Fibre technology is not only known for its high-speed internet capabilities but also for its positive impact on the environment. Unlike copper broadband, fibre uses sustainable materials, leaves a smaller carbon footprint, and reduces waste and pollution. The internet currently accounts for 3.7% of global carbon emissions, which are projected to double by 2025. This has led to a growing concern about environmental damage, prompting individuals to seek more sustainable practices. Although the internet within homes has a minimal environmental impact, the broader internet infrastructure contributes significantly to carbon emissions. By switching to fibre internet, users can support a more environmentally friendly option for internet service.
Contents
- 1 The Global Impact of Networks on Carbon Dioxide Emissions
- 2 Innovation And Productivity
- 3 Cable Internet Consumes More Energy Compared To Fiber-optic Connections
- 4 Fibre Employs More Environmentally Friendly Materials
- 5 Fibre Optic Technology Necessitates Only Minimal Maintenance And Upgrades
- 6 Fibre Has Been Constructed With Long-lasting Durability In Mind
- 7 FAQs
The Global Impact of Networks on Carbon Dioxide Emissions
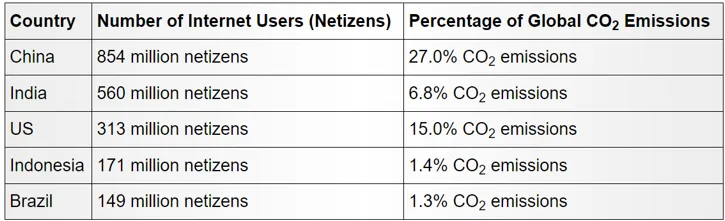
Fig. 1: Country-wise CO2 Emission
Image Credit: 8billiontrees.com
Global carbon dioxide emissions amount to around 39.9 billion tons. Simple calculations show that the Internet has a significant carbon footprint, contributing approximately 4% to global CO2 production. This percentage surpasses the emissions of any individual country except for the USA, China, and India. Furthermore, it exceeds emissions from the aerospace industry, which is commonly regarded as a major contributor to air pollution through CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions.
Innovation And Productivity
Fibre-optic internet has the potential to stimulate creativity and effectiveness across multiple sectors and fields by facilitating the advancement and acceptance of emerging technologies like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, big data, and the Internet of Things. Moreover, fiber-optic internet can amplify the capabilities and effectiveness of current applications like video conferencing, online gaming, e-commerce, and telecommuting.
Cable Internet Consumes More Energy Compared To Fiber-optic Connections
Fibre optic internet consumes significantly less energy than cable internet, making it a more sustainable choice. Fibre optic technology uses up to 12 times less energy when transmitting data than coaxial cables. For example, fibre optics require less than 1 watt to transmit data over 300 meters, while coaxial cables need around 3.5 watts for only 100 meters. This energy efficiency leads to lower heat generation, eliminating the need for coaxial cables’ cooling systems. Coaxial cables average an additional 3,000 to 5,000 watts per hour for cooling.
In contrast, fibre optic does not require cooling, resulting in even more energy savings. As a result, fibre optics emit significantly less carbon dioxide than cable internet. As a result, fibre optic internet offers substantial energy savings, reduced heat generation, and lower carbon emissions than cable internet.
Fibre Employs More Environmentally Friendly Materials
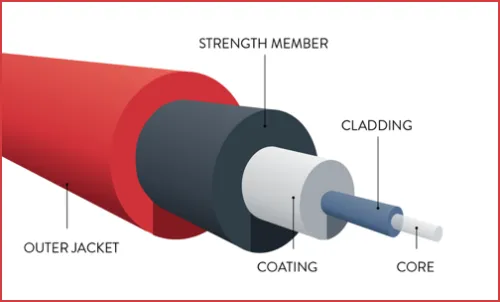
Fig. 2: Fiber Optic Cable
Image Credit: ofsoptics
Traditional cables made of copper wire transmit connections as electrical signals, but copper extraction has significant environmental impacts. It affects biodiversity, generates waste, contaminates groundwater, and has a high carbon footprint. Fibre optic cables, made of glass, transmit data as light beams using abundant silica. Though fibre cables have an environmental cost, it is far lower than copper extraction.
Fibre optic cables are constructed using silicon dioxide, a naturally occurring compound derived from two abundant elements found on Earth: silicon and oxygen. Quartz is a form of silicon dioxide known to collectors of rocks, while those who frequent beaches may recognize it as the primary constituent of sand. It is not a scarce resource and requires no mining procedures for extraction.
Reducing metal extraction, like copper, is key to limiting global warming. Fibre optic cables offer a more sustainable alternative, minimizing environmental harm. Their production conserves resources, reduces waste, protects groundwater, and lowers carbon emissions. Embracing fibre optics is crucial for a sustainable digital future.
Fibre Optic Technology Necessitates Only Minimal Maintenance And Upgrades
Fibre optic technology offers a green and economical advantage through its durability. Fibre optics is less prone to weather disruptions than cable, DSL, or satellite, resulting in fewer repairs and updates. Repairs are 67% faster than cable or DSL, even when fibre networks go down. Additionally, fibre optic’s limitless bandwidth capacity eliminates the need for frequent updates. Unlike other internet types, ISPs can operate a fibre network for up to 25 years without updates. This durability and bandwidth capacity make fibre optics environmentally friendly and cost-effective, reducing the carbon footprint and expenses associated with maintaining and upgrading networks.
Fibre Has Been Constructed With Long-lasting Durability In Mind
Fibre optics are future-proof, far surpassing the gigabit speeds offered by current internet providers. With 10 Gbps broadband becoming commonplace, the existing fibre cables installed in homes can easily handle these speeds. In addition, fibre cables are designed to last for decades and exhibit increased resilience during major storms. Unlike traditional copper cables, fibre networks can be upgraded without replacing the cables themselves, ensuring long-term viability. This minimal long-term impact means they remain in place once fibre networks are installed. Routine maintenance is required, but complete cable replacements are unnecessary. Fibre optics offer a durable, adaptable, and cost-effective solution for high-speed internet, capable of meeting the evolving demands of the digital age.
FAQs
Optical fibres are a sustainable choice due to their economical and space-efficient nature compared to copper-based networking systems. In addition, STL, a company with nearly 30 years of experience in manufacturing optical fibres, has been committed to innovation, aiming for smaller form sizes, reducing plastic usage in installation, and adopting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Optical fibre is an excellent medium for transmitting light signals and typically does not require amplification like copper cables. However, there is a minimal loss of power in optical fibre, known as attenuation. High-quality single-mode fibre can have an attenuation rate as low as 0.1 dB per kilometer.















