We are aware that optical fiber has completely revolutionised the communications industry. A core, cladding, and coating make up an optical fiber in its simplest form, and it’s non-flammable and uses less power. Let’s take a closer look at optical fibres, their various types, how they work, and their applications in this article.
Contents
What is an optical fibre?
Optical fiber is a data transmission method that makes use of light pulses traveling down a long fibre, often constructed of plastic or glass. The less signal damage metal wires can cause, the better for optical fiber connection. Additionally, electromagnetic interference does not impact optical fibers. The total internal reflection of light is used in the fibre optic cable.
Structure of optical fiber:
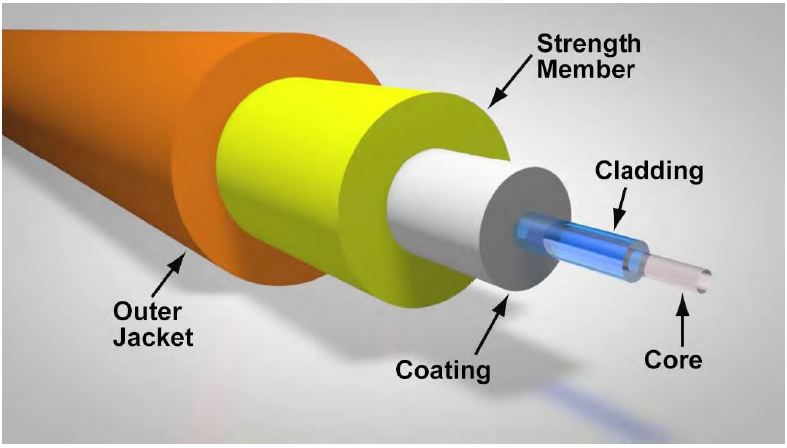
The core, cladding, and outer coating are all components of an optical fibre. While glass and plastic are commonly utilised, various materials can be used based on the desired transmission spectrum.
The section of the fiber that transmits light is called the core. The material used for cladding often has a lower refractive index than the core (usually about 1 percent lower). Because of the index difference, total internal reflection occurs at the index border along the length of the fiber, preventing light from escaping through the sidewalls.
What are the different types of optical fibre?
There are different types of optical fiber that are differentiated based on the following parameters:
- Material
- Number of modes
- Refractive index profile
1. Material used:
In terms of the materials utilised, optical fibres are divided into two categories:
- Glass fibre
- Core: SiO2 Cladding: SiO2
- Core: GeO2- SiO2 Cladding: SiO2
Example:
- Plastic fiber
- Core: Made of Polystyrene : Cladding: Done with Methyl Methacrylate
- Core: Made of Polymethyl Methacrylate : Cladding: Done with Co-Polymer
Example:
2. Total number of modes:
In terms of the total number of modes, optical fibres are divided into:
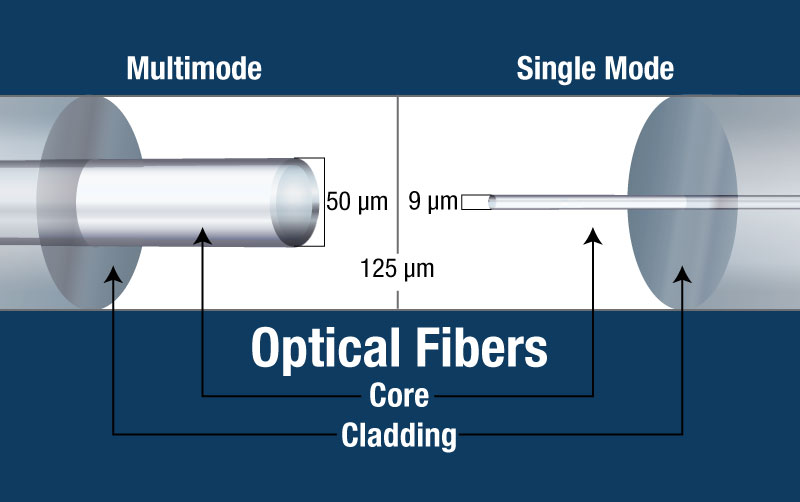
- Single-mode fiber
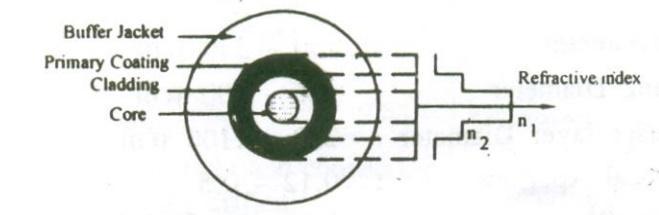
Single-mode fibres are typically step-index fibers. Doped silica is the raw material used to produce these fibers. In order to allow only one way of transmission, it has an extremely small core diameter.
- Multimode fibre
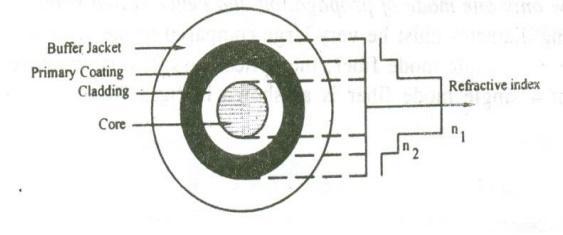
Both step-index and graded-index fibres benefit from the use of multi-mode fiber. Multi-component glass compounds such as Silica – Clad – Silica, Glass – Clad Glass, doped silica, etc., are used to make the multi-mode fibres.
3. Refractive index profile
Optical fibers are further divided into two groups based on their refractive index profile.
- Step Index Fibre
- Single Mode Step Index Fiber: In a single-mode step-index fiber, the core is surrounded by a lower refractive index cladding than the core itself.
- Multimode Step Index Fibre: The core of a multimode step-index fiber is surrounded by cladding with a lower refractive index than the core.
- Graded Index Fibre
Graded index fibers have refractive indices that vary from one end of the fiber to the other, which causes light rays to move at varying rates. There is a lower refractive index of optical fibre at the outer border of the object. To put it in another way, the rays on the outer edge travel faster than the rays in the centre. As a result, rays leave and arrive at the fiber’s end almost simultaneously.
Applications of different types of optical fibre
Compared to typical metallic wires, the application of optical fiber has proven advantageous.
Applications of optical fibre communication:
- Medical industry: In several instruments, it is utilised to observe interior body components by entering into hollow places in the body because of its thin and flexible nature. Surgical lasers, endoscope lasers, microscope lasers, and biomedical lasers all make use of fiber lasers.
- Communication: Optical fibre cables play an important role in the principle of optical fibre communication systems because they are used for both transmission and reception. Speed and accuracy can be improved by using it in many networking applications.
- Defense: High-level data security sectors of military and aerospace applications use fiber optics for data transfer. Hydrophones for SONAR and seismic applications, as well as aviation wiring, make use of this material.
- Broadcasting: Such cables deliver high-speed, high-bandwidth HDTV signals. When compared to the same amount of copper cables, fibre optic cable is less expensive. Broadcasters employ optical fibers to connect HDTV, CATV, VOD, and other services.
- Decorations and lighting: Now that we know what optical fibre is, we can see why it’s so popular in Christmas decorations and trees: it’s inexpensive, easy to use, and beautiful.