Today, more than 13 billion IoT devices are connected across the globe. The industry is expected to surpass 25.4 billion IoT devices by the end of 2030. Its demand and necessity for various applications have made it a quite familiar technology in the past decade.
The Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities have penetrated several industries and are now being used to link larger networks. IoT relies a lot on telecommunications service providers, and therefore a lot of players in the telecom sector are building their capabilities in the IoT space.
But how do telecommunications companies, or telcos, add value to their services or utilities with the help of the IoT? This article will shed light on that logic and implementations for you to understand the potential of the IoT.
Contents
Contribution of Telcos for the Utilities that Use IoT
The telcos consistently pursue opportunities for expanding their offerings and creating modern revenue streams for existing and new consumers. Utility companies, on the other hand, are looking at technology to smooth operations and increase efficiency. IoT, therefore, becomes a common ground for utility and telecom companies.
One such example where IoT brings value to the utilities by Telcos is smart metering. Smart metering and other such IoT implementations within the telecom sector are helping the utilities gain more access to information. It has provided more efficient ways of collecting and managing the utilization data of consumers. This data is then used to enable faster customer payments, detect faults, and reduce downtime.
Utility companies are increasing their efficiency with the Internet of Things in order to reduce their primary operating expenses. This technology helps the telcos build intelligent solutions and be part of the future of smart cities.
Smart metering is an example of IoT in utilities, and it solely depends on communications. There has been an evolution in communication technologies for the smart metering aspects. These communication modes are categorized based on the preferred transmission medium.
You need to divide them into wireless and wired technologies. Power line communications (PLC-wired) or radio frequency mesh (RF Mesh-wireless) are the two most popular communication technologies that are preferably useful for smart metering or IoT utilities.
Shift to Utilization of Low-Power Wide Area Networking (LPWAN)
The telcos use core protocol technologies to connect IoT devices with their networks. These technologies are narrowband IoT and LTE-M. These protocol technologies consume little power and have low bandwidth. They are optimized for connecting IoT devices to cellular networks.
Recently, the telecommunication utilization for utilities using IoT shifted to LPWAN. Cellular IoT technologies are a part of it too. The LPWAN connectivity technologies are growing tremendously as they offer flexibility at a low cost.
LPWAN is a wireless telecommunication network specifically designed to permit long-range communications at a low bit rate among IoT objects. Apart from smart metering, LPWAN is also preferable for many other IoT solutions, such as asset monitoring, smart cities, smart lighting, livestock monitoring, energy management, etc.
The 3 Non-Wireless Technologies that Telcos Use for IoT Utilities
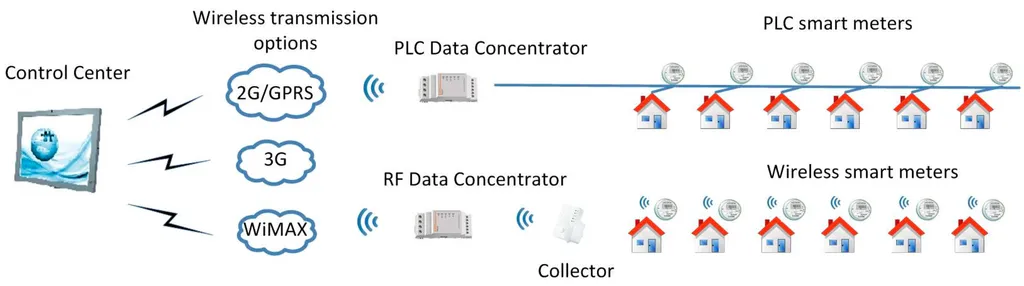
Figure 1 – Use of PLC and RF Mesh for smart meters
Image Source – mdpi.com
Below are the non-cellular telecommunication technologies used as an integral part of the smart grid. Here’s a brief description of all three technologies to help you understand how telcos add value to utilities using IoT:
1. Power Line Communication (PLC)
PLC benefits from the available power-line installations as part of the communication efforts. Thus, it enables the utilities to utilize the widespread infrastructure without laying dedicated cables. The installation of PLC modules makes use of electrical wiring for transmitting the electric power and data without any restricting interferences, as both are at varying frequencies.
PLC system is an old yet reliable medium of communication in comparison to all of the other mediums. Even with the popularity of implementation, PLC being used by the telcos for IoT utilities has some limitations, which include the slower transfer of data, operating switch interruptions and signal distortions. Considering this, the other communication channels were prioritized for smart metering or IoT utilities.
PLC was primarily made with electricity as a core element in mind. Therefore, these negatives of PLC modules can be eradicated by mixing them with RF Mesh technology. Unlike PLC, RF Mesh supports wireless communication and adds core functionalities for AMR (Automatic Meter Reading). It is used for measuring power consumption and acquiring data from the customer who is using the utilities.
When paired with the PLC, there is better coverage and accuracy. It is also implemented by adding modules to the meters, which enables telcos to be part of the utilities using IoT.
2. Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
DSL is another communication technology that uses traditional telecommunications lines to transmit data. It is reliable, and the overall cost is also low. Since the infrastructure is already available in most cases, setting up DSL for smart metering becomes cheaper. This may not be a good option for high-data transmission.
3. Fiber Optic Communications
Fiber-optic communications is an outstanding solution to all of the limitations of other technologies. The cost of implementation is justified by its productive perks. It is mostly preferred when high data transmission rates are important.
The networks made up of fiber optic cables are deployed across the world now. The fiber optic lines are now installed alongside the power lines to serve the purpose. This initiative has been an integral part of grid modernization.
Conclusion
So, this article educated you on how telecom companies are upgrading themselves with the right implementation of communication technologies. They are playing their part in adding value to the utilization of IoT in utilities. Fiber optic cabling is one of the most advanced and performance-rich communication technologies used on demand.
Optical fiber is a future-proof technology that will take telcos ahead in association with utility companies. STL is one of the few quality providers of optical fiber technology and is dedicating its expertise to utilizing this technology in thriving industries around the world. To learn more about the same, visit https://www.stl.tech/fibre-deployment-solutions/
FAQs
1. What type of communication technology is preferred for smart meters?
When mixed with wireless or wired solutions, hybrid communication technology is ideal for offering high levels of system robustness, availability, and reliability. PLC, RF Mesh, DSL, and fiber optic cabling are the best-fit components for the smart meter or smart grid. They have a high-frequency range, data rate, and bandwidth.
2. How are smart meters connected to the internet?
Smart meters are connected to the internet through wireless communication networks. These networks have the role of sending information to the energy provider. This connectivity is similar to all other IoT devices, such as remote keys, TVs, and others.
3. What is the purpose of two-way communication for the smart meter?
Smart meters operate on a two-way communication medium within the central system and the smart meter. Thus, an AMI (advanced metering infrastructure) differs from an AMR (automatic meter reading). AMI extends AMR technology with the use of two-way meter communications. It allows commands to be sent to the home for multiple purposes. It includes demand responses, pricing information based on time, and remote disconnection of services.
4. What is the application of IoT in utilities?
The application of IoT in the utility industry will improve efficiency, generate revenue, and conserve an enterprise’s resources. The use of IoT sensors can optimize water and energy generation as well as distribution. It is to help utility providers meet the rising demand for their services among consumers.















