We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- What really is 5G all about?
- What will 5G mean for you and me?
- Is India Ready for 5G?
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is WiFi?
- What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
Contents
Life in the Times of 5G
It was not long back that India was excitedly ushering in 4G technology which would go on to revolutionise mobile phone usage. The euphoria of 4G has not even settled and we are already latching on to the idea of the internet of the future – 5G
A 5G mention throws up images of people walking about on the streets with virtual reality headsets or driverless cars with several hundred sensors sending and receiving terabytes of data! But, what will 5G bring to common people like you and me?
But first, what really is 5G?
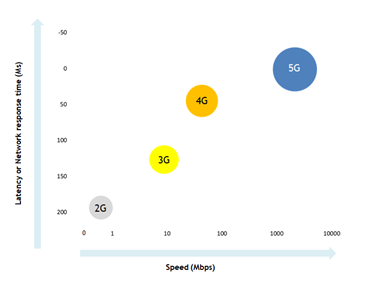
5G or fifth generation of telecom networks will unleash evolution beyond the mobile internet into the ‘Internet of Things’. Each new generation has brought about small and big incremental benefits.
- 2G enabled digital voice services,
- 3G gave us the flavour of mobile data,
- 4G brought about a quantum leap in data usage and use cases,
- 5G is all set to move beyond mobile, to the world of billions of connected devices and pave way for a new era of consumer-technology interactions.
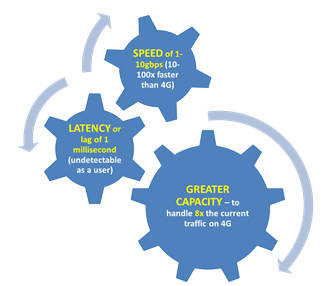
5G Factsheet
Next Generation Technology
What will 5G mean for you and me?
Futuristic applications around artificial intelligence and virtual reality are being developed, but it will be a while before they impact our everyday lives. Yet, given the ultra-high bandwidth, low latency that 5G will usher in, our lives will definitely be impacted through everyday use.
Quality of user experience
For starters, 5G will make our mobile connections much more reliable. According to the Speedtest Global Index (Ookla, Feb 2018) India ranks 109th on mobile internet speeds, with an average download speed of 9.01 mbps. Hence, the quality of user experience especially on video streaming, downloading, live TV, real time video call is far from seamless. With 5G, our mobile data user experience will take a quantum leap, making India a much more connected country.
Smart Students and Smart Schools
With worlds’ largest population of youth, 5G would be instrumental in building and nurturing human capital in India:
- 5G will change the way we learn. Interactive game based learning, virtual tours of the human body, simulation based exercises – these are some examples of what can be accomplished with high bandwidth, bi-directional 5G connections.
- Being auto logged into the classroom, being distracted by a signal on losing concentration during lecture, real-time inputs to the teacher on student specific problems, based on their digital notes. These are a few examples of how 5G & IoT can enhance learning experience.
- The power of 5G can transform education in the rural areas. Through virtual classrooms, we can take high quality education to the last mile.
e-Healthcare
5G will have great ramifications for the state of healthcare in the country.
- The delivery of medical care is currently hospital based and doctor focused. With 5G we could see this changing. The care could be distributed and accessible – from home or health kiosks. Virtualised consultation with the doctors will add great value to both – time constrained urban citizens and distance constrained rural citizens.
- Consumer-oriented medical devices like smart glucometers, insulin pens, asthma inhalers will enable people to handle chronic diseases in ways that only their doctors can currently. Now a patient wouldn’t be somebody ‘seeking care’, it would be somebody ‘needing’ care.
- Robotic surgeries are already being considered. With virtualisation, renowned specialists would be able to conduct remote surgeries as effectively and with reduced costs.
Sterlite Tech – A home grown company building and delivering ‘ Smart Networks’ for their customers, has already made great strides in e-education and e-healthcare.
Sterlite Tech launched the largest virtual classroom program in the country, providing quality education to students from lower income families – creating equal growth opportunities, and nullifying the effects of unavailability of qualified teachers. It has touched the lives of 2.5 children till date.
Sterlite has also launched Lifeline Express – a connected train, where doctors aboard the train can communicate with specialists, evaluate test results and offer treatment advice in real time thereby taking tele medicine to the underprivileged across India.
