We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- What are Ribbon Fibre Cables?
- What are Intermittent Bonded ribbon fibre cables?
- Difference between Ribbon Fibre cables and Loose Tube Fibre Cables
- Features and Benefits of Ribbon Fiber Cable
- How Do We Splice Ribbon Fibre Cables?
- Applications of Ribbon Fibre Cables
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- How many fibers are in a ribbon?
- How do you splice ribbon fiber to loose tube?
- Can you use a single fiber splicer to splice ribbon fiber cable?
- What is rollable ribbon fiber?
- How do you make fiber ribbons?

Industry veterans and experts know that ribbon fiber has been around for decades. However, the utilization and application of ribbon fiber cables like intermittently bonded ribbon fiber cables are only just beginning to grow. This is in response to the growing bandwidth demands in the superfast era of connectivity.
As such, a ribbon fiber cable provides a more fiber-dense, compact, and easy to handle and install solution for network providers compared to individual fiber-based cables. This makes intermittently bonded ribbon fiber a key component of future-ready network infrastructure.
In this blog, we will learn more about fibre optic ribbon cables and intermittently bonded fiber ribbon in detail – right from what they are, their construction, benefits, applications, and more.
Contents
What are Ribbon Fibre Cables?

First things first. What exactly is a ribbon fiber optic cable and why is it constructed in a unique fashion?
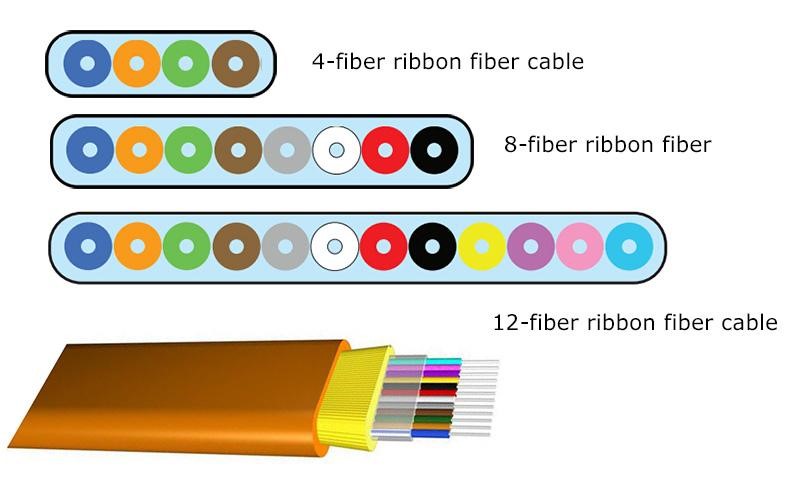
A ribbon fiber cable consists of coated optical fibers which are placed adjacent to each other. Such an arrangement enables individual fibers to be aligned in a single row. The cable ribbons are then impregnated with an acrylate UV curable resin and encapsulated in Mylar tape. As such, these multiple individual optical ribbons allow stacking into a bundle with a matrix structure. They can then be stored in a central core tube or in stranded multi-tubes in the cable core. Additionally, these individual optical ribbons can be stored in two ways: inside a central core tube or in stranded multi-tubes within the cable core.
By joining multiple optical fibers in ribbon form, one can optimize the fiber packing density of the cable. Did you know that 4, 8 or even 12 optical fibers can lie within a single ribbon, and each ribbon can be stacked up to 22 high? As a result, a ribbon fiber cable is much denser than a regular optic fiber cable design, making it suitable for limited space applications.
What are Intermittent Bonded ribbon fibre cables?

It is interesting to note that classic ribbon technology has been replaced with new ribbon technologies. One of them that is making waves big time in the industry: Intermittent Bonded Ribbon.
An intermittently bonded ribbon fiber cable consists of fibers bonded using matrix material. As such, they lack a flat structure. The rollable ribbons in an intermittently bonded ribbon fiber are bundled together and have the appearance of a spider’s web. Hence, they are also called spider web ribbon fiber. Due to their loose fiber bundling, intermittently bonded ribbon cables are perfect for making optic fiber cables with higher packing density. Additionally, they can also undergo mass fusion fiber cable splicing – which is another advantage for manufacturers.
Difference between Ribbon Fibre cables and Loose Tube Fibre Cables

