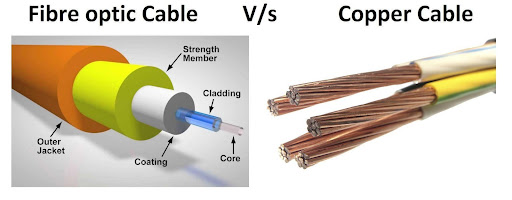
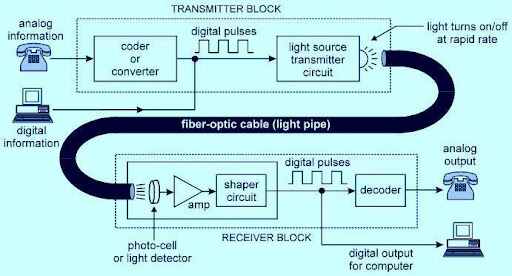
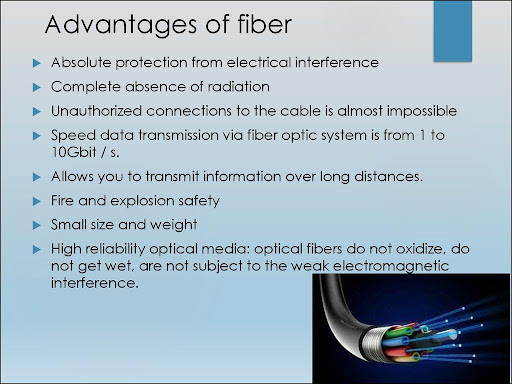
Fiber optics is the technology and medium associated with data transmission as light pulses along a strand of ultrapure glass as thin as human hair. So far, fibre is the fastest home Internet option. With all of the benefits of optical fiber, it is no surprise that fibre optics are gaining popularity.

Optic Fibre
In a highly connected world, light pulses bouncing through thin strands of optical fibers enable people to make phone calls, check websites, or watch videos. While cloud computing and wireless communications have grown exponentially, most video, data, and voice signals continue to travel over fibre optic networks.
As we consume more data, networks are struggling to keep up with the exponential increase in demand. Optical fibers will be used in both 5G and FTTH deployments, but they will need to be deployed much more densely than they are currently.
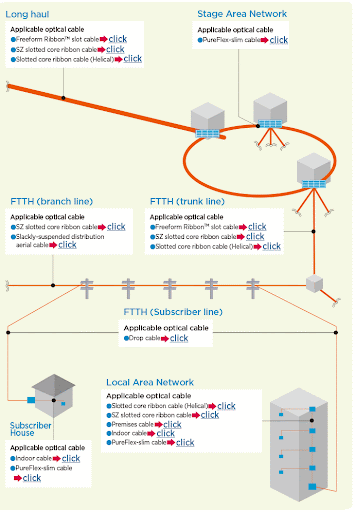
Application of Optic Fibre
There is a lot of uncertainty about how networks will evolve. Still, it is clear that this decade will see a lot of change in the telecom landscape, allowing for the further deployment of next-generation networks. These networks will have in common the fact that more and more optical fibre will be used for deployments.
STL is the global leader among providers of fiber optic solutions providers. Our optical fibre solutions meet all of your needs and serve a wide range of applications. Our lower bend loss optical fiber is ideal for your network, allowing for high network performance while significantly lowering installation costs. We provide 250 um and 200 um Bend Insensitive Single Mode Fibre (BISMF) and Non-Zero Dispersion Shifted Single Mode Fibre (NZDSF) solutions for 5G and FTTx applications.

Fibre Optic Applications
Contents
Optical Fibre: Key Offerings
Optical fiber is generally classified into two types based on the number of modes, materials used, and refractive index. These are explained further below.
The classification based on light propagation mode is as follows:
- Single-Mode Fibres: A single type of light ray can propagate through a single-mode fiber. These fibres are used for long-distance signal transmission.
- Multimode Fibres: A multimode fiber allows light rays to travel through it in a variety of modes. These fibres are used for signal transmission over short distances.
Based on the refractive index, the classification is as follows:
- Step Index Fibres: Core has a constant refractive index. The cladding’s refractive index is also constant. Light rays propagate through it as meridional rays that cross the fiber axis during every reflection at the core-cladding boundary.
