According to Gartner, the cloud computing business is expected to grow by 20.4% in 2022 in terms of global investment in public cloud services. The spending was $410.9 billion in 2021 and is forecast to reach $494.7 billion in 2022 and $600 billion by 2023. Both data centers and cloud computing are vital components of running day-to-day operations for most businesses that use data as their driving force.
Previously, a data center in cloud computing was a separate entity where a physical facility was created to provide storage and processing capability for businesses to run their applications 24×7 and 365 days a year. But now, we are seeing a shift where on-premises data centers are getting replaced by cloud data centers. So, is data center technology in cloud computing the best move forward in achieving business excellence? Let’s discuss the role of data centers in cloud computing to get a clear understanding of how the data center and cloud computing combination can benefit businesses big time.

Data Centers in Cloud Computing
Role of a Data Center in Cloud Computing
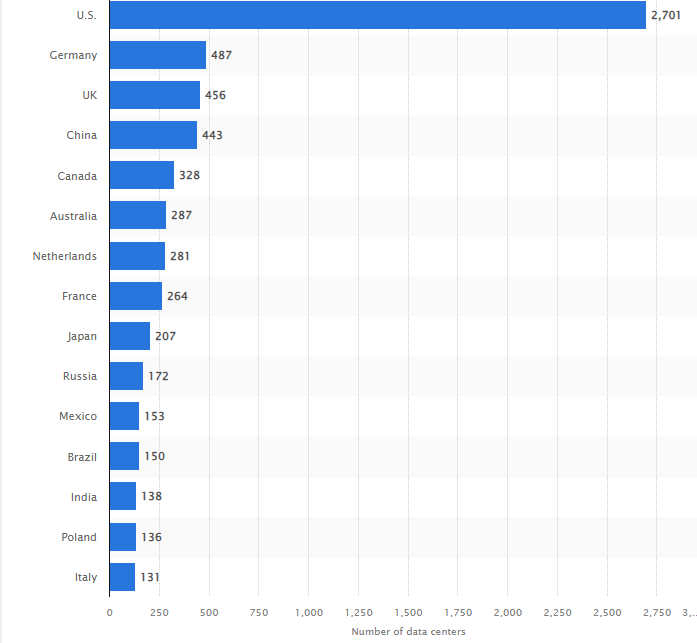
No. of Data Centers in Top Countries Across the World 2022
A data center is a dedicated facility that incorporates computing and storage resources that allow the delivery of shared applications and data required for day-to-day business operations. The facility includes a network of computers, computing infrastructure, and storage systems that firms will use to process, gather, disseminate, and store an enormous amount of data. The different types of data centers in cloud computing are infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), software-as-a-service (SaaS), and platforms-as-a-service (PaaS). Datacenters in cloud computing are integral to any enterprise, developed to support business operations and offer services like,
- Data management, storage, recovery, and backup
- High-volume online transactions
- Support applications like e-mail, payment gateways, etc.
- Facilitating online gaming communities
- Powering Big data, AI, and machine learning
According to Statista, the USA holds the first position for the number of cloud data centers with 2701, followed by Germany (487), and the UK (456), as of January 2022. India ranks 13th on this list with 138 data centers. Based on the population-to-data center ratio, the number of data centers in India is not enough, and there is scope for adding more to offer faster cloud services to end users.
Data Centers vs Cloud Data Centers: Getting to Know Them

On-Premises Data Center vs. Cloud-Based Data Center
On-premises data centers are private systems that enterprises build in-house and operate themselves. These data centers can be utilized to run private cloud networks, in which resources are virtualized in similar ways to public clouds and can be used from anywhere. However, private clouds can be operated and maintained by third-party services. On the other hand, when people speak about cloud-based data centers, they are referring to a public cloud network.
