We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- What are O-RAN Drivers?
- What is an O-RAN ecosystem/
- O-RAN Business View and Market Outlook
- STL’s O-RAN solutions
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is pFTTx?
- What is WiFi?
Contents
Overview
The Telco ecosystem has been evolving through generations of wireless communication and now 5G is there to connect almost everything with better capacity and near-zero latency. While mobile operators have continued capacity growth with lower latency, cutting costs and seeking revenue from new service opportunities are the new things they are focusing on.
These will drive fundamental changes in the economies of the new network. Network infrastructure products with open interfaces are crucial in this context, to reduce costs and create a new ecosystem for service innovation. Mobile operators have been successful in cutting costs at the core of the network by investing in new architectures that leverage Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN), creating a more competitive open ecosystem for software and hardware.
However, the infrastructure of the radio access network which drives the largest share of the operator’s CAPEX remains locked into proprietary hardware and software thereby limiting flexibility and choice of deployment for operators. At STL, together with our partners, we offer an open and virtualized Radio Access Network which helps service providers create an Open, Disaggregated and Virtualized 5GC solution aligned with 3GPP. We are in the process of certifying specific uses cases in the field by working with leading mobile operators as well as private enterprises.
This paper explains how STL solutions bring agility, flexibility, and cloud economics to 4G and 5G networks in the O-RAN Telco ecosystem.
What are Open RAN (O-RAN) Drivers?
Open RAN (O-RAN) introduces intelligence through deep learning-based technologies like trained AI/ML models which are applied at both component and network levels which enables dynamic radio resource allocation and optimizes network efficiency in the RAN architecture. It automates the operation of the network functions reducing OPEX.
Open interfaces eliminate purpose-build and proprietary hardware to facilitate the multi-vendor ecosystem which could lower CAPEX through increased vendor competition and network system improvements. This will make it easier for smaller operators with limited resources to adopt O-RAN. Operators do not have to depend on a single vendor for rolling out new features, minimizing the danger of vendor lock-in, and helping in fast pace deployment of the network while providing supply chain security and flexibility bringing openness to the ecosystem.
Openness also provides operators with an opportunity to customize the network to suit their own unique needs with the ability to select the best solutions for different parts of their radio networks. It encourages more vendors to enter the market and challenge the network problems with their diverse solutions. These new market players will future-proof the network’s evolution.
What is an Open RAN (O-RAN) Ecosystem?
The Open RAN (O-RAN) concept is about disaggregating the RAN functionality by dividing the user plane from the control plane into separate elements, using a fully programmable software-defined mobile network solution based on open interfaces that run on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware.
Traditional mobile networks were built on closed, proprietary software and purpose-built hardware. But today using the O-RAN concepts it can be disaggregated. From a long-term perspective, it is a good sign for O-RAN that operators are the driving force behind the open RAN initiative. There are two main industry initiatives driving O-RAN:
- O-RAN Alliance, established in June 2018 focuses on the development of open, intelligent, virtualized, and interoperable RAN specifications and was created to carry forward the work of the xRAN Forum and the C-RAN Alliance. O-RAN Alliance is also supported by several smaller emerging RAN vendors.
- The Telecom Infra Project (TIP) is an engineering-focused, global community of companies and organizations working together to build and deploy global telecom network infrastructure, with the goal of enabling global access for all.
TIP and O-RAN announced in February 2020 that they would begin collaborating more closely to ensure that they did not duplicate each other’s efforts. The new agreement allows the two groups to share information, reference specifications, and conduct joint testing and integration efforts. This will help to maximize the efforts of both groups towards the common objective of O-RAN.
O-RAN Business View and Market Outlook
Conventional RAN architecture components are proprietary hardware appliances. Mobile network operators spend a major part of their capital expenditure and operating expenditure on RAN. Day to day increasing traffic and flattening revenue per subscriber has made the utmost necessity of network operators to look for a more efficient RAN architecture upgrade.
Future RAN architecture demands the following technological principles:
- Disintegrated software functionality over general-purpose hardware.
- Dynamic allocation of resources through virtualization.
- Open standardized interfaces.
- General-purpose edge compute infrastructure
- Cloud-native capabilities in lifecycle management
- Network functions in the form of APIs.
- Management through Orchestration.
- Real-time optimization.
