
5G networks are hailed as the next-gen wireless phenomenon with higher speeds and expanded connectivity excellent for modern edge devices, cloud computing, and remote working. India stands on the threshold of a change with 350 million 5G subscriptions estimated by 2026 with transformative capabilities.
Contents
What is a 5G network?

Humans always strive for the best, the fastest, and the largest. 5G is the latest in line with the existing 2G, 3G, and 4G mobile communications standards. It is the communications standard par excellence where users can now download data from the internet even faster.
It also enables fast communication between devices, sensors, and machines in the IoT. 5G networks are significantly faster than 4G, with peak data transfer rates of up to 20 Gbps. They can transmit data with a high reliability of up to 99.9999%! This means a data transfer without delay with an extremely low latency of one millisecond!
The full 5G system includes
- eMBB (enhanced Mobile Broadband)
- uRLLC (ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications)
- mMTC (massive Machine Type Communications).
eMBB primarily focuses on higher data rates and bandwidth for prolonged internet connectivity-based applications. This technology enables human-centric connectivity, including access to multimedia content, services, and data. The current mobile broadband use cases include hotspot connectivity, development of AR (Augmented Reality) or VR (Virtual Reality) media and applications, Wide-area coverage, UltraHD or 360-degree streaming video, industry automation, work on the cloud, etc.
uRLLC (ultra-Reliable Low Latency) provides extremely low latency and extremely high-reliability support. Specifically, it targets machine communications. It will cover remote medical surgery and operations, mission-critical applications, wireless control of industrial production and manufacturing, and driverless automobiles that are particularly latency-sensitive.
mMTC (massive Machine Type Communication) enables the simultaneous collection of a huge volume of small data packets from a large number of devices. The focus of the mMTC is on providing connectivity to a massive number of devices. Through the use of IoT, mMTC will reduce energy consumption and make work more efficient.
Benefits and Challenges of 5G Network
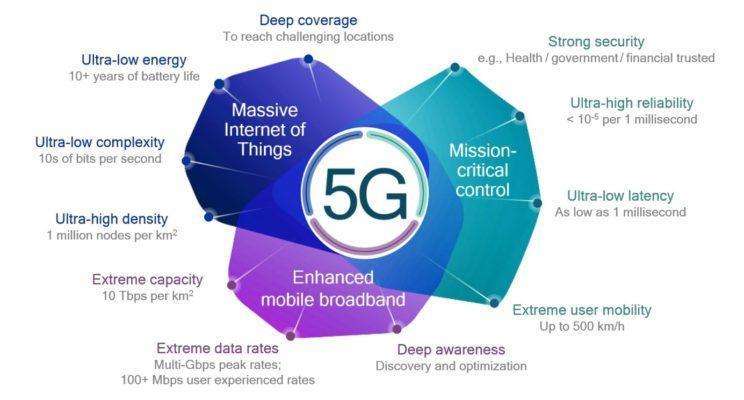
5G networks have limitless benefits across multiple industries, ranging from manufacturing to social, economic, healthcare, education, and agriculture. Increased digital inclusion with 5G networks will power innovation and facilitate improvement in service quality. Such networks have the capacity to deliver content much faster than 4G. With high speeds of up to 20 Gbps, they will enable superfast download times.
The low latency characteristic feature will efficiently help support new applications such as IoT, AI, and virtual reality. Also, more bandwidth will help with faster data transfer. 5G technology can be used to connect with a whole range of different devices, such as drones and sensors.
With all its pros, 5G networks also come with evident challenges. They might lead to overcrowding in the radio frequency spectrum. Moreover, rural areas might require more attention in terms of setting up more transmission towers and antennas for better network coverage. Also, the existing towers need to be upgraded to handle the increased amount of bandwidth provided by the 5G network. Moreover, the issues of security and privacy still loom at large.
How will 5G impact the industry?
Industrial 5G networks have the full capability to cope with the increasing demand for company data and generation. Such networks can be used to implement several key use cases in the manufacturing sector with industrial automation and robotic control to provide intelligent factory solutions.
Companies can employ industrial 5G technologies for end-to-end tracking of goods and materials and simulation of factory processes. They can also be actively used for immersive remote operations related to service, maintenance, or assembly. They can also be used for real-time machine-to-machine communication, augmented reality applications, and monitoring products and asset data.