Immersive Entertainment Data connectivity for entertainment through smart TVs and streaming platforms such as Netflix and Hotstar is commonplace today. But 5G will bring an unprecedented experience to our living rooms. • Imagine a live virtual reality experience of an IPL match or a Coldplay concert where viewers can control the time, target and even the angle from which they are viewing! • With blazing download speeds, we will be able to download (not only stream) a full HD movie in less than 10 seconds on a 5G network. Smart Living 5G has the potential to connect humans with devices ubiquitously. Imagine the following scenarios: • When your Fitbit detects that you are awake, it switches on the lights, opens the blinds and powers your tea machine to brew your tea before you get out of bed • You are busy getting ready for work when your room lights start to blink, indicating that your Uber has arrived. • There is more! You could start your robot vacuum cleaner once you leave home, auto-inform your partner when you leave work, switch on the AC before you reach home – just with the tap of a finger, sometimes even without that! Smooth Commuting In times to come, 5G might be the answer for all of our commuting problems. Here is how: • Our personal connected vehicles could enable auto alerts on over speeding, service reminders (in case of any snags), auto triggered calls in case of an accident and many more such features, making driving easier and safer. • All personal and public vehicles connected to central traffic surveillance system could enable real time re-routing of traffic to make commuting more efficient. • Parking spaces could be identified by a low cost 5G sensor on street lamps which can direct the vehicles to nearby parking spaces, thereby reducing congestion. Next Level Shopping With exciting experiences for both online and retail shopping, 5G could change the way we shop! • For instance our digital grocery shopping lists could liaise with the neighbourhood brick and mortar stores to ensure seamless delivery. • We could download augmented reality apps from furniture giants (think Ikea) to visualise how the selected item(s) would look in our homes. • The in store shopping experience is expected to change massively with check-out and cashier free stores (Think Amazon Go) or interactive try rooms at your nearest Zara! A new way of Working & • Today we commute to office, in the future; we might ‘telecommute’ to office or anywhere! Telepresence & virtual reality solutions would enable seamless two way conferencing and will open up many options for day to day office meetings, client meetings, research interviews and even for catching up with friends & family. • Some years from now, time and space will get crunched into your virtual reality applications and there is a possibility that you would never miss a meeting, or an event or a family wedding. Public Safety In wake of rising crimes and shortage of police personnel, 5G can actually change the way state handles security & disaster management. With high speed, low latency and high capacity 5G networks, extensive surveillance and real-time inputs to policing authorities become feasible.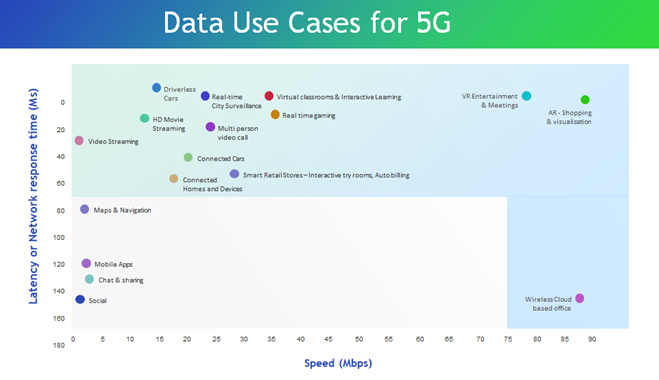
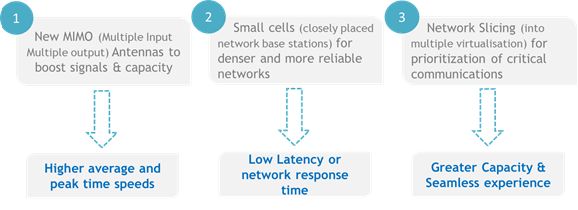
Is India 5G Ready?
There is a lot of buzz around 5G in India. But the current networks in India are in the evolution stage from 3G to 4G, and the next transition to 5G requires investments in network infrastructure. With the hefty ask of delivering upto 1000 times increased bandwidth, 100 times more connected devices and latency of less than 1ms, mobile operators will have to adopt ‘small cell networks’ which strategically bring the network closer to the users. Small cells can be backhauled over copper, microwave or fibre. With fibre being most India’s journey towards 5G has started and the government is expected to unveil a ‘5G roadmap’ in June 18. This exciting move towards an intricately connected future holds a lot of promise for all us common Indians.FAQs
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).
What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
An optical fibre cable is a cable type that has a few to hundreds of optical fibres bundled together within a protective plastic coating. They help carry digital data in the form of light pulses across large distances at faster speeds. For this, they need to be installed or deployed either underground or aerially. Standalone fibres cannot be buried or hanged so fibres are bunched together as cables for the transmission of data.
This is done to protect the fibre from stress, moisture, temperature changes and other externalities. There are three main components of a optical fibre cable, core (It carries the light and is made of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with dopants such as germania, phosphorous pentoxide, or alumina to raise the refractive index; Typical glass cores range from as small as 3.7um up to 200um), Cladding (Cladding surrounds the core and has a lower refractive index than the core, it is also made from the same material as the core; 1% refractive index difference is maintained between the core and cladding; Two commonly used diameters are 125µm and 140µm) and Coating (Protective layer that absorbs shocks, physical damage and moisture; The outside diameter of the coating is typically either 250µm or 500µm; Commonly used material for coatings are acrylate,Silicone, carbon, and polyimide).
An optical fibre cable is made up of the following components: Optical fibres – ranging from one to many. Buffer tubes (with different settings), for protection and cushioning of the fibre. Water protection in the tubes – wet or dry. A central strength member (CSM) is the backbone of all cables. Armoured tapes for stranding to bunch the buffer tubes and strength members together. Sheathing or final covering to provide further protection.
The five main reasons that make this technology innovation disruptive are fast communication speed, infinite bandwidth & capacity, low interference, high tensile strength and secure communication. The major usescases of optical fibre cables include intenet connectivity, computer networking, surgery & dentistry, automotive industry, telephony, lighting & decorations, mechanical inspections, cable television, military applications and space.














