Contents
The Digital Divide in the UK
The “digital divide” is a growing concern in the UK, where access to technology and the internet remains unequal across the country. This disparity affects individuals, communities, and businesses, leading to unequal growth and opportunities. 93% of residents in rural areas in the UK have shown an increase in online service usage since 2020. However, one in six cannot access indoor 4G connections or superfast broadband. There are also massive disparities in digital connectivity and broadband infrastructure among regions. For example, 30% of rural commercial premises and 17% of rural residential premises do not have superfast broadband, which is 30 Mbit/s or more. The County Councils Network analysis shows that only
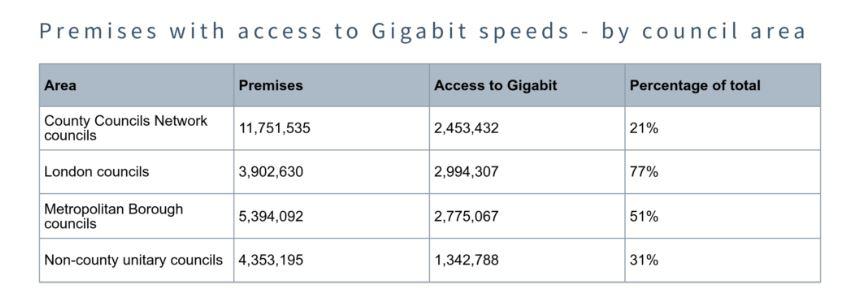
Fig 1: Premises with access to Gigabit speeds – by Council Area
Image Credit:- countycouncilsnetwork.org.uk
In this blog, we’ll explore how fibre networks are key to bridging the digital divide in the UK and ensuring equitable access to technology in 2023.
The Importance of Fibre Networks in the UK
Fibre networks are the backbones of the internet, providing fast and reliable connectivity. Unlike traditional copper-based networks, fibre networks are made of glass optical fibres that transmit data over light, providing faster and more reliable connections. This makes fibre an ideal solution for bridging the digital divide, particularly in areas where access to technology is limited.
In the UK, the usage of fibre networks has significantly increased over the years. According to the Office of Communications (Ofcom), in 2020, the number of homes and businesses connected to full-fibre broadband services reached 4.2 million, an increase of 1.5 million from the previous year. This increase was largely due to the investments made by network providers to expand their fibre infrastructure.
The benefits of fibre networks are also being recognized by UK businesses. In a survey conducted by the Confederation of British Industry (CBI), 97% of businesses reported that having access to reliable and fast broadband was essential to their operations, with fibre being the preferred option for achieving this.
Fibre networks have also played a crucial role in supporting the increasing demand for online services during the COVID-19 pandemic. With more people working and learning from home, the demand for reliable and fast internet connectivity has surged, and fibre networks have helped to meet this demand.
The Benefits of Fibre for Bridging the Digital Divide in the UK
One of the main benefits of fibre is its speed and reliability, which are essential for enabling equal access to the internet. Fibre networks provide faster download and upload speeds, making it easier for people to access online content and services such as online learning and telemedicine. Additionally, fibre networks are less prone to downtime, ensuring that people in under-served communities have access to the internet when they need it.
Another key benefit of fibre is its scalability. Fibre networks can be easily upgraded to accommodate increasing demand, making it easier to ensure that everyone has access to the technology they need. This makes fibre an ideal solution for bridging the digital divide, as it ensures that communities are not left behind as technology advances.
Overall, fibre networks have become increasingly important in the UK, providing fast and reliable connectivity for homes, businesses, and communities.

Fig 2: The flagship programme of the government, Project Gigabit, aims to provide lightning-fast broadband that is capable of gigabit speeds to communities that are difficult to reach. This £5 billion initiative aims to improve internet access for these communities.
Image Credit: gov.uk
STL – Bridging the Digital Divide in the UK
For more than two decades, STL has been building advanced optical fibre infrastructure in the UK. STL enables the leading telecom operators and ISPs in the UK with end-to-end optical solution offerings from fibre, fibre cables, and optical interconnect kits. STL’s optical solutions has applications in FTTx, 5G, Rural, Enterprise, and Data Centre networks. STL is committed to providing a comprehensive approach to planning, installation, testing, and maintenance of fibre optic networks to support a wide range of applications for our customers.
STL has a talented cross-functional team of sales, application engineers, and product developers based out of London and spread across the UK. STL has been at the forefront of enabling the government’s ambitious plan, “Project Gigabit,” to achieve a nationwide rollout of 5G networks and futuristic, gigabit-capable broadband. More can be learned about how STL is enabling rural connectivity around the world here.
Conclusion
Fibre networks are critical for bridging the digital divide in the UK. By providing fast and reliable connectivity, fibre ensures that everyone has access to the technology they need to participate in the digital world. With the UK government investing in fibre infrastructure, it’s an exciting time for the country as we move closer to bridging the digital divide and ensuring equal access to technology for all. The benefits of fibre networks will lead to improved productivity, increased innovation, and better access to online services.
It is essential for vendors and telecom operators to work in partnership and collaboratively address this issue. Vendors, who provide the necessary hardware and software for digital connectivity, can work alongside telecom operators, who are responsible for the provision of network infrastructure and services, to ensure that digital services are accessible to all. By sharing expertise, resources, and technology, vendors and telecom operators can develop innovative solutions to extend the reach of digital services to remote and underserved areas.To know more about our fibre network solutions, click here.
FAQs
1. How can the digital divide between countries be reduced?
Countries can significantly reduce their digital divide by reducing the prices of internet services, technological devices, electricity tariffs, and taxes.
2. How is the government trying to bridge the digital divide?
The government plans to establish high-speed broadband access and wireless connectivity everywhere to advance digital inclusion by creating new rural use cases that will provide higher returns.
3. What are the two disadvantages of the digital divide?
The major disadvantage of a digital divide in a nation based on communication is that it creates segregation between people, thus negatively impacting the economy. Other disadvantages are that it creates barriers to studies, services, and online businesses.
4. Why do we need to reduce or bridge the digital divide?
Overcoming the digital divide provides maximum distribution of digital resources and networks to the maximum number of members of the country. It thus helps create access to job training, employment opportunities, and other benefits.
5. What is digital inclusion?
Digital inclusion refers to all activities undertaken to provide access to and use of communication and information technologies by people, including the most disadvantaged.
6. What factors bring down broadband adoption in an area?
The broadband subscription cost, broadband service device costs, people’s digital literacy skills, and lack of awareness of the benefits of broadband are the major factors that bring down broadband adoption in an area.
7. What are the types of the digital divide?
There are three types of the digital divide:
- Access divide: Difference between the possibilities people have to access a resource.
- Use divide: Lack of digital skills that impede the handling of technology.
- Quality of use gap.















