We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- What is PIA (Physical infrastructure access)?
- How does PIA Work?
- PIA Surveying
- What are the benefits of using a PIA?
- PIA Installation and Testing
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What does PIA stand for is Openreach?
- What does PIA mean in telecoms?
- What is duct and pole access?

Contents
- 0.1 Overview
- 0.2 What is PIA (Physical Infrastructure Access)?
- 0.3 How does PIA Work?
- 0.4 A typical distribution network architecture has two critical functional network nodes:
- 0.5 The cables in the access network can be deployed in three ways:
- 0.6 PIA Surveying
- 0.7 What are the Two Surveying Modules Issued by Openreach?
- 0.8 What are the Benefits of Using a PIA?
- 0.9 Key Benefits of PIA:
- 0.10 PIA Installation and Testing
- 0.11 STL PIA Services
- 1 FAQs
Overview
CSPs admission of providing connectivity as a commodity is also an admission of urgent access for Openreach’s PIA for enhanced customer experiences.
Communication Service Providers (CSP) have evolved over the decades to channel various market disruptions, but in 2021, they will have to emerge beyond a traditional CSP. The service providers will soon be categorized as digital service providers and digital service enablers.
And that’s why this particular decade will be a new ballgame for all the service providers. To make the desired transition, you need Physical Infrastructure Access to deploy your fiber network. Telecom companies are now headed to form long-term ecosystem partnerships for the reinvention of customer experience.
What is PIA (Physical Infrastructure Access)?
The PIA is the solution for fulfilling the dire need of boosting high-capacity broadband around the world. The Physical Infrastructure Access provides service providers with the opportunity of fibre installation in the access network via the incumbent operator’s ducts and poles. The importance of PIA came to the limelight post the European Commission’s Recommendation on regulated access to next-generation access networks. Since then, National Regulatory Authorities (NRA) across Europe have pursued commendable initiatives for the imposition.
The PIA is essentially an Openreach (UK) product that allows CPs access to the poles and ducts. The idea is to make service providers capable of providing public electronic communications services and public electronic communications networks. However, CPs can only gain access to such facilities if Openreach approves them. All the measures initiated by several stakeholders are aimed at the greater use of existing physical infrastructure in place for the reduction of civil engineering efforts made every year to deploy new networks. Thus, it’s mutually beneficial for all the parties, especially for CSPs. Openreach this year selected STL as a strategic partner to help build its new UK full-fibre network.
How does PIA Work?
The key components of PIA include ducts and poles. That’s what Openreach infrastructure offers as products; one for ducts and one for poles. The entire PIA is a typical mixture of underground ducts and buried wires, poles and overhead wires.
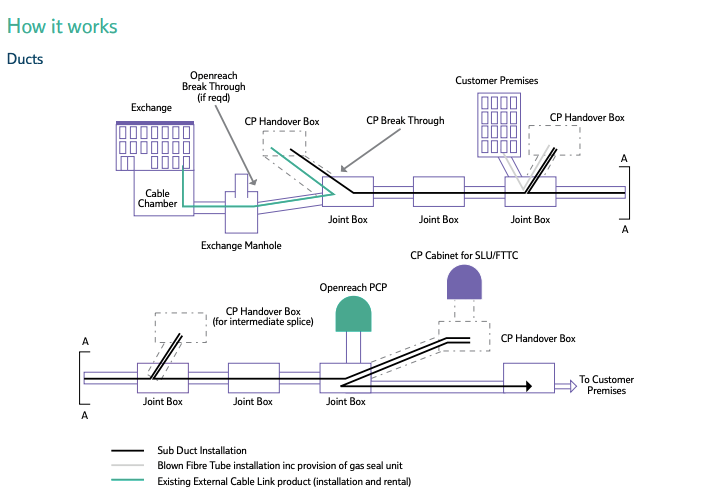
A typical distribution network architecture has two critical functional network nodes:
- Street Cabinets – Also referred to as primary connection points (PCPs) – provide a direct or indirect connection between the access network and the customer premises.
- Distribution Points – It is a flexibility point in the distribution network where a multiple tenacity cable gets split into one. Typically, they are the last interconnection points in the network before the end customer provides the last drop.
The cables in the access network can be deployed in three ways:
- Direct deployment into the ground – A ducted access network contains a feeder network segment between the mainframe distribution (MDF) and a street cabinet/PCP. It is responsible for hosting a distribution frame, which allows the access line to be connected or patched.
- Aerially (on poles) – The aerial deployment also follows the same concept; the only difference is using boxes at the top of poles instead of manholes or handholes.
