Optical fibre and cable connectivity arrangements are the background technology enabling modern communication systems to achieve high speed, broad reach, and increased bandwidth. The individual components such as fibre, cable, connectors, and end-to-end fibre optic have evolved over decades to support current and emerging applications. The demand for data has reached new heights, especially during the pandemic and post-pandemic. To meet this demand, the existing conventional cable deployment method is not enough as there is 10x fibre deployment needed at 3x the speed. This blog will discuss the following topics, which will give us an optimal solution for denser and faster fibre deployment.
- Network Evolution & Bandwidth Growth
- Cable Technologies & Advantages of Micro cables
- Use Cases
Contents
- 1 Major technology & Capex shifts
- 2 Unabated growth in demand for optical fibre
- 3 Micro cables
- 4 How can we build denser networks faster?
- 5 Denser – 4x more fibre
- 6 Why is the Micro-LITE 200μm next-gen micro solution?
- 7 432 Micro cable blow test results
- 8 STL’s success stories of using micro cable technology in the field
- 9 NextGen blowing methods resulting in 3X faster blowing
- 10 Conclusion
Major technology & Capex shifts
The increasing data demand is putting a lot of stress on the fibre plants. Upgrading the fibre plants is inevitable and designing a smarter method of cable deployment is the need of the hour. The primary reasons for such data demands are:
- The arrival of 5G
- Huge data centres installed by cloud companies
- Connecting everything through IoT
- Virtualization (Software disrupting networks)

Unabated growth in demand for optical fibre
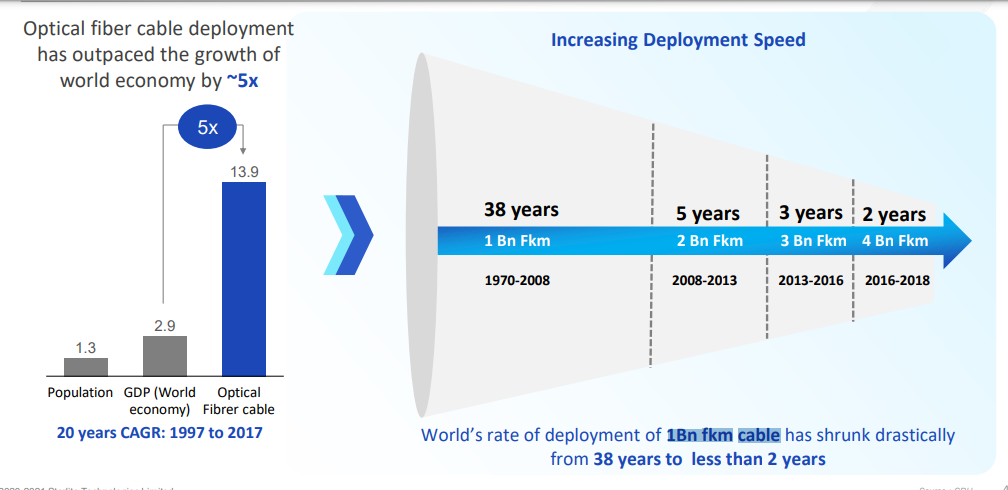
When we look at the 20-year CAGR (compound annual growth rate) from 1997- to 2017, optical fibre deployment has outpaced the world economic growth by 5 times. The rate of deployment of 1Bn fkm cable has drastically reduced from 38 years to 2 years in the period from 1970-to 2008. From 2016-to 2018, 4 Bn fkm cable has been deployed, which is remarkable. But the pandemic has accelerated this journey even more as education and work have shifted to home due to lockdowns, and online viewing of visual content has doubled. Although the cable deployment rate has increased, it is still insufficient to meet the current data needs. As per reports, there is a necessity for 10x fibre deployment at 3x speed which has forced network operators to develop new cabling technology.
Micro cables
Micro cables are the best solution for faster and denser fibre deployment that can meet the current and future bandwidth requirements. This technology will enable network operators to install fibre cable systems faster than before with reduced manpower and equipment costs. These micro cables create the right balance between deployment speed and fibre density.
Micro cables are fibre optic cables which have a reduced outer diameter (OD) and cable weight when compared to conventional cables. Ex: Conventional Unitube Drop cable’s OD is around 4-8mm, whereas micro cable OD is around 2.5mm to even 1.6mm.
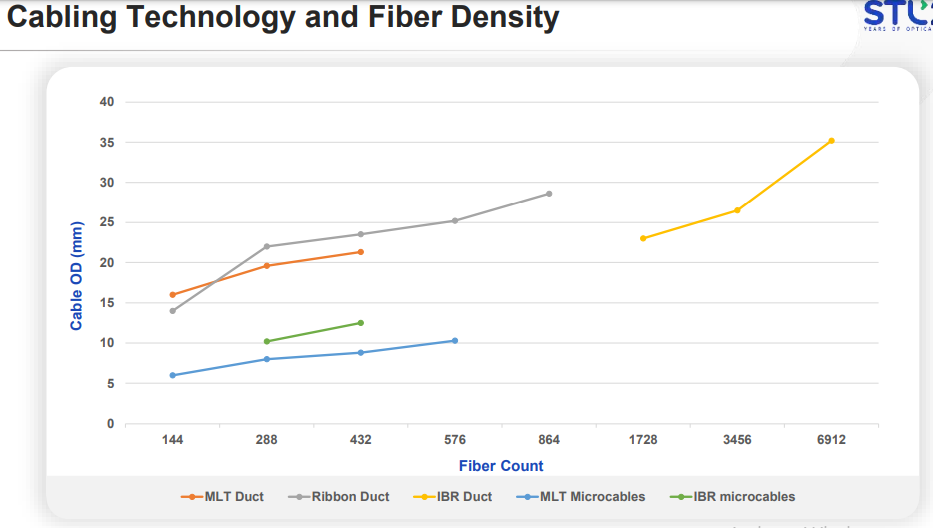
Micro cable designs consist of a stranded loose tube, central tube, and unitube design. The common factors across all these designs are lightweight, OD, and reduced amount of jelly. Usually, micro cables don’t have metal or dielectric covering and hence cannot be buried directly underground. Micro cable designs are suitable for both outdoor and indoor environments. The features and benefits of micro cable technology are:
- Features
- Thinner jacket
- Smaller tubes
- More fibres per tube
- 200um fibre
- IBR ribbon
- Benefits
- Blow optimized
- Reduced cable diameter
- Lightweight
- Easy handling
- Smaller drum efficient logistics
- Reduced risks of cable damage
The different types of micro cables used are shown below.