These types of data centers in cloud computing are run by third-party service providers who make the cloud services available for enterprises on an as-needed basis. The public cloud is a multi-client environment where computing resources are shared by multiple enterprises with data secured by state-of-the-art encryption. Examples of public clouds include Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, etc. Both on-premises and cloud data centers offer different advantages for enterprises running their business operations. Let’s compare both based on various business needs.
| Business Need | On-Premises Data Centers | Cloud Data Centers |
| Data center single ownership | Yes | No |
| Customizable hardware, purpose-built systems | Yes | No |
| Highly secure data encryption | Yes | Yes |
| Ease of scaling up and down | No | Yes |
| Infrastructure needing regular investments | Yes | No |
| Pay-as-you-go and utilization-based pricing | No | Yes |
| Complete data visibility and control | Yes | No |
| Almost Zero Down Time risk | No | Yes |
| In-built, automated data backup & recovery | No | Yes |
Impact of Cloud Computing on Data Centers
Cloud computing has metamorphosed the data center model. The traditional data center that runs on hardware and needs ample physical space is no longer feasible. Cloud service providers have commercialized storage, computing, and network resources, leading to the development of hyper-scale cloud-based data centers. These data centers are owned and run by the public cloud providers themselves. They can provide their services at a significantly lower cost than on-premise data centers. The conventional data center model was built primarily for renting or leasing the facility and power from the owner. With cloud-based data centers, everything is run digitally. Cloud computing has revolutionized how data centers are now managed. The advantages of cloud computing in data centers are numerous, but the three most prominent ones include agility, efficiency, and scalability.
Benefits of Adopting a Cloud-based Data Center
The top 5 benefits of choosing a Cloud-based Data Center are,
- Cost-effective – Companies adopting cloud-based data centers don’t have to pay for maintenance. As the hardware is placed at the cloud service provider’s data center, they consider any repairs their expense and don’t charge the clients. Enterprises don’t need to invest in the physical setup, upgrade, facility management, staff, power, and maintenance, making cloud-based Data Centers extremely cost-effective.
- Scalability: In an on-premise data center, companies have to plan the capacity well in advance and purchase hardware accordingly. This severely restricts when you face fluctuations in the workload. On the other hand, Cloud-based Data Centers are flexible and can manage bandwidth demands without any hassles. They enable businesses to boost their capacity as per demand without making additional investments in cloud infrastructure
- Data security: In a cloud-based data center, the service provider carries out deep testing and provides impenetrable protection for the entire data center and the data that is being stored or transferred. In addition, they deploy security measures such as authentication, blockchain, access control, encryption, etc., and empower companies to add more layers of security to secure their data further.
- Mobility: A Cloud-based Data Center can be easily accessed through smartphones and other connecting devices with security credentials to allow remote working. The stored data can be retrieved, processed, or recovered with just a few clicks on the laptop. This will enable employees to carry out their work from any corner of the world at any time zone.
- Data recovery: Data loss can be a nightmare for any enterprise. Cloud-based Data Centers ensure that any data is always available to you as they always create a backup of every bite. Hence, quick data recovery for any emergency scenario is possible, whether the data is lost due to natural disasters or power cuts.
Cloud vs. Data Center Myths
Some of the common myths surrounding data centers and cloud computing are,
- An On-Premises Data Centre more secure than a Cloud-based Data Centre
The first myth some cloud skeptics believe is that cloud-based data centers are prone to frequent data breaches or cyber-attacks, whereas on-premise data centers are much safer and more secure. However, the majority of professionals and experts agree that cloud computing provides more security for data than an on-premises data center.
- My enterprise is small-scale and can’t adopt Cloud Computing
Cloud computing was once believed to be the pet of big companies equipped with huge computing power and infrastructure. However, this is a myth, and any enterprise can adopt cloud computing, regardless of scale. In fact, SMEs might find it more useful as its adoption saves the cost of building an on-premise data center. Also, SMEs can save on the high cost of human resources required to maintain an on-premise data center.
- Cloud Computing is very expensive
The skepticism surrounding cloud computing adoption costs has been blown way out of proportion. While deployment costs vary from business to business, the “pay-as-you-go” model of cloud computing helps reduce unwanted spending on infrastructure. In fact, some cloud service providers offer their services without any upfront payment or termination fees.