- Installed ducts – The underground cables are accessible via manholes or handholes, which act as a host for branching sleeves. These sleeves can be buried directly. The cable segment present between the last branching sleeve and the end-customer premise is also called building access cable. It is eventually terminated by the building distribution box (BDB.) The in-house cabling is patched to the outdoor access network cables in the case of BDB. As per a Wik Consult report, France, Spain, and Portugal have most effectively used the duct access.
A combination of three deployment forms may take place along the access line to the end consumer. The Openreach network over the years has evolved well enough to accommodate the changing environment and maintenance requirements. Openreach is also planning to benefit from STL’s Opticonn solution, a specialised set of fibre, cable and interconnects offering. The access to STL’s Celesta – a high-density optical fibre cable has a capacity of up to 6,912 optical fibres.
PIA Surveying
Openreach, a central pillar to the PIA, has several accreditation modules to be followed for surveying their infrastructure. When it comes to working with Openreach, there are two other parties involved. One being a CSP and another a contractor. The Openreach accreditation modules were specially designed for PIA. The aim is to provide both the contractor and the communications service provider with the surveying modules.
What are the Two Surveying Modules Issued by Openreach?
- Overhead Surveying
- Underground Surveying
The adherence to the surveying guidelines is the duty of a contractor as they are working on the deployment on behalf of the service provider. All procedures and norms are to be followed before beginning with the route survey. The importance of surveying is of paramount importance because network designers require the information which is eventually inputted into a platform. Post the completion of this task, the contractor will begin with the pre-deployment final checks for assurance.
What are the Benefits of Using a PIA?
The several benefits of using PIA are well known in the industry since the recent market disruptions challenged the service providers to reinvent instantly.
The key findings of IBM’s Institute for Business Value on ‘Outthinking disruption in communications.’
- 90% of service providers believe that cognitive computing will become a major industry technology in 2020.
- CSPs identified four core roles that circle around providing connectivity as a commodity.
- 86 per cent of CSPs view OTTs as their greatest competitive threat.
Key Benefits of PIA:
- A network build can cost a telecom business around 80% of its capital expenditure. Access to Openreach’s duct and pole sharing will help CSPs to roll out services rapidly and cost-effectively.
- An extensive fibre network will not only contribute towards supporting connectivity for homes and local businesses, but it will also allow the wave of investments for 5G mobile networks.
- The PIA will help service providers to mark their presence in multiple downstream markets finally. A report was published in 2017 by Wik Consult on ‘Best practice for passive infrastructure access‘, which stated how PIA as a horizontal measure could support the competition.
PIA Installation and Testing
Openreach’s duct and pole sharing services include various disciplines that the contractor should be able to work on and know about. Various quality checks and requirements are to be adhered to for implementing such technical procedures. Such disciplines include the following procedures:
- Overhead/Underground Distribution Points
- Fibre Jointing, spine and access network
- Overhead Fibre Drop Cabling
- Last-mile installation
- Customer installation
- OTDR Testing
- Quality Audit Checks
- Cabinet installation
- Sub Duct installation
- Blockage Clearance
- Blown Cable
- Blown Fibre Tubing
- Blown Fibre bundles
- Passive Optical Networks (PON)
- Ethernet Delivery
- Overhead Fibre Span
STL PIA Services
Openreach and STL have collaborated in April 2021 for providing optical cable solutions for a new full-fibre broadband network. STL, an industry-leading integrator of digital networks, is committed to benefiting the UK’s landscape of broadband connectivity. The 5G-ready optical solutions are well suited for the network requirements of Openreach. Some of the commitments made by STL:
- Over the next three years, STL is looking to deliver millions of kilometres of optical fibre cable to support the build.
- Implement Openreach’s goals with cutting-edge technological solutions – with a specialised set of fibre and cover the installation at a 30 per cent faster rate.
- The idea is also to develop one of the greenest networks built on Earth by reducing plastic usage across Openreach’s new network.
- Provide socio-economic benefits by optimising the UK productivity with the aim of promoting more home working and for curtailing commuting trips.
The STL and Openreach partnership is meant to transform millions of lives via digital networks.
FAQs
What does PIA stand for is Openreach?
It stands for Physical Infrastructure Access. PIA is typically a product of Openreach.
What does PIA mean in telecoms?
The PIA means “Physical Infrastructure Access” for telecommunications.
What is duct and pole access?
Ducts and poles sharing is an integral part of the PIA and is a product of Openreach for CSPs. Ofcom, a UK communications regulator, gave Openreach the responsibility to share their existing ducts and poles to provide public electronic communications services or public communications networks. It is via this access that service providers get the opportunity of installing fibre in the access network. The companies have to go through an approval process conducted by Openreach for acquiring the ducts and poles access.