As you can see in the image above, the difference between ribbon fiber cables and loose tube fiber cables stems from their construction. Right from the onset, we can observe that optical cables in the ribbon fiber cable are flat like ribbons, while they are round and bundled inside a loose tube fiber cable.
The level of optical fiber arrangement is also different inside both. It is consistent and arranged in the order of color in a banded row in a ribbon fiber jumper. This is what we call a fixed form. On the contrary, a loose tube cable has a beam fiber jumper that is more random, unarranged, and of independent form. However, in a loose tube fiber cable, the optical fibre arrangement is random. This is what we call independent form.
Another point of differentiation is that there is a fiber band inside a ribbon fiber cable. However, a loose tube fiber cable comprises of 0.9 mm loose casing.
Features and Benefits of Ribbon Fiber Cable
As the latest innovation in optical fiber cable technology, ribbon optic fiber cable offers numerous advantages compared to non-ribbon cables. Some of the ribbon fiber cable advantages include:
- Higher fiber density for higher performance: In comparison with cables with individual fibers, a ribbon fiber cable has a greater fiber packing density. This is especially important in applications where there is a need for optic fiber cables with higher fiber counts but the duct space is limited. Additionally, a higher fiber count also yields better network uptime, more revenue, and better customer satisfaction.
- Reduced installation costs and time: As mentioned previously, ribbon fiber cables are usually pre-banded and can be prepped and spliced quicker than a non-ribbon fiber cable of a similar size. This gives installers and technicians a much simpler, faster mass fusion stitching ability as they can stitch the fibers together simultaneously. Think savings in installation time, reduced labor costs, and faster restoration time in emergency situations.
- Comparatively cost-effective: For fiber counts above 72 to 96, a ribbon fiber cable yields higher cost savings.
- Smaller footprint: Using ribbon fiber optic cables makes way for a smaller footprint in telecommunications rooms and splice closures. This is because ribbon fiber is lighter and more compact, and is also easier to handle than cables with individual fibers.
How Do We Splice Ribbon Fibre Cables?
It won’t be far-fetched to say that if you want to achieve quality splicing for ribbon fibre cables, you must go with the fusion splicing method. Everything from FTTx networks to long haul point-to-point networks utilizes fusion splicing for their permanent optical cable connection.
Here, the most important tool is the ribbon fusion splicer (also called mass fusion ribbon splicer). What it does is that it splices an entire cable of ribbons at one time. Here’s how mass fusion splicing works:
- For easy stripping through heat, the holder is inserted in a special stripper.
- Next, to cleave the ribbons, the same holder is placed in a special cleaver. Here, the cleaver cleaves all the 12 fibers in a 12 fiber ribbon cable simultaneously.
- Next, we use the splicing machine wherein the fixture with all the cleaved fibers is placed. As soon as the second ribbon is ready, splicing is set to be automated.
As you can see, ribbon fiber cables are considered as a single assembly and thereafter spliced to perfection through a multitude of reliable tech tools. Today, these tools are not only getting cheaper by the day but can also achieve a splice quality of less than 0.05 to 0.10 dB per fiber.
Applications of Ribbon Fibre Cables
In the last section of this blog, we will finally take a look at some of the advanced applications of ribbon fiber optic cable.
- An optic cable of the ribbon fiber type is typically installed in indoor/outdoor point-to-point networks and indoor FTTH networks.
- They are also used for interconnection and cross-application of MTP fiber wiring boxes.
- They are also typically installed in the urban construction of circle trunk cable networks.
For operators, the increasing implementation of ribbon fibre cables signals a positive change. They can utilize these fibre cables to reduce their roll-out time and optimize duct space usage. Additionally, network operators can also improve network performance significantly, enjoy cost savings and reduce the size of passive network infrastructure!
FAQs
How many fibers are in a ribbon?
Ribbon fiber cables are known for their high fiber density in a compact package. Every ribbon in a ribbon fibre optic cable can contain anything from 4, 8, and 12 to 24 optical fibers. Using such an arrangement makes mass fusion splicing of 12 fibers simultaneously possible, thus making ribbon fiber a very easy-to-manage, install and restore solution.
How do you splice ribbon fiber to loose tube?
Typically, a ribbon fiber cable is spliced using the mass fusion technique that splices 12 fibers in one go. However, when slicing a ribbon fiber to loose tube cable, this technique can’t be used. Instead, the ribbon fiber is first stripped down into individual fibers at the splice cassette, and then a single fiber splicer is used to create a connection to the loose tube fiber cable, one fiber at a time.
Can you use a single fiber splicer to splice ribbon fiber cable?
Yes! While this method is not recommended as it is time-consuming, a single fiber splicer is used to splice a ribbon fiber cable to a loose tube cable. This method is explained in the answer above as well.
What is rollable ribbon fiber?
A rollable ribbon fiber is one of the types of optical fiber cables which typically consists of 12 ribbon fibers partially bonded to each other at predetermined points. It is a very promising technological innovation in the field of fiber optic infrastructure and is used to double the fiber density of network infrastructure in comparison to traditional cables. Rollable ribbon fiber is now being used in fronthaul applications, fiber to the home, and mobility network backhaul.
How do you make fiber ribbons?
Fiber ribbons are made by joining multiple optical fibers in ribbon form. Each individual fiber in a ribbon is aligned in a single row and impregnated with an acrylate UV curable resin. These fiber ribbons are stacked into a matrix structure to form a bundle inside a central core tube or in stranded multi-tubes.