The economic impact of 5G on industries
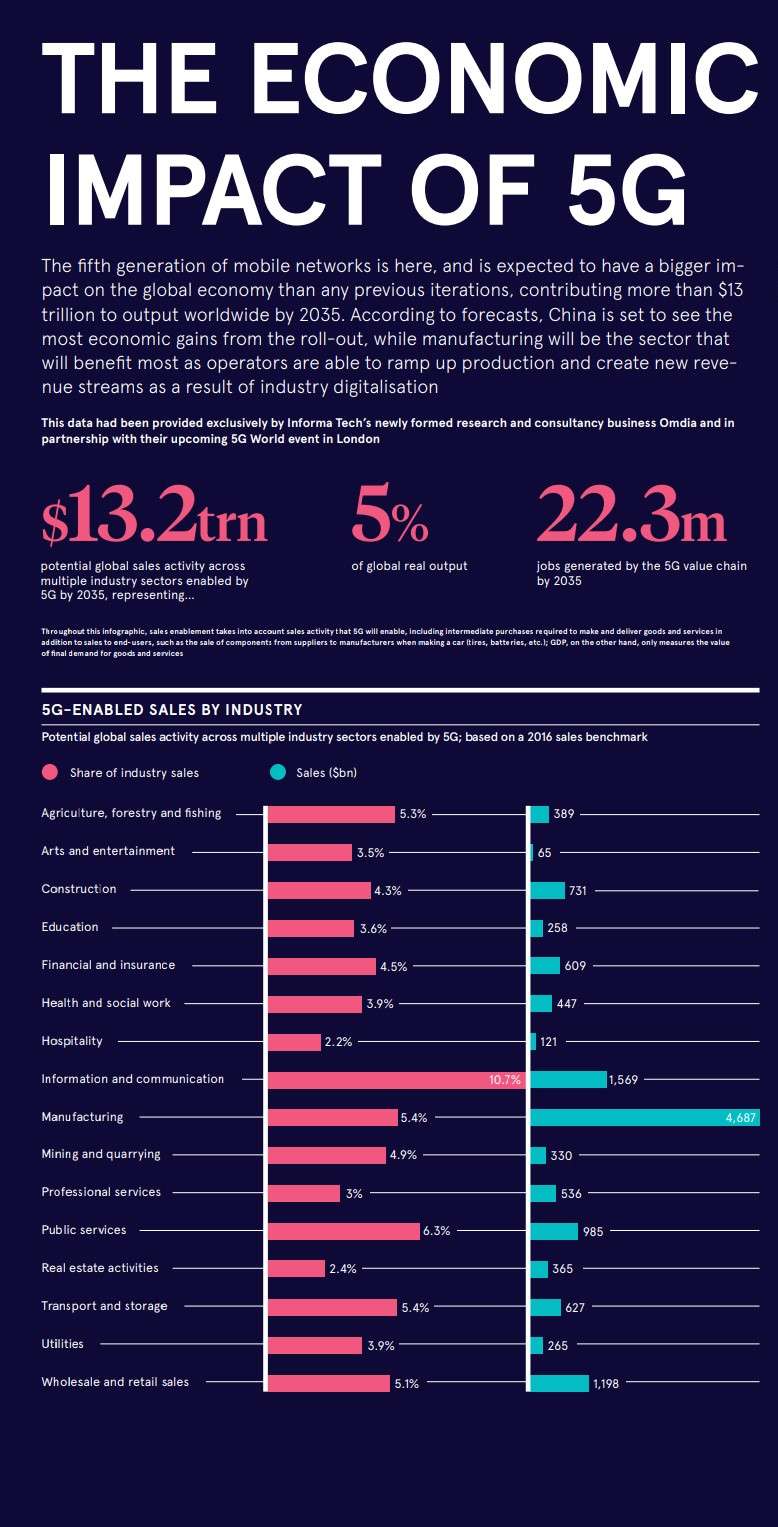
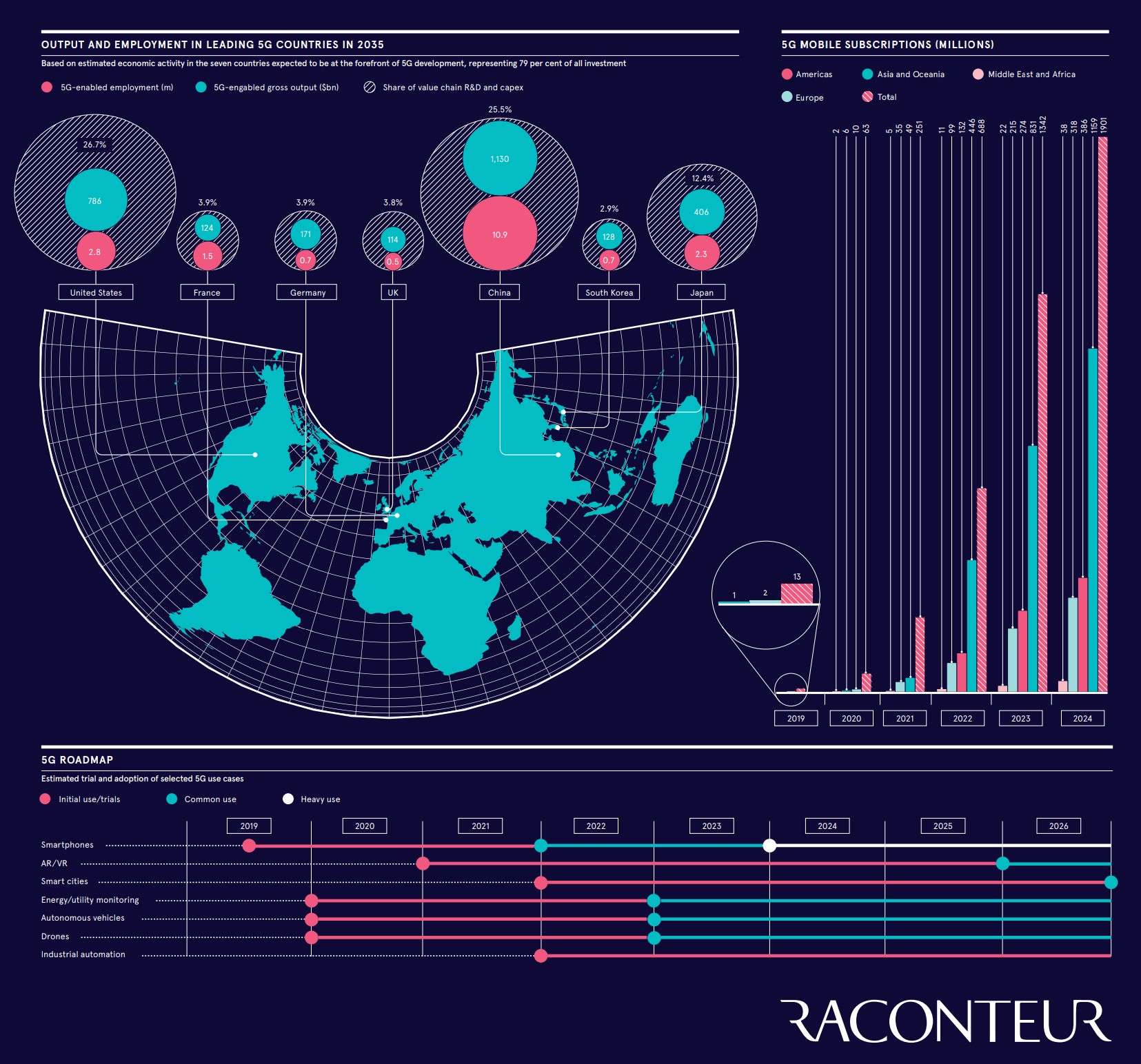
5G networks are fully capable of creating socio-economic value. At the same time, the impact of 5G technology will be significant on specific industry sectors. 5G networks are expected to create $13.2 trillion in revenue in global sales activity by the year 2035.
The top 5 industries which are expected to gain maximum profit are:
| Rank | Type of Industry | Sales ($B ) | Share of Industry Sales (%) |
| 1 | Manufacturing | 4,687 | 5.4 |
| 2 | Information & Communication | 1,569 | 10.7 |
| 3 | Wholesale & Retail Sales | 1,198 | 5.1 |
| 4 | Public Services | 985 | 6.3 |
| 5 | Construction | 731 | 4.3 |
For example, the manufacturing industry will witness smart factory advancements due to IoT and automated manufacturing.