- Graded Index Fibres: The core of this type of fiber has a non-uniform refractive index that decreases gradually from the center to the core-cladding interface. The refractive index of the cladding is uniform. Light rays in the form of skew rays or helical rays pass through them.
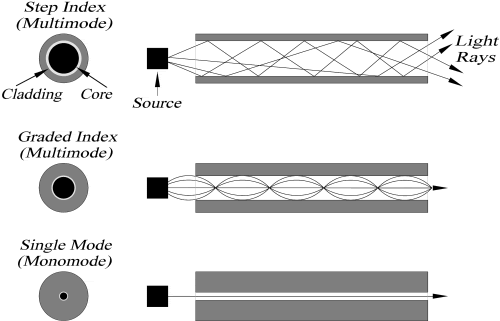
Types of Optical Fibre Cables
The mode of propagation and refractive index of the core is used to create four different types of optical fibers:
- Step index-single mode fibers
- Graded index-Single mode fibres
- Step index-Multimode fibers
- Graded index-Multimode fibres
The following is the classification based on the materials used:
- Plastic Optical Fibres: Polymethylmethacrylate is used as a core material in optical fibers.
- Glass Fibres: It is made up of extremely fine glass fibers.
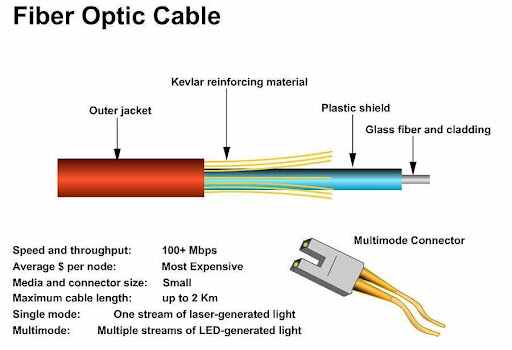
A Fibre Optic Cable
Why choose STL’s fiber optic solutions?
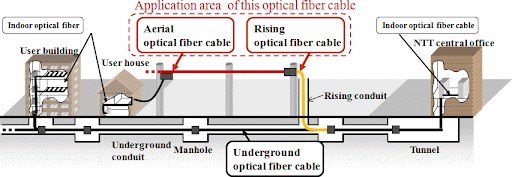
Fiber optic cables are now the foundation of how we communicate. The majority of the data is carried by thousands of miles of fibre optic cables laid underground, in building walls, in the sea bed, and in tunnels. Computer networking, defense, broadcasting, medical scanning and research, home networking (via FTTx), and mechanical inspection of inaccessible areas are all applications for optical fiber in India.
Optical Fibre In India
STL is a market leader in optical fiber technology and provides fiber optic solutions providers. introduces a line of bend-insensitive optical fibre products. STL emphasizes the importance of world-class optical fiber deployments in a connected world where next-generation networking is critical. STL’s fiber optical solutions are suitable for a variety of applications, including:
- StellarTM Collection: StellarTM, the installer’s fibre, is the first G.657.A2 macro-bend insensitive fiber in the world. This fiber is compatible with legacy networks, including G.657.A1 and G.652D. StellarTM Fiber is used in many different parts of a data communication network, including core, metro, and access.
- BOW-LITETM Series: STL’s BOW-LITETM series optical fibre products are bend-insensitive single-mode fibers that are ideal for FTTx applications and high fiber-density cables.
- OH-LITE® Series: STL offers a variety of G.657.A1 and G.652.D type optical fiber with enhanced attenuation, geometry, dispersion, and macro-bend loss properties. This enables improved performance in a variety of application areas such as long haul, metro-city, access, and CATV networks.
- DOF-LITETM Series: This series of non-zero dispersion-shifted single-mode optical fiber, which complies with ITU-T G.655 recommendations, is primarily suited for long-distance and metropolitan networks. DOF-LITE (LEA) is intended for long-distance networks, whereas DOF-LITE (METRO) is designed for metro networks.
STL’s customized fiber optic cabling solutions are designed to support high-bandwidth applications in data centers, global internet companies, ISPs and telcos, and citizen network services. Aerial, microduct, underground, IO and indoor, ribbon, last mile connectivity, and special application cable are all available in STL’s range of fiber optic solutions.