How can we build denser networks faster?
Combining micro cable technology and blow installation equipment, we can build a denser network at a faster rate. The advantages and challenges are:
- Denser urban deployments
- Micro-trenched green field installs
- Augmentation of existing duct spaces
- Service Segregation
- Multi-way ducts
- Reduced risk to service continuity
- Challenges
- MLT designs – longer splice time
- Specialized equipment
Denser – 4x more fibre
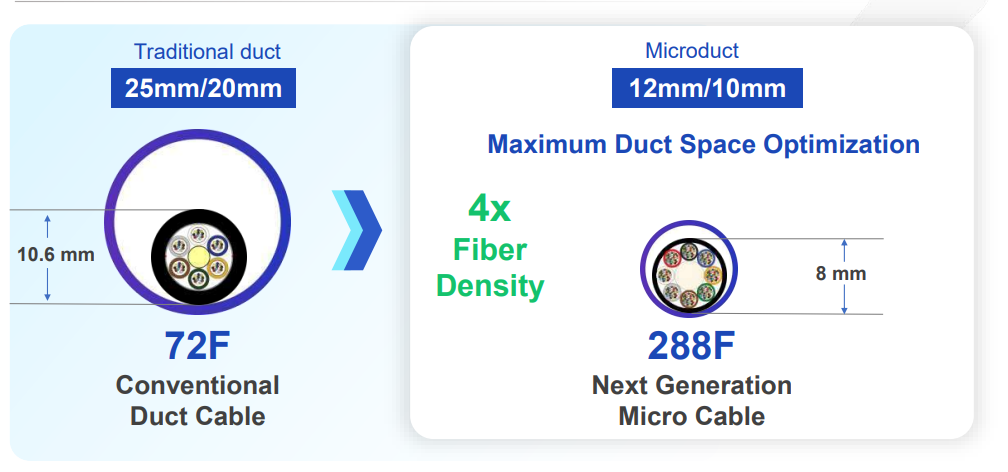
Generally, full-size underground cables have been installed inside polyethylene subducts called inner ducts. These 25-51mm diameter sized inner ducts are located inside the telecommunication duct system. For installing micro cables, a matching micro duct has to be placed first, and then micro cables are inserted using blow installation. These micro ducts allow denser micro cables to be installed based on current demands and have sufficient left-over space for future installations based on future demands.
Why is the Micro-LITE 200μm next-gen micro solution?
The following features make STL’s Micro-LITE 200μm the next-generation micro cable solution:
- High fibre density
- 432 fibres can be stacked in an 8.8 diameter cable
- Greater duct capacity
- Existing 2” duct retrofit option #1 – (864f + 2 x 432f) = 1,728 fibers
- Existing 2” duct retrofit option #2 – (5 x 432f) = 2,160 fibers
- Greenfield ~ 2” 7-way micro-duct (7 x 432f) = 3,024 fibers
- Greater blow distance
- 1.5 km for greenfield duct (14/18 mm)
- Smaller Diameter
- Ease of future capacity expansion
- Sub-unitized design
- Individual fibres are more accessible when adding new customers or services
- Easy to repair
- F1 – F2 separation
- Troubleshooting/Isolation
- Easier segregation of services
432 Micro cable blow test results

