The pandemic has unravelled the importance of reliable connectivity. From smart classes to online groceries, the internet is everywhere. Yet, tens of millions of people living in rural areas and tribal lands don’t have access to optical networks. In fact, 3 out of 10 people living in rural areas lack a reliable connection.
Other research suggests that Americans deprived of broadband could be over 163 million. In fact, this digital divide could lead a person to a life of isolation and deprive them of growth opportunities. Two reasons behind this lack of access to broadband are 1) cost; 2) affordability. When it comes to ISPs, they need a return on their investments to bring optical networks. But the issue is that low-income American families cannot afford a connection.
Yet, there are various models being considered to bring broadband to rural America. State policymakers have sought new solutions to improve its availability. Among the strategies being considered are regional utility facilities and investor-owned utilities.
The challenge of bringing broadband to rural areas is two-fold. The infrastructure required is extensive and sparse populations mean that the customer base is smaller for traditional ISPs. We will talk about the strategies being put into place to tackle these issues. Also, we will talk about how STL can help in the shift towards extensive rural connectivity.
Contents
What is the digital divide?
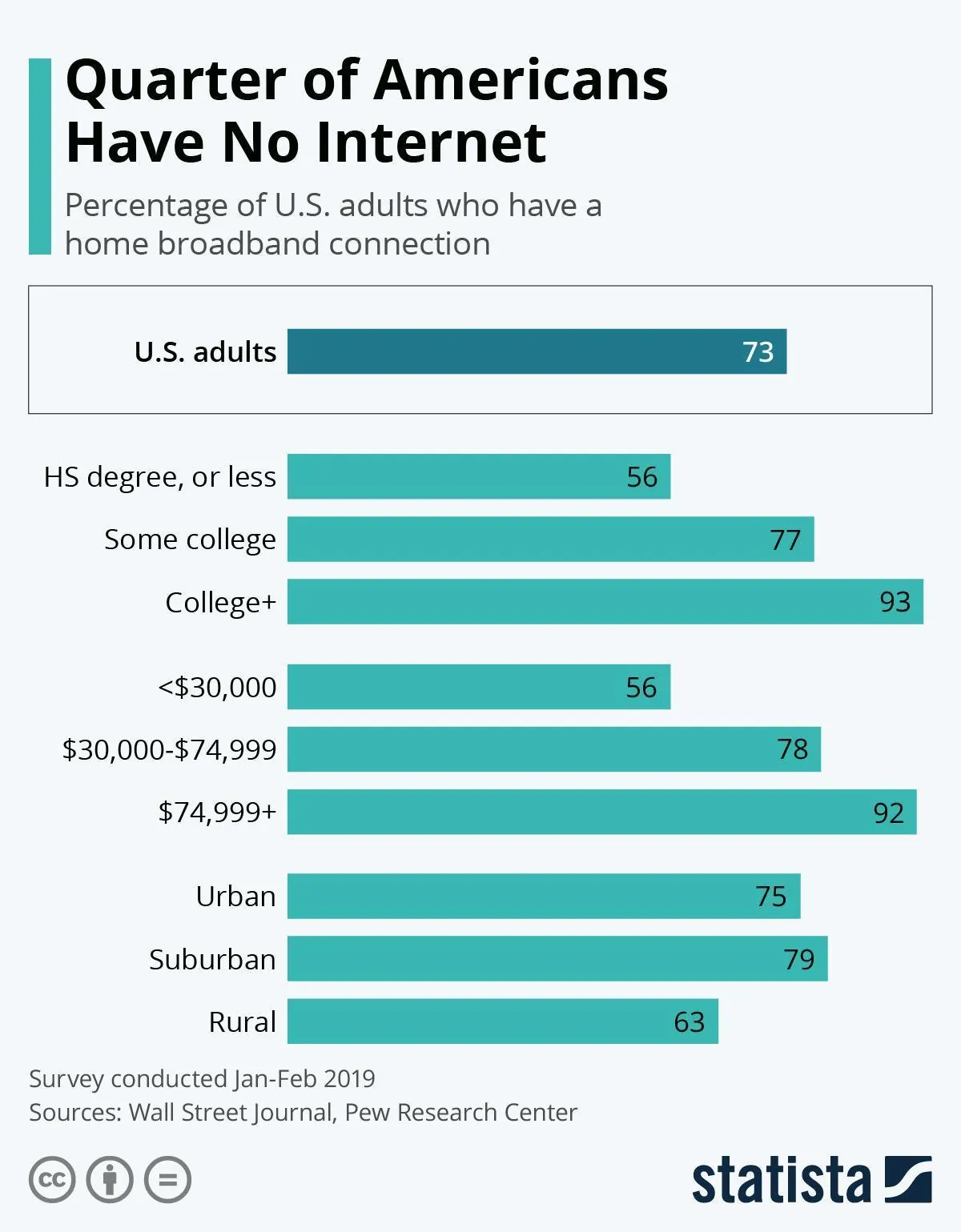
Image Credit : statista.com – Over a quarter of Americans don’t have an internet connection
Currently, 24 million Americans lack access to high-speed internet, and many more cannot afford the service. At a time when having optical networks is increasingly essential, it is a precarious situation for such communities to lack access to the internet. Its effects are noticed in what researchers call the “homework gap.” The term refers to the difficulty students face submitting homework when they lack internet access at home.