- Cloud Computing is Only useful for Storage & Analytics
Although data storage and analytics are two popular features of cloud computing, that doesn’t mean only data scientists and IT departments benefit from them. Cloud computing can also be used in customer service, sales, marketing, manufacturing, and HR management. In addition, seamless data flow can be leveraged by every department of an enterprise to help them streamline each operation, which will further lead to revenue and brand growth.
Can your business benefit from Data Center & Cloud Computing Services?
Data centers and cloud computing can only benefit your business since you don’t have to invest in setup, recruit staff to maintain it, and constantly upgrade to improve speed and security. They offer other advantages like unlimited data storage capacity, automated backup and restoration of data, a pay-as-you-go model, better mobility, and many more. As the third-party cloud service provider takes up most of the responsibilities of upgrading, adding more security layers, maintaining facilities, etc., you can invest your time and effort in improving the other areas of your business operations so that from development to delivery, every task is streamlined to give the most profitable outcome.
FAQs
- Why do we need data centers in cloud computing?
A: In cloud computing, data centres are capable of supporting all types of computing, applications, and storage related to both the company and its end users. Cloud-based data centers allow employees to work from any corner of the world through a secured network and server system. Suppose there is some major problem and data is lost; data centers always have a backup, and you can easily retrieve the data within minutes. Cloud-based data centers don’t require maintenance and upgrades from the company’s end, as they will be taken care of by the cloud service providers. Now, enterprises can focus on the following:
- Add more employees to IT and data processing
- Improve computing and infrastructure for network connectivity
- Boost Computing Facility Security.
2. What are the three types of cloud data centers?
A: The threetypes of cloud data centersare,
- IaaS: It is a type of cloud computing data center that offers computing resources to users via the internet. Through IaaS solutions, the task of maintaining equipment completely falls on the shoulders of the cloud service provider. Ex: AWS, Linode, Azure, etc.
- PaaS: It can be regarded as a toolbox equipped with cloud-based services that enable developers to build all business and end-user applications. The benefit of building applications in the cloud-based data center is the fact that it’s much faster than any on-premises data center. Ex: OpenShift, Heroku, etc.
- SaaS: It is one of the most popular cloud-based data centers and is a typically used business solution in the cloud market. These solutions use the internet to deliver applications operated entirely by third-party service providers to their end users. Ex: SalesForce, DropBox, etc.
3. How data centers are connected?
A: The four primary components that connect data centers are,
- Facility. This is a physical location that houses the data center’s infrastructure and equipment. It must have access controls and enough space to manage data center operations around the clock.
- Enterprise data storage. Here every bit of enterprise data is stored and protected with the help of servers, networking switches, storage subsystems, routers, firewalls, cables, and physical racks.
- Support infrastructure. This arrangement will provide high sustainability in terms of uptime. The components include
- Electrical switching
- Power distribution & additional power subsystems;
- backup generators
- UPS
- Data center cooling and ventilation systems like Air conditioning
- Sufficient provisioning for network carrier and connectivity.
- Operational staff. These employees are responsible for maintaining and monitoring the data center’s IT and infrastructure equipment 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
4. What is the relationship between cloud computing and a data center?
A: Cloud computing is a version of a data center that is not present at your firm’s physical premises. A data center in cloud computing allows you to access your business-related data through the internet. The cloud service provider will take care of maintenance and upgrades and usually owns numerous data centers across the globe to protect your data during natural disasters and other issues that can destroy data. However, an on-premise data center is limited when it comes to data storage and retrieval. In contrast, a cloud-based data center is flexible and can adjust accordingly to the fluctuations in the workload.
5. Does cloud computing require data centers?
A: The answer is both no and yes. No, in a sense, as an enterprise, you don’t have to deploy any data centers on-premise when you adopt a cloud-based data center. Third-party service providers from whom you use cloud services, on the other hand, must establish their own data centers in multiple locations in order to store and secure data. Also, they handle multiple clients simultaneously, creating the need for enormous data centers to store, process, and backup data so that there is zero downtime whenever there is a loss of data due to natural calamities at the enterprise end.















