We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- Why Legacy Charging Systems are Losing Touch?
- Need for Superior Customer Experience Calls for New-Age Charging Models
- Why We Need a New-Age Charging Mechanism for 5G Networks?
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is WiFi?
- What is Data Center?
Contents
Why Legacy Charging Systems are Losing Touch?
Have you ever wondered how long the traditional charging is going to run the world? Traditional Charging is going to be dead soon. Its existence served the demand of typical telecom use-cases of rating and charging the time and data units. The legacy charging system is capable of rating the telco service usage and manage the service balances in real-time through standard protocols.
However, there are various challenges in 4G network as well as security like IP spoofing, User ID theft, intrusion attack and quality of service issues like video buffering, low bit rate, high probability of packet drop and many more. Hence, there is a need of upgrading to a network which can provide increased speed with high quality-of-service and improved bandwidth, reduced latency and support newer technologies like Augmented Reality/ Virtual Reality and Internet of Things (IoT).
Moreover, there is a constant need to nurture new revenue streams to stay relevant in this competitive market.
Need for Superior Customer Experience Calls for New-Age Charging Models
Traditional systems will no longer serve the need of modern monetization techniques. The new charging models have brought a shift in paradigm that allows the business operators to rate and charge ‘anything and everything’. New age charging is not only about the low-latency, unlimited usage and uninterrupted services, but it is more focused on providing the lucrative business offering to not only the telco industry but non-telco industries as well while keeping the end customer on the highest priority.
It allows building alliances among adjacent as well as non-adjacent businesses using a multi-party business model (B2B2X). It also gives significant opportunities to build more compelling offers for consumers and businesses and thus enabling business operators to introduce new revenue streams
Why We Need a New-Age Charging Mechanism for 5G Networks?
Accelerating 5G launch readiness, is pushing operators to innovate across a range of issues like faster 5G deployment, densification of networks, backhaul fiberisation and achieving the right balance between reach and density. The same is true for the world of charging too.
Most important charging and billing considerations for 5G:
- Critical/ delay-sensitive applications
- Charging for Hosted Applications
- Heterogeneous Alliances with charging in various units/ conditions
- Network slicing: Mobile Broadband, Mission Critical IOT and Massive IOT
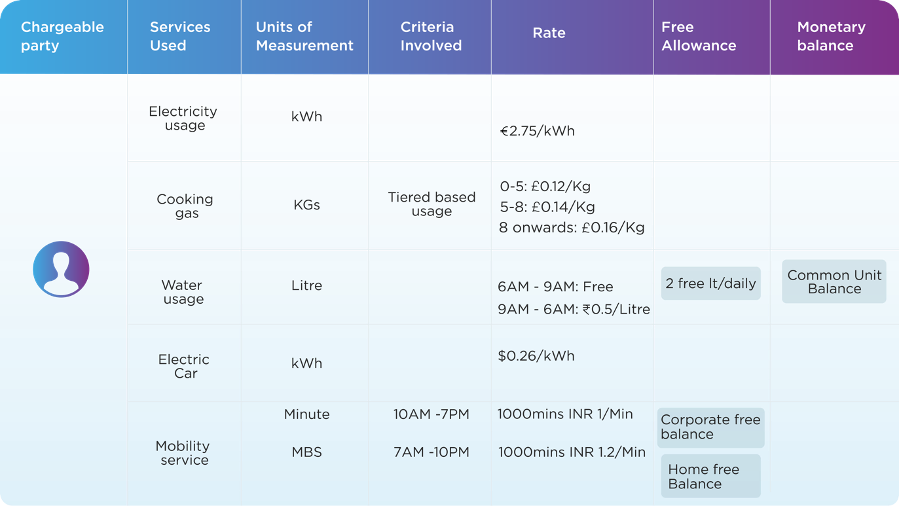

