We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- 5G and WiFi6 driving connectivity
- Role of STL in Making 5G a Reality for Businesses
- Wi-Fi 6 and 5G Inflating Opportunities to Digitize Multiple Industries
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is 5G NR?
- What is WiFi?

Contents
Overview
When we talk about the 5G and WiFi 6 revolution, we don’t mean uninterrupted movie streaming or faster downloads; we are talking about making sci-fi movie fiction a reality. Things you once only saw on TV – robots doing chores, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, virtual reality gaming experiences, remote surgeries, telemedicine, automated assembly line production, augmented reality marketing campaigns – the way you shop, travel, work, get medical consults – everything will undergo a transformation beyond imagination and 5G will make it happen.
How Are These Two Driving Connectivity?
With the pandemic acting as a catalyst in the changing connectivity landscape, businesses can not wait to jump on this deadly combination bandwagon. To give an idea about 5G – it is ten times faster than your current network and WiFi 6 brings with it 3X speed compared to the previous technology.
5G brings along with its capabilities such as reduced latency, faster speed, energy conservation and increased capacity systems, making it way superior to any of the other wireless predecessors. The greater benefits of 5G connectivity in India and globally are for all to avail despite geographic and demographic differences. 5G wireless services come with unprecedented possibilities and bring the dream of ‘Internet of Things revolution to life.
5G and WiFi 6 – Critical for Businesses
In a survey done by the consulting group Deloitte, it was inferred that the priorities of the businesses were 5G and WiFi 6, the importance of which was only expected to increase in the coming years.
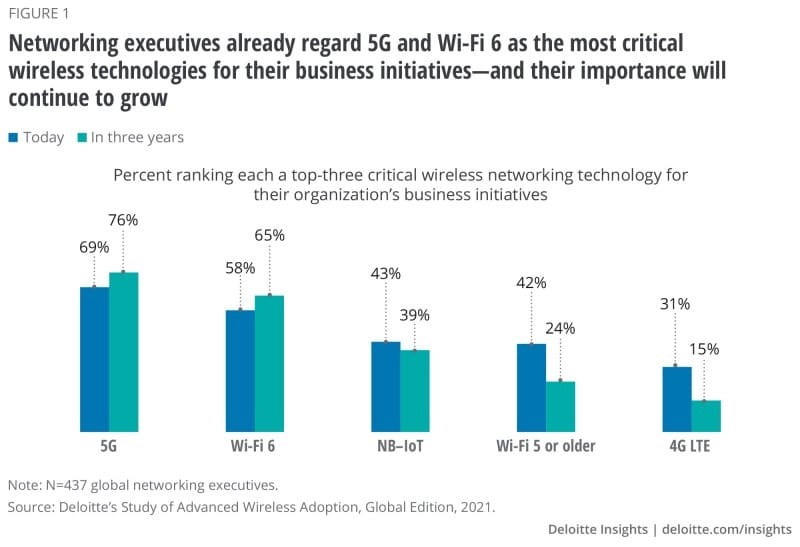
The adoption of Wi-Fi 6 and 5G is considered a strategic requirement and will introduce businesses to a new age of wireless access. With the convergence of WiFi with 5G, organisations can conduct business anywhere while keeping the workforce super productive and enhancing the best user experience.
By shifting to this advanced wireless 5G, the main objectives businesses will achieve are:
- Enhanced efficiency
- Improved security
- Piggybacking on the advantages of these two forces such as big data analytics, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Edge computing
The explicit desire to leverage this lethal combination is to unleash the potential of other emerging technologies such as IoT, cloud, Edge computing, big data analytics, VR, AR, robotics and more. 5G and WiFi 6 together act as a transformative multiplier.
What is the Role of STL in Making 5G a Reality for Businesses?
STL has been preparing itself for the 5G technology revolution for a while. We are making this dream a reality through a multitude of investments across categories of hardware, software and people recruitment. 5G connectivity globally is what STL aims to achieve through its end-to-end capabilities of a joined network.
As industry experts, STL can forecast the digital evolution of the telecom infrastructure to be more virtual, separated yet connected seamlessly and close to the Edge. With STL’s digital network integration expertise, we have positioned ourselves at the forefront of the next-gen digital network delivery for our customers worldwide.
Keeping the future in mind, STL is one of the first companies which is equipped with an end-to-end 5G ecosystem through its robust portfolio of optical fibres and wireless technology.