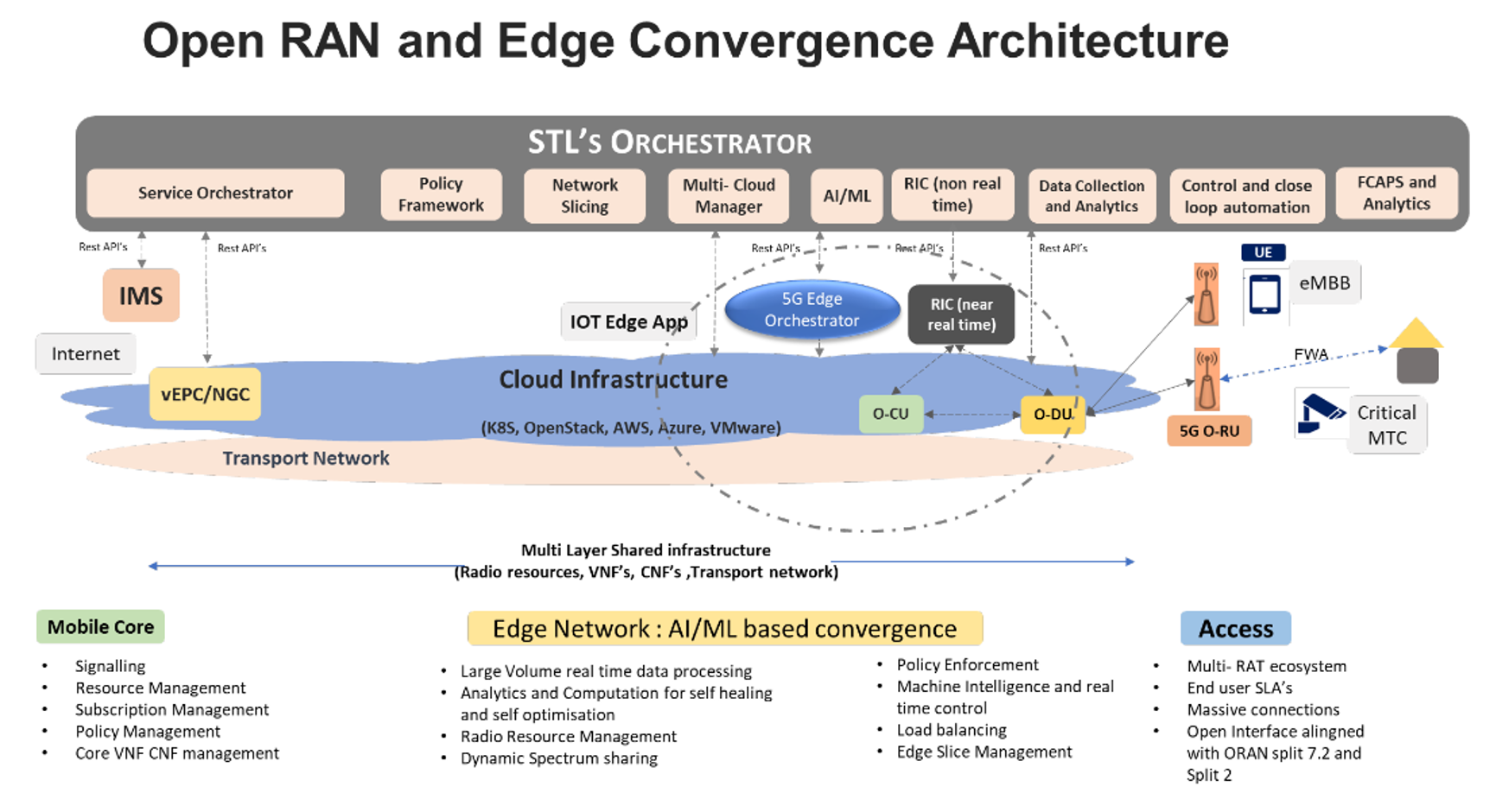
STL’s Open RAN (O-RAN) Solutions
Sterlite Technologies Limited provides the finest optimum key solutions to the O-RAN architecture to address the business challenges.
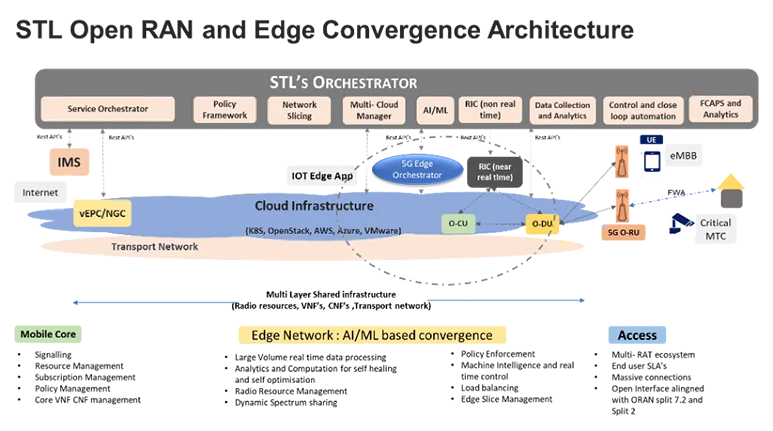
- STL’s RU solution: Radio unit is the distributed frontend of the RAN architecture which performs radio resource management. It is a hardware equipment comprising RF signal processing circuitry and antenna. It communicates with the user equipment over the air interface and handles the complete Front haul Gateway of the RAN architecture.
