In 2021, active IoT devices reached 12.3 billion and became a USD 15.85 billion industry. However, while IoT has touched most of our lives, it has still not bloomed to its fullest.
And the one thing that is not letting IoT reach its maximum potential is connectivity.
Every IoT device needs to be connected to work and perform its task, and the connection has to be reliable and vigorous. There comes Wi-Fi. A good Wi-Fi allows the IoT devices to stay connected.
Contents
The Current State of IoT
The emerging spectrum of IoT devices has made its presence in multiple industries. Some sectors that have benefited include manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, smart cities, security, etc.
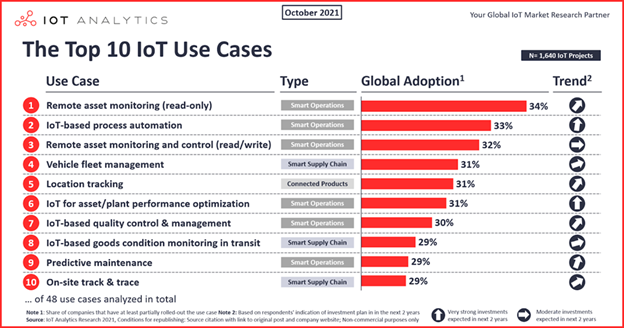
Source: The Top IoT Use Cases
For instance, before IoT entered the scene, the interaction between doctors and patients was confined to texts, visits, and telecommunications. There were no ways to enable doctors to monitor their patients continuously and provide suggestions in real-time.
This scenario changed after the arrival of IoT–it empowered doctors to deliver excellent care by remotely monitoring the patients using IoT-enabled devices.
And this is just one of the plenty of use cases of IoT in the healthcare industry.
If we talk about the corporate world, IoT makes it possible for companies to offer flexible working options to their employees. With the help of IoT devices, companies can let their employees work from home, connect with their colleagues effortlessly, and make their offices safer using social distancing monitors.
The last example is from the automotive industry. Connected vehicles are some of the latest developments in the automotive industry. In simple words, they’re computer-enhanced vehicles that automate several driving tasks, making them more accessible and safer.
This shows the extent to which IoT is entangled in our everyday lives. But, while it will deepen its roots in the coming years, it still needs faster, more reliable, and safer Wi-Fi connectivity to reach its true potential.
How the Next-Generation Wi-Fi is Going to Change IoT
Unlocking the full potential of IoT devices requires high bandwidth and lower power, low latency connection. This is where Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, and Wi-Fi Halow come into the scene.
To put it simply, Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, and Wi-Fi Halow are the next generation of Wi-Fi. While they still do the same work of connecting users to the internet, they offer a bunch of additional technologies that help make the process more efficient, faster, and better. Next-generation Wi-fi borrows several multi-user technologies from the cellular industry, like OFDMA and MU-MIMO, to improve wireless network performance and enable simultaneous connections to several devices.
Features of Wi-Fi 6
The evolution of the latest Wi-Fi 6 standard has introduced several new technologies that overcome the traditional limitations of Wi-Fi networks.
For one, the Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) makes Wi-Fi 6 a much better-suited option for IoT than its previous versions, providing better performance, lower latency, and faster data rates.
In addition, it comes with advanced capabilities like Target Wake Time (TWT) for better scheduling and longer device battery life and directional beamforming that focuses wireless signals toward specific clients instead of having the signal spread in one direction.
Lastly, when it comes to security, Wi-Fi certified technologies like Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, and Wi-Fi Harlow support strong WPA3 security and worldwide interoperable assurances, letting vendors deliver the best experiences to their customers.
Conclusion
To wrap up, IoT is here, and it is here to stay. While it has already transformed many industries, there is more to come. But IoT demands connectivity and that demand can only be met by next-generation Wi-Fi. By adopting Wi-Fi 6, companies can decrease latency, increase throughput and deliver the best connectivity to their customers.















