We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- Increased density of 5G access points increasing urbanization
- STL’s Fiber Density 432F Optical Fiber Cable
- Advantages of 432F
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
- What is WiFi?
Contents
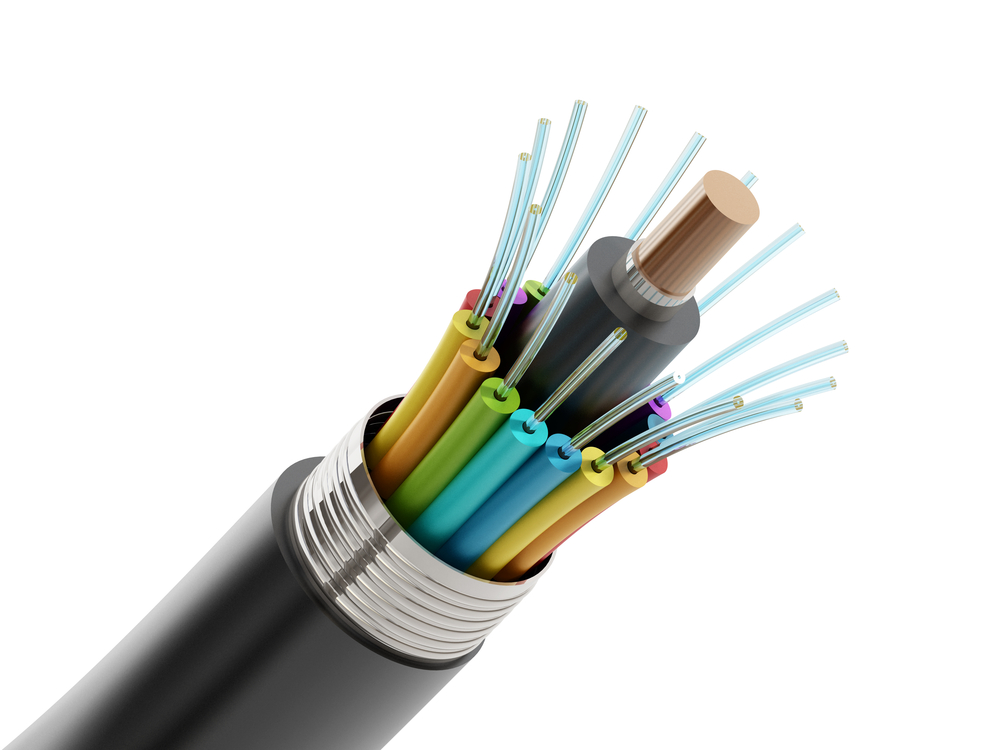
Can STL’s 432F next-gen Micro Cable Enable 5G?
Introducing the world’s slimmest 432f next-gen micro cable by STL in order to provide efficient 5G services there has to be an increased density of 5G access points increasing urbanization and rapid expansion of municipal areas in cities have led to a rise in the number of access points hence FTTh needs additional fiber to enable 5G front haul networks and efficient FTTh connections. STL has developed the world’s slimmest 432f cable.
Fiber Density 432F Optical Fiber Cable
Significant improvements in fiber density can be achieved in optical fiber cables by using slimmer bend insensitive 200 micron optical fibers in comparison to a standard 250 micron fiber. Next generation fiber is 20% slimmer. Our bend insensitive fiber is designed to be operated in tighter bends without any signal strength losses it is ideal for deployment in access or FTTx networks. It enables better bend radius and minimizes macro bend signal losses.
What are Some of the Advantages of 432F?
- The 432f micro cable by STL allows for easy and quick deployment.
- The tube diameter has been reduced leading to a 50% increase in fiber density.
- This in turn enables more efficient blowing performance.
- This micro cabling solution uses G.657 bow light A1 bend insensitive fiber which enables reduced macro bend signal losses by up to 20 times.
- The cable is engineered to withstand extreme temperatures from -40 degrees celsius up to 70 degrees celsius.
- The tensile strength has been augmented to 1000 newton.
- These features enable up to 40 percent reduction in deployment and fixed costs.
- The world’s slimmest 432F cable is future ready for system evolution.
- 432F is a step towards next gen ultra high definition future.
Conclusion
We shared everything about the worlds slimmest cable 432F. How the increase in urbanisation has contributed to the increasing need for access points. To enable 5G networks STL has developed the worlds slimmest cable. We have compared 432F with other standard cables available. Ideal for Access or FTTX networks.
Temperature, tensile strength, area required are all explained. These are bend insensitive cable can operate in tighter bends. Bends do not cause loss of signal. The diameter has been reduced leading to increase in fibre density. 432f is next gen ultra high definition future ready.
FAQs
What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
An optical fibre cable is a cable type that has a few to hundreds of optical fibres bundled together within a protective plastic coating. They help carry digital data in the form of light pulses across large distances at faster speeds. For this, they need to be installed or deployed either underground or aerially. Standalone fibres cannot be buried or hanged so fibres are bunched together as cables for the transmission of data. This is done to protect the fibre from stress, moisture, temperature changes and other externalities.
There are three main components of a optical fibre cable, core (It carries the light and is made of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with dopants such as germania, phosphorous pentoxide, or alumina to raise the refractive index; Typical glass cores range from as small as 3.7um up to 200um), Cladding (Cladding surrounds the core and has a lower refractive index than the core, it is also made from the same material as the core; 1% refractive index difference is maintained between the core and cladding; Two commonly used diameters are 125µm and 140µm) and Coating (Protective layer that absorbs shocks, physical damage and moisture; The outside diameter of the coating is typically either 250µm or 500µm; Commonly used material for coatings are acrylate,Silicone, carbon, and polyimide).
An optical fibre cable is made up of the following components: Optical fibres – ranging from one to many. Buffer tubes (with different settings), for protection and cushioning of the fibre. Water protection in the tubes – wet or dry. A central strength member (CSM) is the backbone of all cables. Armoured tapes for stranding to bunch the buffer tubes and strength members together. Sheathing or final covering to provide further protection.
The five main reasons that make this technology innovation disruptive are fast communication speed, infinite bandwidth & capacity, low interference, high tensile strength and secure communication. The major usescases of optical fibre cables include intenet connectivity, computer networking, surgery & dentistry, automotive industry, telephony, lighting & decorations, mechanical inspections, cable television, military applications and space.
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).