Similarly, the mobility sector will benefit from autonomous driving, massive car infotainment, and connected travel with telematics. Smart traffic control and remote vehicle health monitoring will be possible.
With an increasing demand for data storage and patient safety, the healthcare industry will benefit from 5G services. The role of 5G in remote patient monitoring, remote surgery, and AR/VR-enabled healthcare will be massive. Some of the advantages offered by 5G to the healthcare industry are
- Easy and fast transfer of large imaging files (ex: MRI, PET, etc.)
- Expansion of telemedicine
- Enhanced AR, VR & spatial computing
- Dependable and real-time remote monitoring of patients.
The Fintech sector can finally incorporate wearables for payment and smartphones as remote tellers. Widespread peer-to-peer lending, digital deposits, and virtual personalized financial advisory services will now become possible.
Energy sector industries can now have enhanced smart grid and drone monitoring capabilities with smart energy management and hazard sensing.
Some of the research related to the impact of 5G on the economy may lead to the following outcomes in the future:
One billion users are estimated to have access to 5G technology by 2023. It is set to take data transfer capabilities to an entirely different level, with speeds as high as 1 Gbps.
Qualcomm surveys state that 5G-related services will see an investment of around $12 trillion worth by 2035. These will include enhanced mobile broadband services, mission-critical services, and significant IoT advancements in retail, healthcare, transportation, education, and entertainment.
Qualcomm estimates that the 5G value chain in a digital economy will generate revenues of up to $13.2 trillion by 2035 and provide as many as 22 million jobs.
5G and the future of the digital economy.
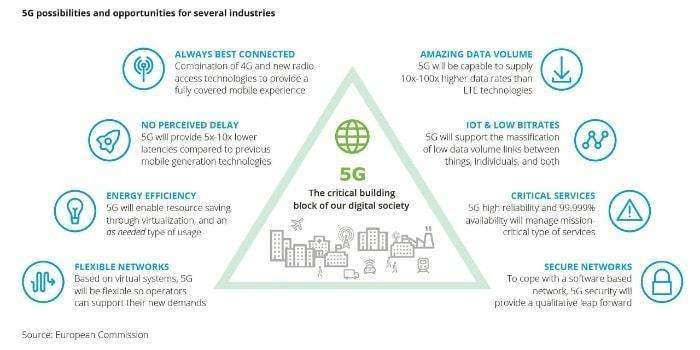
5G networks offer manufacturers and telecom operators the opportunity to build smart factories based on smart technologies such as automation, AI, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Alongside energy and utilities, manufacturing represents a promising sector with the next wave of industrial productivity known as Industry 4.0. The Industry 4.0 vision includes connected production with tracked and configured components in a self-managing system in a digital economy. Some of the areas where 5G can impact various services and improve the digital economy are:
Internet of Things (IoT)
The older devices and sensors had the capability to ”talk” to each other while they were utilizing the 4G LTE data capacity inefficiently. The introduction of 5G, however, will boost connectivity, speed, efficiency, and user experience, thereby generating more profit for telecom service providers and business owners.
Connected vehicles
It will work based on an autonomous model where precise and real-time information about car conditions, road conditions, or drivers will be received by automobile manufacturers and owners, which will help them offer better support and driving experience.
Better governance
Governments can develop an effective smart city architecture and e-governance framework by utilizing 5G. We can experience better public service, quick processing, and receive real-time information from officials during an emergency. We may call it a proactive and ”connected” government providing a quality public service experience.
The rollout of next-generation mobile networks will create value for many industries. The technology can be innovatively used in a wide variety of settings. Hospitals will be equipped with 5G-assisted devices to facilitate patient monitoring remotely and smart ambulances that connect in real-time.
Also, we can hope for smooth financial transactions through digital wallets and applications that connect wearable devices, smartphones, smart gadgets, automobiles, and many other devices. Factories will be 5G-enabled to connect devices and more sensors. 5G, combined with AI, edge computing, IoT, and extended reality (XR), can enable businesses to realize the full benefits of these technological advancements.
Conclusion
The impact of 5G on the economy will be considerable, and it will give an extra boost to the fourth industrial revolution with the acceleration of the Internet of Things. Its fast and reliable real-time data transfer will massively benefit the sensors and control units installed in facilities, machines, and logistics chains across industries.














