Gaining incredible traction since the 21st century began, cloud computing has become the talk of the town. Consider any sector, like education, food, beverages, IT, or any other, where cloud computing has become the core of operations. Any network service that aims to serve individual customers or large enterprises must employ cutting-edge communication technologies to effectively handle cloud computing demands.
Fig 1: How do fiber optics prove instrumental in cloud computing
Image credit: versitron.com
To cater to the everyday requirements of personal data as well as stores of data being generated and managed by large enterprises, cloud computing technologies need to run on an infrastructure that offers seamless connectivity and massive data handling capabilities.
Fiber optic interconnects provide high-bandwidth and low-latency connectivity, making them an ideal infrastructure for cloud computing operations.
Contents
Understanding What is a Fiber Optic Interconnect
Modern data centers and telecommunications networks require an infrastructure that can handle multiple high-performance components simultaneously. Fiber optic interconnects are used to connect different parts of a fiber optic system and are typically made up of one or more optical fibers. These interconnects provide high-bandwidth, low-latency connectivity, making them the preferred option over traditional electrical interconnects for copper-based communication networks.
Fiber Optic Interconnects vs. Copper Interconnects
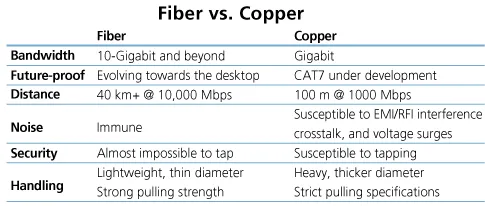
Fig 2: Key differences between fiber and copper interconnects
Image credit: data-connect.com
While businesses relied heavily on traditional copper connections in the past, fiber optic interconnects have emerged as the preferred option for business applications that function with large data loads.
Here are some differentiating factors that make fiber optic interconnects superior:
1. Transmission speed – Copper cables transmit data through the movement of electrons, and the maximum data speed for copper cables is typically around 10 gigabits per second (Gbps), although some advanced copper-based technologies can support higher speeds.
In contrast, optical fibers use light to transmit data, which allows for significantly higher transmission speeds. The theoretical maximum data speed for optical fibers is around 100 terabits per second (Tbps), although in practical applications, speeds are typically lower. However, speeds of up to 60 Tbps have been demonstrated in laboratory settings, making optical fibers capable of transmitting data at much higher speeds than copper cables.
2. Distance – Optical fibers are a superior option if you want to send data over large distances. Some single-mode fibers are capable of carrying data up to 25 miles, whereas copper cables lose about 90% of their data within 100 meters.
3. Network reliability – Being a good electrical conductor, copper cables are susceptible to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI), which causes network interruptions. Optical fiber is impervious to moisture and temperature changes. Additionally, optical fibers don’t present a fire hazard as copper cables do.
4. Security – Since optical fibers don’t run on electrical signals, the data carried in optical fiber cables are impossible to tap into. Networks transmitted through copper cables can be tapped, which can hamper connectivity.
5. Associated costs – While copper cables may seem to be more economical initially, there are hidden costs associated with their deployment and maintenance over time. Copper cables require regular maintenance and replacement, especially in harsh environments where they are more susceptible to damage and wear.
Additionally, copper cables are less secure than fiber optic cables, making them more vulnerable to security breaches and cyberattacks. As a result, organizations may need to invest in additional security measures to protect their networks, adding to the overall cost of deploying and maintaining a copper-based network.
In contrast, fiber optic cables are more durable and have a longer lifespan than copper cables. They also require less maintenance, making them more cost-effective in the long run. While the initial investment in fiber optic cables may be higher, the lower maintenance and replacement costs, combined with the increased security and reliability of the network, can make fiber optic networks more cost-effective over time.
Primary Cloud Service Models
Initially, cloud computing was only implemented for remote job entry and time-sharing and was utilized by large internet-based service firms like IBM and DEC. However, after 1970, cloud computing was adopted by IT organizations for core IT applications.
In the digital era of communication, cloud computing finds its uses in areas like service-based infrastructures, high-capacity networks, remote data management, etc. The core cloud service models are
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
To yield the maximum results for these data-intensive applications and make network service dependable, cloud computing needs to be optimized.
How do fiber optics augment cloud computing networks?

Fig 3: How fiber connectivity is advantageous to businesses
Image credit: cables.com
Here’s how fiber optic interconnects bring out the maximum efficiency in cloud computing networks:
- Higher bandwidth – Optical fiber enables the transmission of large amounts of data over a large bandwidth. This proves especially useful for large-scale data transfers and high-definition online streaming and video applications. Optical fibers are commonly used to connect cloud servers and data centers, with data transmission rates up to several terabits per second, depending on the type of fiber and equipment used.
- More energy efficient – Since data is transmitted using light in optical fibers compared to copper interconnects, which require electricity, there are significant cost savings when enormous amounts of data are transmitted over cloud networks.
- Lower attenuation – Signal loss is very less even over large distances in the case of optical fibers. The typical intrinsic attenuation for single-mode fibers is approximately 0.40 dB/km at 1310 nm. This value is a little higher for multimode fibers. However, they don’t require signal repeaters like copper interconnects need, resulting in an efficient cloud network.
- Scalability – Optical fibers deliver the perfect amount of scalability to keep pace with the expanding cloud environments and sophisticated applications. High-density optical fiber cables with wavelength division multiplexing permit rapid cloud network scalability, something that copper interconnects don’t allow.
Final Thoughts
With the risk of disasters and extreme weather conditions, fiber optic interconnects can ‘weather’ the storm better than traditional electrical interconnects. This ensures that cloud networks actually offer what they promise – 24/7 high-speed network connectivity and availability.
STL is innovating the way to faster and more reliable cloud computing services with its modern optical fiber solutions that make unreliable network serviceFiber optic interconnects a thing of the past.
To know more about STL’s optical interconnect products, click here.
FAQs
1. What is a fiber optic interconnect?
They are optical fiber cables that are used to connect the various components of a fiber optic network.
2. What are the primary cloud computing service models?
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) are the three main cloud computing models implemented by the majority of enterprises.
3. How do optical fibers perform on the level of attenuation?
Optical fibers have significantly lower signal loss or attenuation compared to copper cables over long transmission distances. This is because optical fibers use light signals to transmit data, which have very low loss as they travel through the fiber. On the other hand, copper cables use electrical signals that experience significant signal loss over long distances due to factors such as resistance and interference.
The actual amount of attenuation in optical fibers can depend on various factors, such as the quality of the fiber, the wavelength of the transmitted light, and the distance of the transmission. However, in general, the attenuation of optical fibers is much lower than that of copper cables, making them a preferred choice for high-speed and long-distance data transmission.