Slice-aware CHF is capable of managing multiple network slices to provide the best quality of experience to the end-users. Mission-critical applications and massive IoT like health services, connected cars, aircraft, emergency communication, surveillance and others will also demand a change in the charging system to support slice-based rating. Multi-party charging in a single flow/ usage allows the service providers to grow more business with alliances and provide the best-class service and attractive offers to the subscribers.
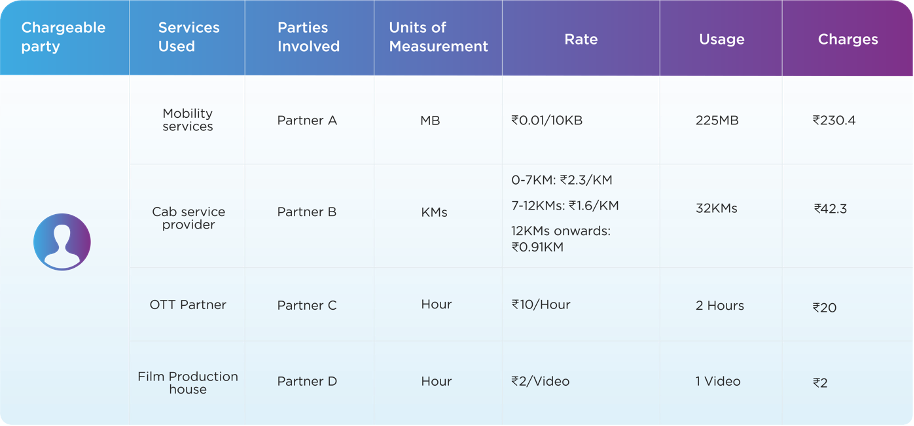

As evident from the use cases mentioned above and the nuanced charging approach required to provide these services, there needs to be a converged charging system that allows for operators to launch new services and monetisation models with ease and flexibility
Leaving the legacy way behind, the new-age, HTTP/2 based charging allows service providers to build a robust charging solution that can integrate with the 5G networks in a uniform and optimized way.
Figure 3 – Traditional vs 5G converged charging system, a comparison
| Traditional Charging | 5G Converged Charging System (CCS) |
| Rating based on a single unit- duration, volume, count | Rating based on multiple units- kWh, litre, square meter, Kg and many more |
| Balance Types: Monetary and Non-monetary | Any balance types for any unit |
| Rating based on fixed criteria | Rating based on “any” criteria |
| All charges could be applied to either one or a combination on balances | Charges need to be applied to specific balance types |
| Charging based on multiple types/ conditions to the single chargeable party | Charging based on multiple types/ conditions to multiple chargeable parties |
| Single/ double charging unit based on charged party in a single flow | Multiple charging units based on multi-charged party in a single flow |
| Charging the service usage in a single currency in a single flow | Charging the service usage in multiple currencies in a single flow |
| SPR for subscribers | Single UDR for subscribers and parties |
FAQs
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).
What is Data Center?
A datacentre, sometimes referred to as a server farm, is a centralized physical location housing compute resources (high-end servers), storage (SSD, HDD, Flash, Optical), and networking equipment (routers, switches, firewalls, etc.) for collecting, storing, processing, distributing and allowing access to large amounts of data.
Apart from the IT equipment data center also houses environment controls (airflow, humidity & temperature sensors), server racks, power supplies (backup systems, generators), and cabling systems (ethernet, copper, optical fiber). Initially, data centers were introduced to manage the large influx of service requests and store user-generated data.
In contrast, it has now evolved to adopt technologies such as virtualization, cloud computing, mobile, Internet of Things (IoT) applications, machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics.
There are four main types of data centers:
- Enterprise data centers – Built, owned, and managed by a company for particular use-cases for their target user set. They are usually built on-site but can also be built away from the company premise.
- Managed services data centers – Deployed, managed, and monitored by a third-party datacentre service provider for a company. The features and functionality can be accessed by the company using a managed service platform (MSP)
- Colocation data centers – Consist of one data center owner selling space, power, and cooling to multiple enterprises and hyperscale customers in a specific location. The company focuses entirely on running the compute, storage, and networking equipment while the data centre service provider takes care of the space, power, cooling, security, and IT racks.
- Cloud data centers- An off-site data centre provider such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud that stores the data of various enterprises. The data is fragmented and stored at various locations across the internet (i.e. datacentres across the world). This offers enhanced security, scalability, management, reliability, customization, and cost-effectiveness.
















1 Comment
Raj Kumar
October 27, 2020Very Nice Write Up