Faster – blow vs. pull installation
Pull installation is a method to place ducts and cables for short-length runs. It is popular for placing large diameter conventional cables and ducts. On the other hand, blow installation is an equipment-driven installation method for placing micro ducts and micro cables. When we compare both methods, blow installation appears to be far superior and much faster than the pull installation method.

The combination of micro cables, 7-way micro duct, and blow installation method will help network operators to place denser fibres at 16x speed than traditional cable deployment.
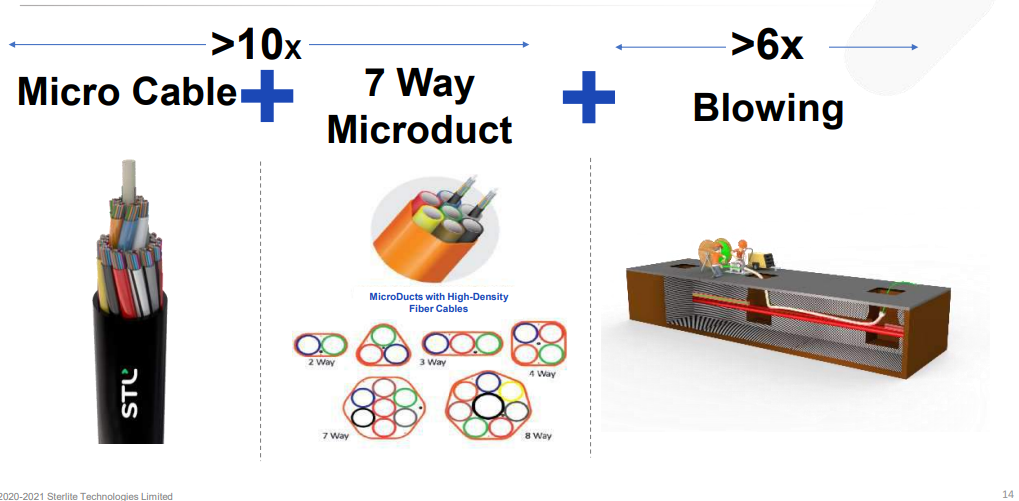
STL’s success stories of using micro cable technology in the field

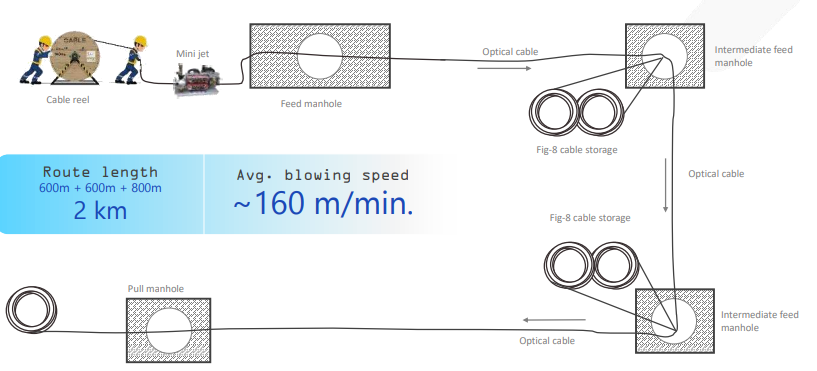
NextGen blowing methods resulting in 3X faster blowing
The latest blowing methods adopted by STL in installing micro cables are capable of 3 times faster deployment than conventional deployment.
Conclusion
As we move forward with 5G and other next-generation technology and Capex shifts, the demand for data will skyrocket, needing faster and denser optical fibre deployment. If we don’t adapt to changing requirements and continue to follow the traditional cable and pulling method, then there is no chance of meeting future demands. Hence micro cable technology is the only optimal solution with all the necessary attributes to fulfil current and future data and bandwidth requirements.