- 4G/5G Macro radios: STL designs and manufactures the radio units for mobile towers to ensure the 4G and 5G wireless connectivity. These 4G upgradable to 5G macro radios are located over distributed cell sites and can connect to 1000 users. These radio units can provide the maximum bandwidth of 100 MHz and uninterrupted throughput of 10Gbps.
- 5G Small cells: STL provides small cell radio units for 5G connectivity at home and workplaces. STL has designed small cell units for both indoor and outdoor deployments. These radio units can connect up to 32 users for indoor and 128 users for outdoor deployment.
- STL’s radio unit solutions also provide the MIMO configuration to enable more throughput for the end user.
- STL’s radio unit solutions are ORAN compliant with split 7.2 and split 2 configurations.
- STL’s CU and DU solutions: In O-RAN architecture, virtualization platforms enable a highly efficient execution environment for complex functionalities with the ability to distribute operations between multiple network functions. The Baseband unit functionality of the RAN architecture is split into two separate network functions. STL provides the following network functions in the form of virtualized entities through SDN-NFV.
- CU: Control unit of the baseband functionality of RAN architecture.
- DU: Distributed unit the baseband functionality of RAN architecture.
STL’s VNF solutions, vCU and vDU are software-defined network entities constructed through a network function virtualization process. They possess cloud-native capabilities with security isolation, virtual resource allocation, accelerator resource encapsulation, etc. benefits. STL’s VNF solutions are compliant with ORAN standardized interfaces and can run on any standard COTS servers.
- RAN Intelligent Controller: STL has developed
a RAN intelligent controller which performs real-time control functionalities
including RAN slicing, QoS control, and optimal resource management.
- RIC leverages Real-time analytics through machine learning and artificial intelligence to empower the network management.
- RIC effectively balances the RAN load to reduce the network congestion.
- RIC control loops running between network functions make it possible to deal with dynamic situations like mobility, mobility, scheduling, beam management etc. which enhance the network performance during user handover management.
- Network Orchestration: STL has a centralized
application management system for RAN operation and management functionalities.
- STL Orchestration performs network operations through network slicing, multi-domain life cycle management, cloud infrastructure management, and closed-loop automation capabilities.
- Challenges like zero-touch automation, real-time network service and quality assurance, policy design and management, etc are meticulously addressed by the STL Orchestrator.
- STL Orchestrator is envisioned in the multi-vendor environment with the integration of VNFs in the form of open APIs.
Conclusion
Foreseeing to 5G technology, O-RAN architecture leads towards a multi-vendor environment with interoperability functionality. STL contributes to strengthening the Make in India 5G technology by assembling an ecosystem of partners in hardware manufacturing and cloud computing. STL has invested in building a one-of-a-kind end-to-end development of fully programmable, open and disaggregated 5G-NR and Private LTE solutions. STL solutions leverage real time intelligence to enhance network performance.
With use of Edge Convergence Orchestration, they ensure the best quality of service with maximum throughput. Digital networks ecosystem includes next-gen wireless (5G) portfolio for all markets. STL partners with global telecom companies, cloud companies, citizen networks and large enterprises to deliver solutions for their fixed and wireless networks for the current and future needs.
FAQs
What is pFTTx?
FTTx, i.e., Fibre to the x is a collective term used for various optical fiber delivery topologies categorized by the infrastructure deployed for last-mile/access connectivity (The variable x is here represents the deployed infrastructure, i.e., B for buildings, H for Homes, P for Premise, N for Node, O for Offices, etc.). On the other hand, pFTTx, i.e., Programmable FTTx, adds a layer of software intelligence to the existing monolithic white-box-based FTTx infrastructure. It can be called an SDN-NFV, micro-services-oriented, cloud-based network solution that brings more flexibility, cost efficiency, and service excellence to digital networks. It drastically reduces time to market for new digital services, sets the ball rolling for edge computing by disaggregating broadband networks and re-architecting central offices. This technology will shape the future of broadband while connecting millions of people and devices seamlessly.
Some of the key features of pFTTx include: Programmability – across hardware and software empowers operators to have better control; Open ecosystem – through API interfaces defined by the community allows true vendor-neutrality; Disaggregation – of hardware and software allows launching new services up to 8-10 times faster, using cloud delivery models and technologies; COTS deployment – COTS brings flexibility to the procurement and integration of network equipment; Zero-touch provisioning – automates regular functions keeping human intervention to a minimum.
Business benefits of pFTTx include:
a) Reduction in hardware and software costs with white boxes at the edge for RAN, GPON/XGSPON/NG-PON2
b) Service providers can have complete control over their network and can solve their business problems and innovate as required
c) With last-mile network becoming programmable and agile, and with the control over translating business requirements to technical features, the infrastructure of the service providers will become lock-in free
d) Open infrastructure at the last mile significantly reduces the time-to-market and leads to revenue growth
e) Faster roll-out of premium and innovative services lead to an increase in average revenue per user
f) Programmable and agile network ensures a better quality of experience, reducing subscriber churn
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).