We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- Why’s 5G so Popular Even Before the Launch?
- What are the Three Major Use Cases for 5G?
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is WiFi?
- What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
Contents
Overview
While 5G is right around the corner to open a world of opportunities, most people still haven’t fully understood how it’s a revolutionary technology. 5G will let the world run on secured connectivity options among all kinds of devices, including smartphones, robots, sensors, vehicles, and drones.
With technological advancements in several industries, it opens up new ecosystems while directly impacting the economy. From agriculture and healthcare to manufacturing and warehousing, every industry will benefit from the launch of 5G.
5G is powered by low latency and high output. As such, it will take a fraction of a second to transfer data from one network to another. Simply put, 4G features approximately 50 milliseconds of latency. In comparison, 5G requires only 1 millisecond to transfer the same amount of data.
The decrease in latency will bring revolutionary changes in several industries, thereby making it possible to manufacture autonomous cars, perform remote surgeries, and streamline logistical operations.
Why’s 5G so Popular Even Before the Launch?
With 5G, it’s possible to consider a world with numerous opportunities of connecting anything to everything. Imagine a world where doctors are connected to medical devices of patients, cars drive autonomously in traffic, and shoppers purchase basis augmented reality. All this will be possible with the launch of 5G.
5G will be the driving force for billions of connections. Moreover, these connections will be instantaneous and more secure. In the coming years, 5G will undoubtedly impact every major industry in the world. A huge network of IoT (Internet of Things) will be the catalyst to build a smarter and better-connected world.
5G will be a gamechanger in providing low latency, high speed, and better connectivity. It will empower a new generation of business opportunities, services, and applications. As far as use-cases are concerned, there are several as shown in the image below (Source: GSMA) .
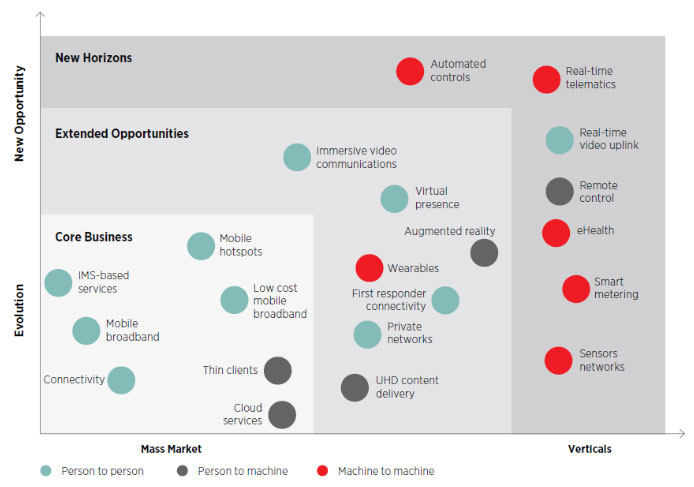
What are the Three Major Use Cases for 5G?
Internet of Things (IoT) – 5G will allow seamless connections among billions of devices. Using 5G networks, machine-to-machine communications will be faster and streamlined. Moreover, human intervention won’t be needed to manage these large-scale platforms. 5G has the potential to revolutionize industrial applications and processes at a scale never seen before.
- Reliable low latency communications – 5G will allow critical communications with real-time control. Some industries that would benefit from low latency include safety systems in vehicles, safer transport networks, and autonomous driving. Additionally, low latency will open up a world of opportunities in healthcare treatments, procedures, and devices.
- Improved mobile broadband – 5G will ensure greater capacity networks with faster data speeds. Among new applications, you’ll find outdoor broadcast mediums, fixed wireless internet connectivity for homes, reliable broadcast vans, and better connectivity for individuals using smartphones.
Smart Cities and Businesses – As mentioned earlier, 5G will allow connections among billions of devices. As such, it’s potential for impacting smart cities can’t be overlooked. Using 5G, communities and governments will be able to provide better facilities in schools, homes, transport systems, healthcare, and education.
Similarly, businesses will have a much better grasp on the wealth of data available to gain insights. Data analytics will help businesses and industries take smarter decisions to impact revenue and operations. With 5G, innovations in agriculture, manufacturing, logistics, aviation, and fintech can’t be overlooked. Data-driven decisions will pave the way for long-term growth, better customer experience, and cost savings.
Emerging Technologies – Virtual and augmented reality are examples of two latest technologies that have made it possible for enhanced connections and experiences. The addition of 5G will make these technologies accessible and available to everyone. With VR and 5G, people will be able to enjoy live concerts, seamless virtual meetings, remote gaming competitions, and several other remote opportunities empowering digital economies.
The smart cities of tomorrow will benefit from 5G and allow for better connections while opening up new avenues for the world to explore and experience. 5G will bring forth a new era of globalization that will benefit all and offer opportunities that haven’t yet been realized yet.
FAQs
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).
What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
An optical fibre cable is a cable type that has a few to hundreds of optical fibres bundled together within a protective plastic coating. They help carry digital data in the form of light pulses across large distances at faster speeds. For this, they need to be installed or deployed either underground or aerially. Standalone fibres cannot be buried or hanged so fibres are bunched together as cables for the transmission of data.
This is done to protect the fibre from stress, moisture, temperature changes and other externalities. There are three main components of a optical fibre cable, core (It carries the light and is made of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with dopants such as germania, phosphorous pentoxide, or alumina to raise the refractive index; Typical glass cores range from as small as 3.7um up to 200um), Cladding (Cladding surrounds the core and has a lower refractive index than the core, it is also made from the same material as the core; 1% refractive index difference is maintained between the core and cladding; Two commonly used diameters are 125µm and 140µm) and Coating (Protective layer that absorbs shocks, physical damage and moisture; The outside diameter of the coating is typically either 250µm or 500µm; Commonly used material for coatings are acrylate,Silicone, carbon, and polyimide).
An optical fibre cable is made up of the following components: Optical fibres – ranging from one to many. Buffer tubes (with different settings), for protection and cushioning of the fibre. Water protection in the tubes – wet or dry. A central strength member (CSM) is the backbone of all cables. Armoured tapes for stranding to bunch the buffer tubes and strength members together. Sheathing or final covering to provide further protection.
The five main reasons that make this technology innovation disruptive are fast communication speed, infinite bandwidth & capacity, low interference, high tensile strength and secure communication. The major usescases of optical fibre cables include intenet connectivity, computer networking, surgery & dentistry, automotive industry, telephony, lighting & decorations, mechanical inspections, cable television, military applications and space.















