The era of internet connection has now been revolutionised with the introduction of optical fibre technology. With the incorporation of optical fiber cable, innovation has enabled millions of people around the world to achieve faster data transfer speeds.
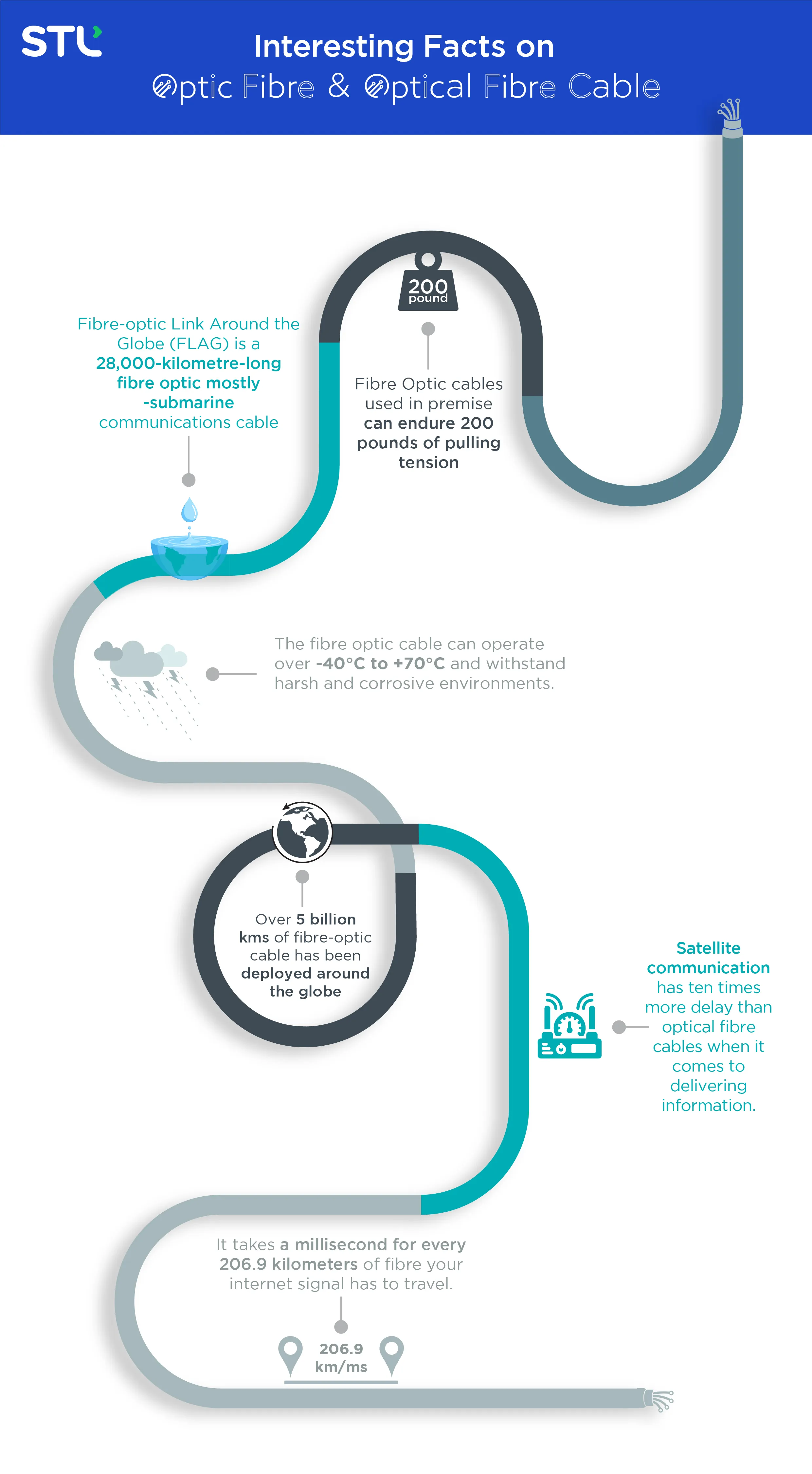
Figure 1: Interesting Facts on Optical Fibre and Optical Fibre Cable
It has also modernised businesses and altered their perspective on operational efficiencies. With all of these advantages and more, optical fiber is a truly fascinating innovation that will continue to evolve with many more advancements.
However, in our quest to use optical fiber, we frequently need to pay more attention to the true potential of this technology.
There are ample technical and interesting attributes of optical fibre and optical fibre cable, which makes it an astounding technology. So, to give you a glimpse of the efficacy of optical fibre, here are some amazing facts associated with it.
1. Feasibly Operates in a Temperature Range of -40°C to +70°C
The best thing about optical fiber cables is their ability to withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to +70°C. It can also stand up to bad weather and climate disasters. Unlike traditional copper cables that break down due to heat, cold, or rain, optical fibre withstands all corrosive and harsh environmental effects to continue consistently offering quality and faster data transmission.
2. Capable of Withstanding a Pull Tension of up to 200 Pounds
The use of aramid yarn in the internal Kevlar is what adds strength to the optical fibre cable cables. Thus, it develops a whopping maximum pull tension of 200 pounds. It is the maximum pull tension for the cables when used within enterprises. But, considering the cables are designed for outdoor usage, the pull tension can be extended to 500 to 600 pounds.
3. FLAG (Fibre-Optic Link Around the Globe) is 28,000-Kilometre-Long Fibre Optic Connection
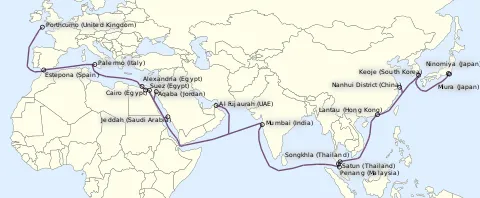
Figure 2: FLAG Stech on the Map
Image Source: Wikipedia
One of the jaw-dropping facts associated with optical fibre cables is the implementation of FLAG. The FLAG is a nearly 28,000-kilometer-long optical fiber connection line. It is mostly the submarine communication cable connecting the UK, India, Japan, and many other places.
This entire cable is operated by Global Cloud Xchange, a licensed subsidiary of RCOM. This long optical fiber connection runs from the eastern coast of North America to Japan.
The fun fact here is that 28,000 kilometers of optical fiber cable is equivalent to 14 trips to the moon. Isn’t it amazing how adaptable optical fiber cables have become in today’s world?
4. A Millisecond is Needed for the Internet Signal to Travel 206.9 km within the Optical Fibre
People often talk about optical fibre supporting data transmission at the speed of light. But, the actual relatability of this saying is associated with the speed of light in a vacuum. Light travels slower than usual when passing through some medium, such as air or fibre optic cables.
As far as mathematics and scientific evidence are concerned, light travels through optical fibre cables at a 31% slower rate. Thus, your data intend to travel at a speed of 206,856,796 m/s.
If we narrow it down to a more understandable unit, the light, in the form of internet signals or data, takes one millisecond to cover a distance of 206.9 km within the fibre cables.
5. Optical Fibre Cables Deliver Information 10x Faster than that of the Satellite Communications
The best thing about optical fibre cables is the passage of light during transmission. When it happens, the light is restricted to the core due to the total internal reflection. Thus, it permits the signal to chase the cables at the curves, turns, and bends. In this way, data loss and delays are minimised.
But in the case of satellite or wireless signals, the data must travel in a straight line. Thus, sending out the signals through curved or bent surfaces becomes a lot harder.
Thus, when you intend to talk to someone in a different country, the satellite will make your message travel with a delay of 238ms. And this specifies a 10x delay in transmitting the signals compared to the optical fibre.
