without duct infrastructure. However, the drawback with slot cutting is that the cables are prone to breakage when there is relaying of roads as these cables run at the top.
Speeding up fiber rollout
A mix of automation and processes is required to generate speedy fiber rollout services. Advanced technological breakthroughs, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, help create plans to deploy fiber cables. Surveys and geographic mapping technologies suggest the ducts, trenches, deployment modes, and terrain layout for an optimal fiber layout. There will be a corresponding cost saving on manual surveying, and by automating, we can ideally ensure these costs are a bare minimum. Innovative trench construction techniques like micro trenching save the cost and labor involved and speed up deployment time. The traditional method of digging up and laying cables cannot achieve the output and speed achieved by micro trenching. It doubles up the rate of completion of projects, thereby ensuring faster fiber rollouts. Robots, when used in specific terrain settings, can reduce manual labor to a great extent. They can perform a range of work from digging up trenches to laying the fiber cables while minimal supervision from humans is all that is required. Integrating these robots eliminates the need for skilled resources in your workforce and further speeds up the actual fiber rollout. With augmented reality and virtual reality still nascent, there is sufficient innovation in this area to utilize the technology to offer practical on-the-job training to the workforce. The headsets help simulate real-time scenarios and have sensors to guide you through each activity while wearing the VR headsets. This technological breakthrough will cut down the initial training period and considerably reduce training costs.
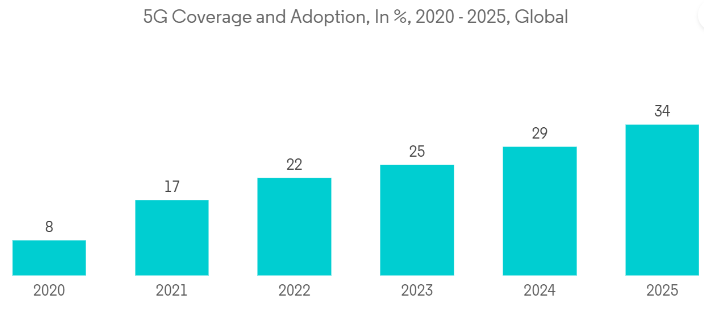
Fig 2: Global 5G coverage and adoption
Image credit: mordorintelligence.com
Conclusion
Findings have pointed out that many fiber deployments have been delayed or failed primarily due to external factors, such as digging or relaying work for installation and maintenance. The workforce must follow adequate procedures and best practices to mitigate such factors early in the design phase. The other crucial factor that has caused delayed rollouts is the non-existence of skilled staff. Upskilling and automation are necessary to solve this problem, ensure quality, and reduce fiber damage.
A better analogy would be to compare how the optical fibers have started growing across the nation like a dense network similar to how electricity cables panned out ten decades back, connecting the remotest parts of the country. Building hyper-scale fiber cable networks would have innovations at the core of the optical fiber design. For example, a reliable fiber cable deployment with little or no interruptions can offer good quality, lightning speed, and high availability.
Learn more about STL’s Fibre Deployment Services, click here.
FAQs
1. What are some of the primary challenges encountered while deploying a hyper-scalable fiber network?
The hyper scalable fiber network is responsible for the digital revolution. But, there are certain challenges that are hurdling the deployment pace, which includes:
- There is a need for multiple approvals at all stages of deploying the cables.
- The cost and time extends due to unavoidable situations
- Incomplete surveys result in poor decision making
- Lack of good workforce
- Automation possibilities are very limited
2. What is the aerial deployment of fiber optics?
Aerial deployment of the fiber optics states that the cables will be used for outside applications and will be installed over the poles. The design of such aerial cables are robust to withstand the weather and man-made adversities. This cable is mostly rolled out between the electricity pylons and the utility poles.
3. Why is the ocean deployment of a fiber network considered as a future-centric deployment method?
By choosing the ocean deployment method for the fiber network, the bandwidth, capacity and spectrum increases immensely. Even though the cost overshoots, this deployment strategy is a futuristic move, as the data demand is rising significantly. The consistent growth of IoT and cloud applications will make this deployment more common in the future.
4. How can we speed up the fiber rollout process?
There is a substantial need for automating several processes to ensure the fiber rollout services are carried out at a faster pace. AI and ML concepts are to be implemented for creating advanced plans on deploying the fiber cables. In this way, there will be no unwanted delays due to inaccurate surveys or assessment of the deployment lands.














