We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- Increased bandwidth for higher speed and reduced latency
- Installation of fibre-reinforced plastic poles.
- Customized light poles designed as per customer requirements
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is WiFi?
- What is an Optical Fibre Cable?

Contents
Demands for Increased Bandwidth
To cater to market demands for increased bandwidth and to provide higher speed and reduced latency the telecommunications industry is expanding fiber networks however aerial and overhead deployment of pole possesses certain challenges such as pole transportation installation activities, operational maintenance, geographical and local issues to solve these problems Sterlite Tech with its vision to lead the technology industry has introduced new generation fiber reinforced plastic poles for seamless and quicker deployment of telecom networks.

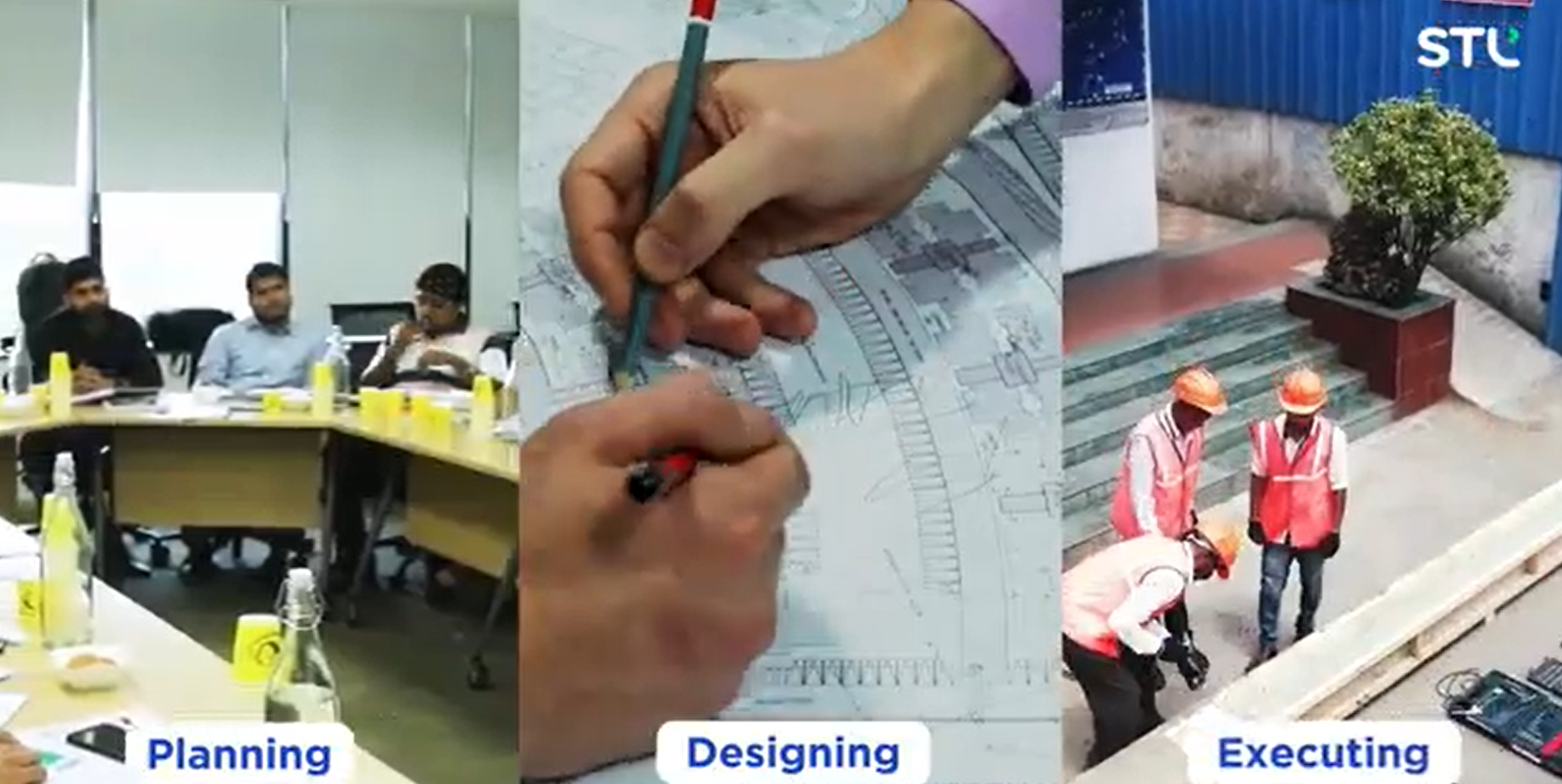
How to Install Fibre Reinforced Plastic Poles?
The process of installing fibre reinforced plastic pole begins with planning, designing the plan, and executing the next step is to ensure the availability of resources such as materials and manpower briefing them about the project, and explaining the process. This is followed by installing accessories on the FRP pole at the plant location a pit measuring 1.2 meters is jugged to install the pole.
After FRP pole is securely installed the process ends by stringing an aerial cable for smooth and faster deployment of telecom networks installing FRP ensures optimization of time and cost pertaining to manpower transportation speed of deployment and the product life cycle in comparison to conventional steel and RCC poles. STL’s leading FRP poles are light and weight has robust properties that can withstand wind speeds of up to 200 kilometers per hour are durable and immune to all weather conditions. Moreover, it requires less installation time minimum maintenance and is versatile in nature.

How Light FPR Poles Reduce Manpower?
It can also be customized and designed as per customer requirements usage of the FRP poll will lead to around a 50% increase in deployment almost zero maintenance with five times increased life span. Additionally, since FRP poles are around 60% lighter in weight than traditional poles as per STL POC field study it reduces 50% of manpower for transportation and installation STL simplifies the process of installing the FRP pole and aims to stay a step ahead in the industry.
Watch The Deployment Process
FAQs
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).
What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
An optical fibre cable is a cable type that has a few to hundreds of optical fibres bundled together within a protective plastic coating. They help carry digital data in the form of light pulses across large distances at faster speeds. For this, they need to be installed or deployed either underground or aerially. Standalone fibres cannot be buried or hanged so fibres are bunched together as cables for the transmission of data. This is done to protect the fibre from stress, moisture, temperature changes and other externalities.
There are three main components of a optical fibre cable, core (It carries the light and is made of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with dopants such as germania, phosphorous pentoxide, or alumina to raise the refractive index; Typical glass cores range from as small as 3.7um up to 200um), Cladding (Cladding surrounds the core and has a lower refractive index than the core, it is also made from the same material as the core; 1% refractive index difference is maintained between the core and cladding; Two commonly used diameters are 125µm and 140µm) and Coating (Protective layer that absorbs shocks, physical damage and moisture; The outside diameter of the coating is typically either 250µm or 500µm; Commonly used material for coatings are acrylate,Silicone, carbon, and polyimide).
An optical fibre cable is made up of the following components: Optical fibres – ranging from one to many. Buffer tubes (with different settings), for protection and cushioning of the fibre. Water protection in the tubes – wet or dry. A central strength member (CSM) is the backbone of all cables. Armoured tapes for stranding to bunch the buffer tubes and strength members together. Sheathing or final covering to provide further protection.
The five main reasons that make this technology innovation disruptive are fast communication speed, infinite bandwidth & capacity, low interference, high tensile strength and secure communication. The major usescases of optical fibre cables include intenet connectivity, computer networking, surgery & dentistry, automotive industry, telephony, lighting & decorations, mechanical inspections, cable television, military applications and space.