STL is equipped to create reliable, high-speed, low-cost and secure digital networks through strategic partnerships and the right investments. In fact, our acquisition of a solutions company further strengthened our design and deployment offerings, allowing us to deliver hyper-scale data centres to support 5G for one of the biggest software companies in the world.
Keeping in mind the to digitize the world network, STL has end-to-end capabilities for a converged network that consists of both wireless and wireline and has successfully delivered full-stack solutions to enterprise and telco customers.
Will Wi-Fi 6 and 5G Inflate Opportunities to Digitize Multiple Industries?
The presence of WiFi 6 and 5G offers a plethora of exciting opportunities for task critical IoT devices to be connected reliably. The improvised broadband will enable an immersive AR and VR experience.
At the workplace – Employees can work from any part of the world without any hindrances – freedom from desktop phones and wired connection, and advanced quality audio and video meetings will increase productivity at the workplace. With the field workforce and the new work-from-home trend that set in due to the pandemic, collaboration between employees will be augmented to high resolution and fastened data transfer.
Retail – Analysing the data collected – purchase history, inventory trends and footfall to predict what product should be displayed where, how much quantity per product and how to develop a product – these decisions will become a breeze.
Manufacturing – The advanced wireless networks – 5G and WiFi 6 play a critical role in linking machines and devices to drive smart factory solutions. They will ensure seamless tracking of the products in an assembly line, collect huge amounts of data to predict production patterns as per demand and maintain quality control and standardisation. Because it is super reliable and offers low latency, 5G can drive flexible human-robot interactions to replace slow wired connections.
Healthcare – With 5G and WiFi 6 working in tandem, the healthcare sector can introduce remote surgeries and remote diagnosis making facilities available for all. Transmission of health records for detection at early stages will become a part of the way the industry works.
Supply Chain and Logistics – With the increase in e-commerce, the entire structure depends on Supply chain companies. The introduction of 5G and WiFi 6 can be a real game-changer for the last mile interaction with the end consumer. Apart from making logistics operationally efficient, personalised and enhanced customer experience can be achieved.
According to IDC, by 2025, over 152,000 IoT devices will be connected per second and Cisco believes there will be 12X increase in AR/ VR traffic between 2017 and 2022.
The pandemic has further strengthened the need for enterprises to be digitally agile. The enterprises already had an adoption plan of wireless networks in place, but CoVid-19 has further accelerated this shift. The value of linking people with technology through advanced wireless networks to transform businesses successfully digitally is an additional motivation, further wired by remote working. Digital connectivity is the anchor for economic activity, making the adoption of 5G and WiFi 6 inevitable to sustain and survive.
FAQs
What is 5G NR?
5G typically refers to the fifth generation of wireless technology. NR, commonly known as New Radio, is a standard developed by the 3GPP Group (Release 15 being the first version introduced back in 2018) outlining the technology required to harness the newly-available millimeter-wave frequencies. The two frequency bands in which 5GNR operates are Frequency Range 1, i.e., Sub 6GHz band (410 MHz to 7125 MHz), and Frequency Range 2, i.e., millimeter-wave (24.25 to 52.6 GHz). Over 4G LTE, 5G NR provides better spectrum utilization, faster data rates, hardware efficiency, and improved signal processing.
From a deployment standpoint, we have Non-Standalone Mode(NSA), Dynamic Spectrum Sharing(DSS), and Standalone Mode (SA). The initial deployments of 5G NR are based on NSA standards, meaning the existing 4G LTE network will operate on the control plane, and 5G NR will be introduced to the user plane. This particular standard was introduced by 3GPP, keeping in mind the industry’s push to faster 5G services rollout while utilizing the existing 4G LTE infrastructure currently in place. On the other hand, operators are also implementing Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) to accelerate the deployment cycle, reducing costs and improving spectrum utilization. In this standard, the same spectrum is shared between the 5G NR and 4G LTE, multiplexing over time per user demands. Lastly, we have the Standalone Mode (SA), which moves towards a complete 5G based network where both signaling and the information transfer are driven by a 5G cell.
In the future, 5G will enable new services, connect new industries and devices, empower new experiences, and much more, providing mission-critical services, enhanced mobile broadband, and various other things.
a) Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) Applications: High device connectivity, High mobile data rates, and Mobile AR & VR applications
b) Ultra-reliable, low-latency communications (uRLLC)Applications: Autonomous vehicles, Drones, Data monitoring, Smart mfg.
c) Massive machine-type communications (mMTC)Applications: Healthcare, Industry 4.0, Logistics, Environmental monitoring, Smart farming, Smart grids
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).