Fibre Optic Application
Centre of excellence
We have witnessed focused efforts by the Government of India on maximizing the reach of broadband and enabling higher speeds in order to increase Internet penetration. It has been STL’s continuous endeavor to help build capacity in this direction.As a pioneering step, STL has established a state-of-the-art Center of Excellence at Aurangabad dedicated to research on helping India meet the challenges of higher data transmission speed and capacity demands. Five core laboratories and an installation testing facility have enhanced STL’s capabilities in the design and manufacturing of optical fibers and optical fiber cables to service the ever-increasing global demand for bandwidth.
Optical Fibre Application
Other Related Products
- Glass Preform
Made of very high-purity (5N) chemicals, which results in the best quality optical fibers. - Optical and Speciality Cables
Customized cables for data centers, enterprises, and citizen networks. - Optical Interconnect Kits
Modular, customizable, Plug-n-Play solutions for FTTx applications.
Want to know more?
- What is Fibre Optics?
In contrast to other transmission methods, fiber optics, also known as optical fibre, refers to the medium and technique associated with transferring information in the form of light pulses through a glass or plastic strand as well as fiber. Fiber optic is the dominant technique for long-distance and high-performance data networking.
Fiber optics, which have higher bandwidth and transmit speeds, are widely used in communications services such as the internet, television, and telephones. Fiber optics are used by companies such as Verizon and Google in their respective Verizon FIOS and Google Fiber services, which offer gigabit internet speeds to subscribers. - What is an optical fiber network?
One of the fastest communication networks is the optical fibre network. It converts an electrical signal into light pulses, which are then placed on a fiber optic cable for transmission to a receiving device. An optical receiver device converts a signal into an electrical signal, which is then sent to a recipient node.
Light pulses in an optical network can travel a long distance before being regenerated by an optical repeater device, making it less susceptible to external inference and attenuation and capable of significantly higher bandwidth speeds than copper networks. - What is the science behind fiber optics?
The principle of total internal reflection governs fiber optics. Light enters the higher-index material, strikes the upper interface, is reflected downward, strikes the second interface, is reflected upward, and so on. Light will travel down the waveguide like a marble, bouncing off the internal walls of the tube as it travels through it. Light entering the fiber at the critical angle will reflect off the interface and propagate down the fibre.
Some light will be absorbed by fiber impurities or scattered out of the core. Modern fibers are made of very pure materials, which minimizes these effects. - What are the uses of Fibre Optics?
Fiber-optic technology is constantly improving and becoming an increasingly inconspicuous part of our daily lives:- Optical fibers are used in defense. Fiber optics are used in high-level data security fields such as military and aerospace applications for data transmission.
- Aircraft wiring, hydrophones for SONARs, and seismic applications
- Wireless and telecommunications networks
- Fiber-optic lasers will be used to boost network capacity even further.
- Fiber-optic stress and strain sensors are used on structures, bridges, and industrial process monitoring.
- Doctors can use fiber-optic endoscopes to perform non-invasive internal examinations.
- Researchers can remotely monitor pollution levels using fiber-optic chemical sensors.
- How is optical fiber installed?
Fiber optic cables are typically installed by either pulling or blowing. Cable pulling is the process of pulling a cable into place using a winch or other mechanical device. Cable blowing, on the other hand, uses compressed air to push the cable into place. The network installers will be able to advise you on the best method for your project.
Underground installation of fiber optic cable is a standard method. The cable is routed through ducts in an underground conduit. This shields the cables from environmental changes, such as shifting rocks, rodent dens, or landscaping tools like shovels. - What is FTTH?
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) is a technology that uses optical fibers to connect a central point to residential premises (as shown in the following image). It offers continuous high-speed Internet access. In this case, “H” refers to both home and small businesses.
FTTH is the ultimate fiber access solution that connects each subscriber to an optical fibre. The following are the most significant benefits:- Extensive information-carrying capacity
- Easily upgradeable
- Simple to install
- Supports fully symmetric services
- Lowers operating and maintenance costs
- Covers extremely long distances
- Strong, flexible, and dependable
- Allows for small-diameter and lightweight cables
- Safe and secure
- Immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI).