In this age of data ubiquity, localization policies’ emergence and wide adoption is a story to be told. India finds itself at such a crossroads as to whether it should embrace restrictive measures that limit processing or storage within its confines, an action driven by multiple concerns regarding data flow across borders. What remains to be seen is how successful these localized practices will prove in achieving stated hopes for Indians everywhere.
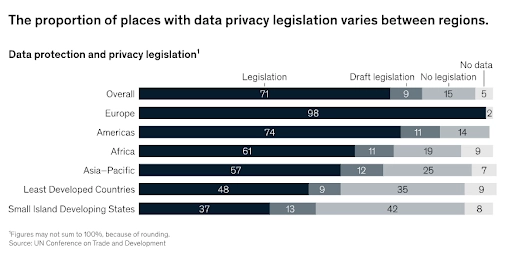
Image Credit : mckinsey.com – Data privacy legislation
India is quickly becoming a leader in the data localization debate. To ensure their objectives are met, it’s essential to understand all the existing variants that dictate how personal data should be handled – from requiring local storage for certain types of info to mirroring and free-flow arrangements with other countries.
Recently, data has become the norm rather than the exception. Today’s data is crucial to the operation of our digital economy. So it’s natural to have numerous questions regarding data storage and management locations and the myriad of current privacy problems associated with such data. Data center services archive, manage, and process information in highly specialized, computer-networked storage facilities. They’re located in hazard-free regions.
Data centers, an essential aspect of every company, are a treasure trove of useful information for running a firm. They offer the following services:
- Data storage, backup, and recovery
- High-volume e-commerce transactions
- Productivity apps like email
- Big Data
- Machine learning
- Artificial intelligence
Contents
Who uses data center services?
To store, process, and transmit massive quantities of data, businesses, organizations, and other entities that operate in the internet environment rely on data centers. By partnering with scalable cloud service providers, data centers may be accessed anywhere in India or the globe. Any company or entity may pay a fee and use the data center services regardless of location. Consumers are understandably concerned about the privacy implications of organizations’ data-gathering tactics and the storage implications.
Three tailwinds fuel India’s demand for data center services: booming data consumption, digitization, and localization.
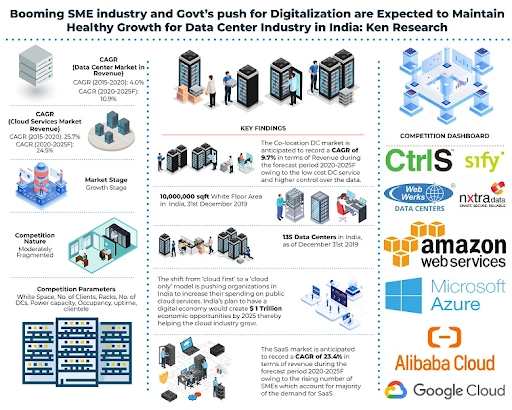
Image Credit : kenresearchreport.wordpress.com – Digitalisation
Taking advantage of data localization solutions
Businesses in India plan to address the growing concern about data security by using data localization. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) mandated in 2018 that any businesses that handle financial information for Indian customers must do it on Indian soil. It is shorthand for various policies that restrict cross-border data transfers. Data localization is helpful because it restricts data storage and processing inside a country’s borders. Several nations have instituted data localization regulations in response to security fears associated with cross-border data transfers. As a result of data localization laws in India, businesses are required to gather sensitive customer information for storage and processing in data centers within the country.
Data localization situation in India
Data localization has become a major political hot potato in India, as both sides of the debate are determined to make their voices heard. On the one hand – businesses and industry reps have called for access to Indian consumer data so they can take advantage of the perceived economic benefits brought about by harnessing its potential. At the same time, on the other side, government officials emphasize an essential need to protect personal information and improve national security measures via better enforcement capabilities. In 2019, these discussions took center stage when parliament introduced a nationwide data protection bill seeking approval from all members – with deliberations still underway amidst high tensions between opposing views.
The Indian economy is taking precautions to ensure data security – from the telecommunications sector requiring subscriber information be stored and processed locally to India’s Reserve Bank mandating payment data must stay within its borders. These measures show that local economies are taking steps toward a secure digital future.
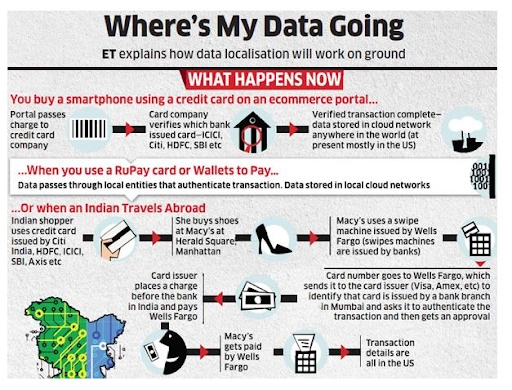
Image Credit : civilsdaily.com – Data localisation
Several official papers explain why the Indian government has decided to enforce data localization. However, the committee of experts’ report led by Justice B. N. Srikrishna is significant. The report’s proposal to localize personal data has been justified in full. Based on its findings, the same committee proposed a new legislation in 2018 called the Personal Data Protection Bill. Following this outline, the Indian government presented legislation for 2019 to the Indian parliament.
There are four goals that the Indian government has outlined for its pursuit of data localization.
- Protecting law enforcement’s ability to acquire private information quickly and efficiently.
- Fostering expansion of the economy and job creation.
- Protecting against spying from outside.
- Stricter compliance with privacy regulations.
India’s Economic Growth: How data localization can help?
A school of thought holds that keeping Indian customers’ data inside India, rather than letting it flow freely, would be better for the country’s economic development and innovation. Although there is little body of work on localization’s effects in India, studies have yet to examine data localization’s overall benefits and expenses.
For two reasons, it may hurt international enterprises if India moves towards data localization.
- These businesses would incur sunk costs if they invested in data storage and processing facilities in India.
- There would be recurring expenses for renting or running data-related infrastructure.
If that were to happen, doing business in India would be more expensive than in other nations. But on the other hand, if it gets difficult to use data storage facilities in India, the prices of these services might rise.
These changes will also impact Indian businesses that retain consumer data outside India. It is also unclear how retaining Indian data inside India can foster local innovation, although some hold this theory. While there may be economic advantages to boosting data availability, doing so would need further legislation to prevent sharing private personal data. Although these precautions should be considered, it is still being determined whether data localization is necessary to implement them. Additionally, the localization of data is irrelevant to jurisdictional data access claims.
Regarding labor, space, and connectivity, India is at least 60% less expensive than the United States or Singapore. Consumers that are searching for rack space will benefit from these price reductions. In addition, since many major corporations now have their means of generating and distributing electricity, we should expect to see a considerable decrease in the price of data center services. However, some service providers will also use government subsidies in the form of reduced rates for electricity and import fees and taxes.
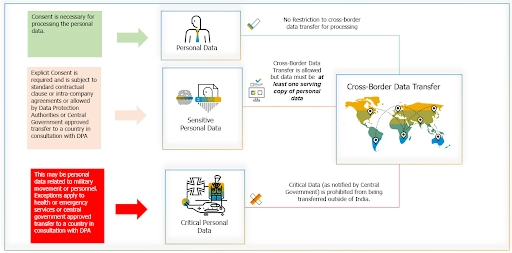
Image Credit : blogs.sap.com – Data Transfer
Data localization for MSMEs
There are 6.3 crore micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) in India, according to the India Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF). As more micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) embrace cloud computing, the notion of local clusters delivering cloud services may emerge.
Among the MSME sectors expected to uphold customer privacy and comply with data localization are accounting firms, hospitals, pathology labs, online marketplaces, stock brokers, commodity brokers, cooperative banks, tutoring services, and educational institutions. In addition, their method of operation will change because of this. Therefore, protecting the privacy of customers’ sensitive information is more crucial than ever.
It will be up to the individual to attest that their data complies with local regulations. Sometimes, authorities may need more resources to ensure and track compliance. In addition, due to their distrust of the cloud, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) tend to store their data locally, making audits of their data flows a potentially costly and time-consuming endeavor. At the same time, enterprises must make a deliberate choice, get their act together, and treat data as a valuable digital asset before they can leap into cloud computing.
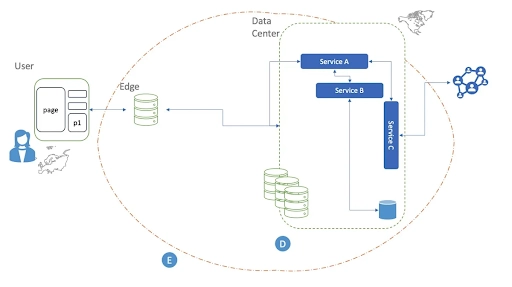
Image Credit : infoq.com – Data center
Conclusion
Data localization and access may appear similar, but they are quite distinct! Policies that try to mix them up only stand a little chance of meeting their objectives – with the potential for unexpected costs. So what’s India’s best bet? A framework that requires local storage without limiting global processing – should help unleash growth & innovation within our boundaries. India could experience unprecedented economic growth with a localization framework that stores data locally and processes it globally. This is closely followed by mirroring of data or an absolute hard localization requirement that would significantly increase the demand for goods & services in India.