In fact, the digital divide has been the concern of educators for over two decades. While there has been some progress made, existing inequities persist within communities and they are glaring, for instance, 70% of children in the Kansas City school did not have internet access at home.
But many significant efforts are being made to improve access to smart learning in lower-income school districts. The worry is that as technology advances, many communities may get left behind.
Due to the serious implications of the digital divide, Congress appropriated $100 billion to help states widen connectivity. It is an effort to move the country towards a more “equitable and prosperous future.”
We will now discuss the measures taken to move towards this future.
How regional utility districts can change things?
Regional utility districts are one of the emerging frameworks for bringing optical networks to rural areas. Multiple towns or municipal entities form them to manage the transmission of electricity and other public utilities. Historically, these utility districts provided essential services.
This model is often employed in rural America to provide water and emergency medical services. In recent years, Vermont and New Hampshire have supported the formation of such districts to provide high-speed internet. By bringing key policies, they made this possible.
For instance, lawmakers in Vermont passed legislation allowing for the creation of communications union districts (CUDs). In these CUDs, two or more towns joined together to support the construction of communications infrastructure. Vermont’s broadband program recognizes CUDs as entities eligible for funding. In 2021, Vermont awarded $9.9 million in preconstruction grants to four of the CUDs for various purposes.
So, how does it improve the situation?
Well, we discussed that extensive infrastructure and sparse populations are the biggest challenges. To combat this supply-demand gap, regional districts combine populations of different towns with raising aggregate demand. It offers the following benefits:
- It increases the number of potential customers.
- The risk facing individual towns gets mitigated.
- Services get provided more efficiently through one regional network than many individual systems.
How partnerships with electrical utilities are enabling change?
Investor-owned utilities can play an essential role in spreading connectivity to rural areas. By utilizing existing infrastructure to provide the middle mile network, high-speed internet connections are possible. To comprehend the middle mile network, it’s crucial to grasp the three phases of interconnected infrastructure:
- The global internet network comprises of a network of massive undersea and inter-country cables connecting to hubs called “internet backbones.”
- Middle mile infrastructure: transports data nationwide via high-speed fiber lines from a global internet hub to an Internet Service Provider (ISP), such as Comcast or Charter.
- Last mile infrastructure: moves data from the intermediate stage to final users such as homes and companies.
Connecting rural areas, as we mentioned, poses a challenge. These regions are more costly and less profitable to serve than denser urban and suburban areas. To accomplish this massive undertaking, we need middle and last mile networks. These networks are owned or operated by those that work together to provide high-speed internet service. The challenge lies in the fact that building middle-mile infrastructure in certain regions often involves installing thousands of miles of fiber, making it a risky investment that may not be feasible if there isn’t a last-mile provider available to connect households and small businesses.
However, without adequate middle-mile infrastructure, last-mile providers may not be able to serve the community. Investor-Owned Utilities (IOUs) can play a crucial role in this scenario. These electricity distributors, which serve 72% of all electric customers nationwide, issue stocks. IOUs are now incorporating fiber optic cables into their smart grid modernization projects, which enhance the efficiency and reliability of their electric operations.
How can STL help?
As the Biden administration makes concerted efforts towards rural digitization, STL can lend its expertise and help in many ways. Our company offers 30 years of optical knowledge and has executed large-scale projects. We help address key issues such as:
- Sheer magnitude
- Harsh terrains
- Network economics
- Rural fiber deployment speed
STL has rich experience in large-scale system integration projects while facing challenging topographies. Also, we understand the role digital technology can play in transforming lives. These insights have helped us understand the need for customized connectivity products and the deployment challenges rural areas present.
As STL is constantly working to innovate, we have a vast array of projects ranging from rural broadband to smart cities.
Our T-Fiber project has enabled the Government of Telangana to make significant progress in providing broadband infrastructure through BharatNet, an initiative to bring broadband access to rural India. As a result, we estimate that six million rural Indians will now be able to join the broadband network.
Conclusion
The digital divide in the US is a cause for great concern. It pushes inequities across different communities. Also, it leaves a large portion of the country in the dark. After all, without having access to broadband, you are basically isolated from the rest of the world.
But with innovative strategies, the country is slowly closing the gap. With Congress signing $100 billion for structuring broadband connectivity to reach rural America, we are moving in the right direction. STL can help design optical fiber networks needed to make a digitized rural America a reality. With expertise in rural broadband, we can take on this massive responsibility and deliver.
FAQs
Does STL deal in optical networks?
STL is an integrator of digital networks, offering All-in 5G solutions. Our capabilities include optical networking, services software, and wireless connectivity.
Has STL taken on rural broadband projects?
STL has undertaken the T-Fiber project to provide digital infrastructure to Telangana’s six million rural residents. The project aligns with the vision of creating a “Digital Telangana” and STL and T-Fiber will collaborate to bring broadband connectivity to these six million citizens.
How many countries have STL worked with?
The company is driven by the purpose of “Transforming Billions of Lives by Connecting The World.” It designs and manufactures in 4 continents with customers from over 100 countries.
Why should I choose STL’s Fiber Optics Solutions?
STl maintains its own laboratory for creating and testing next-gen optical fibers and cables. Also, the STL’s fiber optics connection allows you to improve operations and boost output with speeds of up to 100 Gbps of internet speed.















