With the pandemic affecting the global business paradigm, growth and scalability are the important necessities to count on. As a modern business, you face immense competition to stay ahead and continue to offer great services to end customers.
With that approach, data centres are now an undeniable part of operations in businesses around the world. Therefore, companies need to pick the right infrastructure solutions in order to make complex implementations possible. This article will give you an insight into the latest technologies which impact modern-day data centres.
Contents
Latest Advancements & Infrastructure Optimisation in the Data Centre Applications for Businesses
The data demands are exceptionally higher for businesses with every passing day. And all of these necessities are significantly increasing the demand for a highly efficient data centre.
So, here are some of the latest advancements in data centre design and applications and the infrastructure demands that come along with it for businesses across all industries:
1. Server Virtualisation
To ease the load on the existing data centre infrastructure, the managed service providers will help you migrate your data centre to the SDDCs (Software-Defined Data Centres. Upon utilising this model, the server virtualisation techniques will recreate the storage and computing powers in the form of software.
The concept of server virtualisation will enable the data centres and the MSPs to accommodate various users over a single server by segmenting it. Earlier, this process was approached in an inefficient manner, where one server was issued to every user. With virtualisation, data centres will be scalable when the workloads get distributed across the multiple servers.
Server virtualisation works best when deployed upon a cloud model, where MSPs will parcel out the processing and storage abilities as per requirements. This advancement in data centre utilisation will ensure that all resources are used to the best of their potential.
2. Deployment of Hybrid Cloud
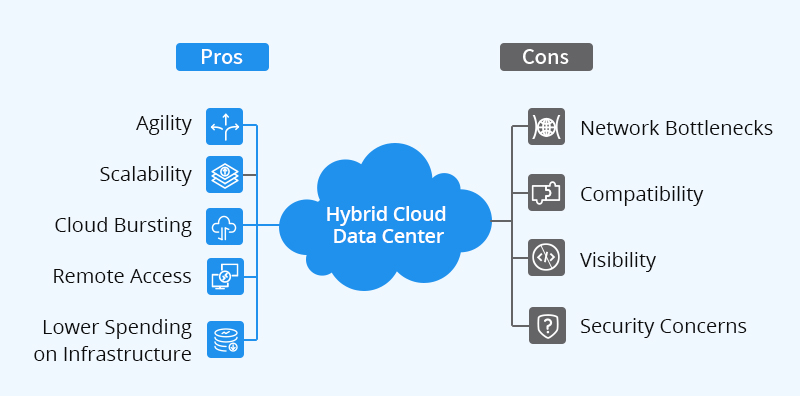
Figure 1: Pros & Cons of Cloud Data Centre
Image Source: community.fs.com
Organisations can now store sensitive data on the private cloud platform while utilising the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of a public cloud for less intensive workloads. The hybrid cloud application on the modern-day data centre allows businesses to move the workloads between public and private clouds to be able to use the resources of multiple cloud solutions.
It is an ideal benefit for businesses that have special or complex data centre needs. Apart from that, the hybrid cloud implementation prevents vendor lock-in situations, which makes the new data centre infrastructure more fluid in performance.
The private cloud has the potential to offer enhanced security and control, whereas the public cloud has immense computing abilities. Therefore, developing a data centre architecture that can support easy accessibility to cloud solutions is of utmost importance for attaining business success in 2023 and years beyond.
3. Hyperscale Data Centres
The hyper-scale data centres, as the name suggests, are large-scale implementations meant to support the quick deployment of a lot of servers within the system. The data centre infrastructure of hyper scalers is much bigger and more complex than that of traditional construction, which supports the enhanced internet demands and a vast amount of data processing requirements by the companies.
The infrastructure changes that businesses need to make to their data centres include the replacement of single components to obtain the efficiency of hyper scalers. If not, then in the conventional method, the entire server will be replaced to upgrade to hyper-scale data centres.
As a result, it will cut down the overall data centre expenses and reduce the possibility of downtime. Apart from that, you can also add the components modularly for quickly scaling up the hyper-scale data centre operations. As a result, it enables great flexibility for the businesses to bring in new high-intensive applications and process ample data at ease.
4. Edge Computing
When the number of devices connected to the data centre increases, the centralised processing of such a large amount of data becomes economically challenging and equally inefficient. Therefore, edge computing is one of the modern advancements in data centre architecture, utilising the processing abilities of the devices on the edge of the network for resolving data requests or actions.
The edge data centres will lower the latency and enhance the overall performance of all connected devices. With edge data centres, you can expect fewer service interruptions.
Conclusion
Apart from these popular advancements and infrastructure revamps, there are many other technology solutions that are pushing data centre applications to modernise. For instance, the 5G network, intelligent monitoring, automation and other such trends are also taking over! So, you can expect that as businesses are growing with more data-intensive applications, the data centres are also gearing up with modern solutions to accommodate them all.
To learn more about the advancements in data centre applications and infrastructure, get in touch with STL Tech.
FAQs
The anatomy of the data centre infrastructure includes:
- Building the structure
- Physical security
- Building the management systems
- Climate control and cooling
- Main power systems
- On-site operations centre
- UPS systems
- Backup generators
- Multi-tenant cloud pod
- Customisable space management
- Compliance certifications
- Business continuity workspace
As standard applications, data centres will help you with the storage, backup, recovery and management of business-critical data. Moreover, the data centres are being used for productivity applications such as email, high eCommerce transactions, powering the online gaming communities, machine learning, big data and AI.
The four different types of data centres are hyper scale, colocation facilities, edge data centres and onsite data centres. The choice of data centres will depend on the individual business needs, based on density requirements, physical limitations, structure and other such factors.
















