A gateway is a computer on a network that provides the interface between two applications or networks that use different protocols. They are also used to provide a connection to the Internet. A gateway in a network converts information from one protocol to another and then transfers it over the web. For example, if a computer on the Internet sends an email to another, the gateway converts the message from one protocol to another and sends it back.
This post will discuss gateways’ needs and functions in computer networks.
Contents
How Does a Gateway Work?
A computer gateway is a server with software installed to connect networks and route data. The gateway node can be linked to different routers or have a router that connects it with other networks or the Internet. The connection can be wired or wireless.
A computer server may serve as a gateway node in any development team of any commercial organization, and it may also act as a proxy server or a firewall at times. A computer gateway in a network examines the data packet and then passes it to the other network. It checks compatibility between the two networks and then converts the data packet to ensure that it can be transmitted between them.
The gateway node may also be linked to servers for specific purposes such as email, web hosting, and database storage. It can also be part of a more extensive network like the Internet. In this case, the gateway node will have its IP address, thus making it possible to route incoming traffic from different networks to its primary interface and out onto the Internet. However, this is one of many possible configurations for a gateway node; other configurations are also possible.
Functions of Gateways
The gateway in networking is a device that connects the Internet to the LAN. It can even be used as a bridge between two networks.
A network gateway has two functions.
● A LAN-to-WAN function that connects the LAN to the Internet.
● A WAN-to-LAN function connects the Internet to a remote LAN.
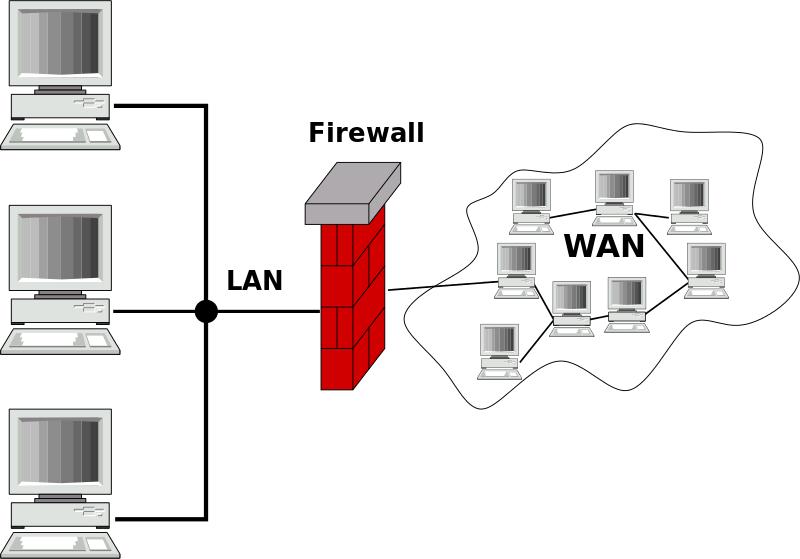
When a data packet reaches a gateway, it verifies the header information first. Once it validates the destination IP and checks for any data packet errors, it converts the data packet’s data and protocol according to the demands of the destination network. Finally, it transmits the data packet to the target IP address by establishing a dedicated transmission channel.
A gateway in networking is also a part of any telephony system. It provides a bridge between the phone network and the Internet. For example, let’s say you wanted to set up a direct call for your customer. Your real-time communication gateway will perform several tasks, automatically detecting the customer’s current location and converting audio back and forth between different technologies.
A network gateway filters packets and separates a corporate network from the public Internet. It is typically used to segregate networks, keeping local and public networks safe. A gateway provides the same protection as a firewall using a technique called NAT.
Types of Gateways in Computer Networks
There are two types of gateways in computer networks – bidirectional and unidirectional. Let us look at a brief introduction of both types.
- Unidirectional Gateways: They can only transmit data in one direction. You make changes in the source terminal, which are replicated to all the other destination nodes or applications without being changed themselves. These gateways serve as archiving tools.
Unidirectional gateways are made up of both hardware and software. The technology allows data to flow from one source network to another but is physically incapable of sending any data back into the source network. Instead, the gateway software emulates protocol servers and devices while replicating databases.
- Bidirectional Gateways: These gateways in networking enable the two-way flow of data. They can perform all tasks with synchronicity as they replicate changes made on the source node to the destination and vice-versa. In a nutshell, the bidirectional gateway serves as a synchronization programme or tool.
In a bidirectional gateway setup, changes made to the content of a source ObjectServer are transferred to a destination ObjectServer, and the destination ObjectServer copies its alerts to the source ObjectServer.
Examples of Gateway in Networking
IoT Gateway is a central hub between IoT devices and cloud servers. They usually allow two-way data flow, with the incoming data stream processed by the ‘cloud’. An IoT gateway is also known as a control tier or an intelligent gateway.
Network Gateway: Network gateways are intended to transform traffic across protocols. These translations make it possible to connect networks that use various protocols or data formats, with the network gateway doing an in-line translation.
Network gateways are critical for linking business LANs to the public Internet. Many companies use protocols that differ from those used on the public Internet, yet some of this communication may be headed for the Internet.
Payment Gateway: The system that gathers and sends payment data from the client to the acquirer is known as a payment gateway.
Media Gateway: It’s a device used in a telecom operator’s main network to transform and interconnect media streams that use various wireless standards, codecs, communication protocols, and physical connections, allowing phone calls to work correctly between networks that use different systems.