6. Optical Fibre Cable Rollout Count Around the World Has Surpassed the Count of 5-Billion Kilometres
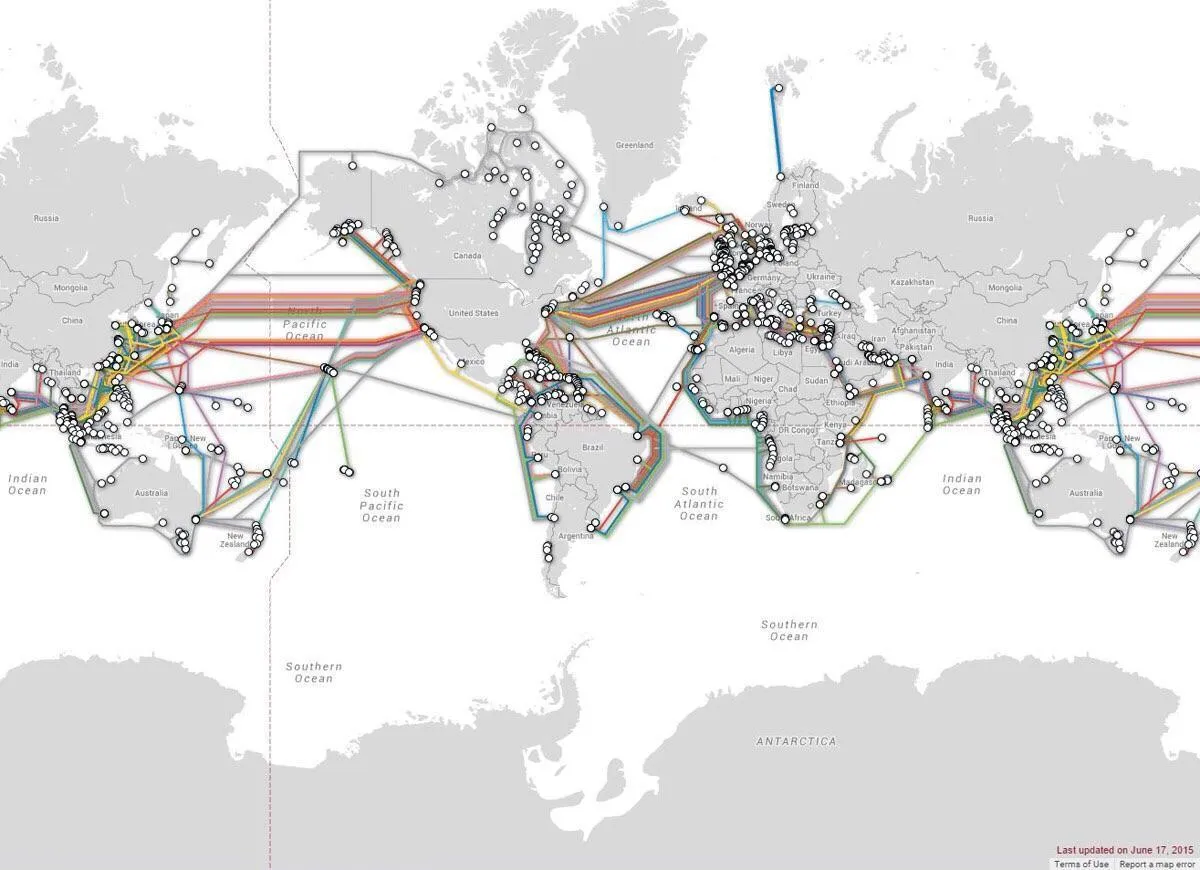
Figure 2: All Underwater Optical Fibre Cable Connectivity throughout the World
Image Source: reddit.com
Optical fibre cables have been rolled out worldwide, which equals a total length of 5 billion kilometres.
To let you know the significance of this number, 5 billion kilometres are equivalent to 57 times the distance to Mars from Earth.
Also, the approximate distance between you and Planet Pluto is 5 billion kilometers.
Conclusion
These are some amazing facts associated with optical fibre cables and technology. It explains the revolution this world has experienced with the innovation of this modern technology. The improved data transmission, high-end internet speeds, and many more such features will change the face of communications and connectivity worldwide.
FAQs
1. How fast is an optical fiber connection?
An optical fibre connection provides internet speeds of around 1 Gbps, which is 10x to 20x faster than standard 100 Mbps cables. Fibre optic cables can even transmit data faster than wireless networks.
2. Where is the longest fibre cable in the world?
The longest submarine optical fibre cable 2Africa, which stretches to around 45,000 km long, is connected to Port of Marseille. It was initiated by Meta, which is destined to connect across three continents and 33 countries.
3. What type of fibre optic cables are used for communication links longer than 1,000 metres?
Single-mode fibers are preferred when using optical technology to establish communication links for distances greater than 1000 meters.















