We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- Rising unemployment and erosion of wealth during lockdown
- Divisive and polarising tactics gaining popularity worldwide
- Imperatives that global leaders should consider to avert these emerging threats
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is WiFi?
- What is Open RAN?
Contents
What is the Magnitude of Threat That Awaits Us?
Almost 2 months of lockdown and COVID-19 is still on the rise. The past few weeks have been unkind to various small and medium businesses. The world at large is beginning to realize the scale of this coronavirus pandemic in terms of rising unemployment and erosion of wealth generation opportunities[1].
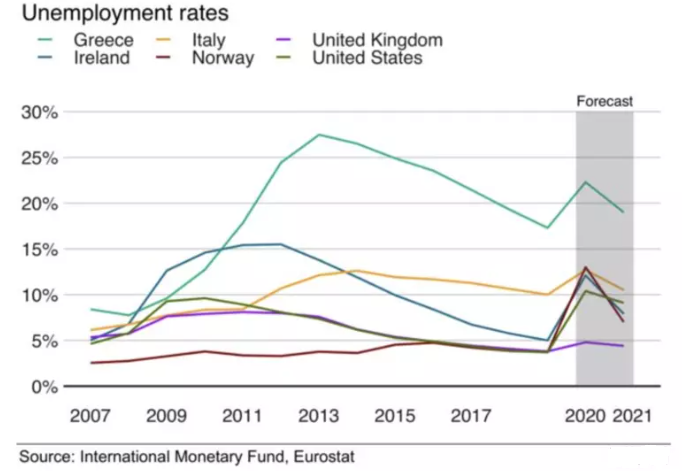
A similar trend seems to have appeared on security radars across the globe. According to a recent report by World Economic Forum, scientists predict that the COVID-19 pandemic is here to stay, perhaps for years. In addition to accounting for unemployment and adverse economic implications, rising insecurities are poised to pave the way for geopolitical unrest and violence.
Has the World Become Dangerously Volatile?
With tension-related sentiments, groups of people in Kosovo, Brazil, South Africa and India have taken to the streets in protests opposing various lockdown initiatives by their respective governments. The escalating situation between the U.S. & other western countries and China isn’t helping ease global war-like tensions either. Diplomatic relations are completely strained to avoid war at all costs. We are thus, at a point where the balance could easily tip in favour of worldwide violence. Public confidence is frail at the moment. In times such as these when solidarity and collaboration are the urgent need of the hour, we are beginning to witness divisive and polarising tactics gain popularity[1].
What we need to also realize is that such situations are often ripe for exploitation by armed terror groups, militia and criminals, be it in the physical world or the cyber world. The world needs to come together and accept the severity of these emerging threats to society.
In spite of the prevailing dark undertone to life these days, not all might be lost. In such times, it might be worth considering whether technology can help avoid security crises across the world. With automated and self-learning security solutions in operation, critical areas and infrastructures such as national borders, government offices and other important state establishments can be secured around the clock with real time automated action orchestration and with minimized human involvement. Interestingly, companies such as Honeywell, Schlumberger Ltd., STL among many others have been doing some path-breaking developments in areas such as fibre optic sensing, IoT based surveillance, and AI-based action orchestration. These developments have the potential to make a great case for digitally enabled security.
Here are the top three imperatives that nations and global leaders should consider to avert these emerging threats
- First and foremost, our leaders must agree upon reprioritizing human value over economy. Through established platforms such as the UN, G20 and other regional bodies, sentiments of safety and security must be prioritized as key focus areas at least till the time a cure is found. A global ceasefire must be announced and implemented at all costs along with an alignment of respective strategies to ensure on ground peace and security.
- The situation, that this pandemic has put us in, should be viewed as an opportunity to strengthen digital transformation in the defence landscape and aggressive investments in strategizing and implementing technology-led security solutions must take precedence. One of the very first initiatives on this path must be to digitally enable security setups with secure connectivity and application frameworks. It will definitely help reduce dependence on human intervention while providing the much needed around the clock, real-time protection to our physical and existing digital infrastructures that allow essential services to reach us during these times.
- Member nations and non-member nations to the aforementioned forums must realize that they are fronting the on the ground situations and are responsible for ensuring the safety and security of the lives they govern. Critical calls such as reallocation of budget and pooling of underutilised funds must be made to ensure a continuous supply of supply of essential products and services during these times.
[1] https://www.worldpoliticsreview.com/articles/28664/building-trust-confidence-and-collective-action-in-the-age-of-covid-19
[1] https://business.financialpost.com/news/fp-street/jpmorgan-profit-plunges-to-lowest-since-2013-on-virus-fallout
FAQs
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).
What is Open RAN?
From a deployment standpoint, we have Non-Standalone Mode(NSA), Dynamic Spectrum Sharing(DSS), and Standalone Mode (SA). The initial deployments of 5G NR are based on NSA standards, meaning the existing 4G LTE network will operate on the control plane, and 5G NR will be introduced to the user plane.
This particular standard was introduced by 3GPP, keeping in mind the industry’s push to faster 5G services rollout while utilizing the existing 4G LTE infrastructure currently in place. On the other hand, operators are also implementing Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) to accelerate the deployment cycle, which will reduce costs and improve spectrum utilization. In this standard, the same spectrum is shared between the 5G NR and 4G LTE, multiplexing over time per user demands. Lastly, we have the Standalone Mode (SA), which moves towards a complete 5G based network where both signaling and the information transfer are driven by a 5G cell.
















1 Comment
Dhani
November 9, 2020Very well written!!