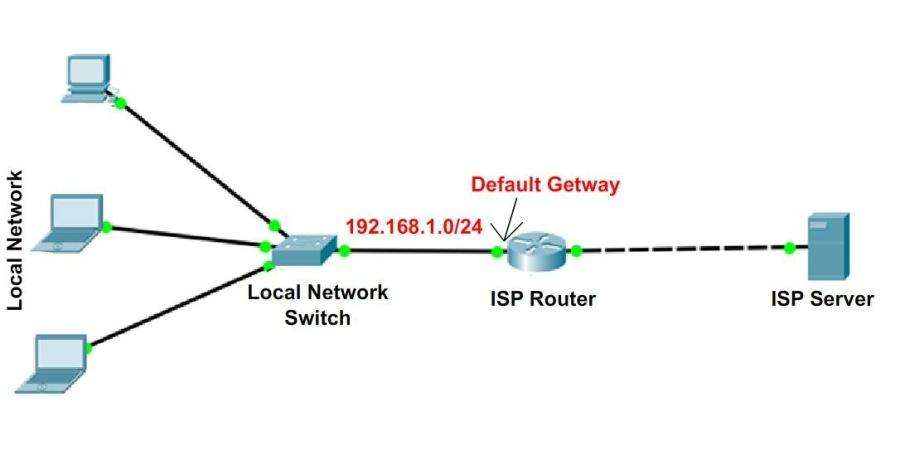
Default Gateway: It’s a node that establishes a link across networks for computers on different networks to communicate with one another. The ‘default’ element of the phrase refers to the fact that it is often the first and default route used.
Email Security Gateway serves as an email security solution between the public Internet and the business email server. This location enables it to scan emails for malicious content before they reach corporate networks. However, this gateway’s architecture renders it unsuitable for securing newer cloud-based email platforms.
VoIP Trunk Gateway: A VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) trunk gateway is a device that connects PSTN equipment to a VoIP network. It does that without the need for an operator. These gateways provide a wide range of services, the most common of which is a low-cost telephone.
Web Application Firewalls: These provide safe network system connectivity at a high level. When a client seeks access to server resources like web pages, files, and databases, initially, the client establishes a connection with the proxy server, which then connects to the primary server.
Conclusion
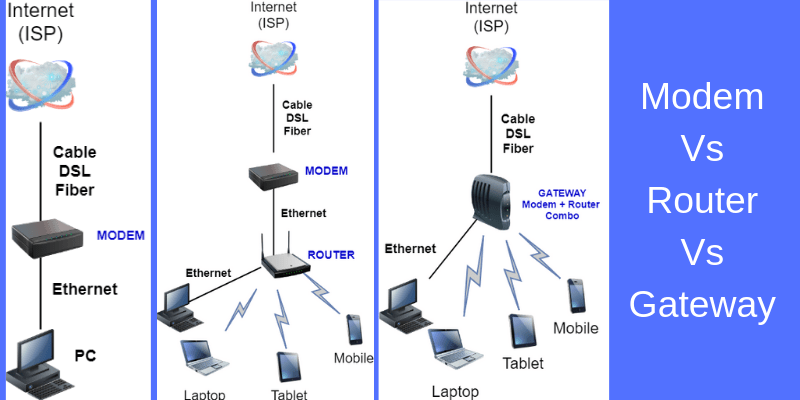
A gateway in a network is frequently used in tandem with a router. A router is a tiny piece of computer/network gear that links you to the Internet. The router comes with specific software that you install for in-home networks.
Routers can act as gateways in networking because they can regulate the path by which data is transmitted in and out. It accomplishes this by determining where data packets should be routed using built-in headers and forwarding tables. These data packets contain your emails, transactions, internet activities, etc.
A gateway is one of the various methods through which our data is transferred over the Internet for us. The gateway allows us to connect to many networks, send an email, browse websites, and make purchases online, among other things. Gateways effortlessly give us the freedom, knowledge, and convenience we enjoy online.
Installing fixed routers inside a home to regulate traffic will no longer make sense when individuals possess hundreds of wearable and mobile gadgets that need to interact inside and outside the home: devices will all talk with each other and the Internet directly.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a gateway and a router?
A router is a device or piece of hardware in charge of receiving, processing, and routing data packets to other networks. A router detects the packet’s destination IP address, and therefore the optimal path to send the packet is identified with the assistance of headers and forwarding tables.
A gateway in networking is a device or piece of hardware that operates as a “gate” between networks. As a result, it might also be characterized as a node serving as an entry point for the other nodes in the network. It is also in charge of allowing traffic to flow across the web. Because a gateway communicates via many protocols, its operations are far more complicated than those of a switch or router.
2. Is a gateway the same as a firewall?
A gateway is essentially a hardware or software interface that enables two networks to connect. It effectively connects two different networks, allowing users to interact across many networks. A firewall is a security tool that tracks and regulates network traffic. It is the core of an organization’s security architecture. Firewalls keep unauthorized users out of private networks linked to the Internet, notably intranets. They also prevent suspicious traffic, such as viruses and hackers, by monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic based on pre-defined criteria.
3. What layer device is a gateway?
A gateway is commonly implemented on the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) architecture’s network layer, but it may be put on any OSI layer. Virtual or standalone gateways can be placed anywhere in a network that requires translation. They can be unidirectional (enabling data to travel in only one direction) or bidirectional (providing data to flow in both directions).
4. Does a gateway have an IP address?
The default gateway IP address is the router’s private IP address. The router uses this address to interact with a local home network. In addition, the gateway is assigned two IP addresses. The first is an external IP address issued by your ISP (internet service provider), while the second is an internal IP address accessible exclusively within your network.















