The internet has become an integral part of our lives. We rely on it for everything from communication to entertainment to work. However, as our dependence on the internet has grown, so too has the demand for faster and more reliable connectivity. This is where fiber to the home broadband comes in. Fiber to the home (FTTH) broadband is a technology that uses optical fibers to deliver high-speed internet directly to homes. Unlike traditional copper or coaxial cables, which are prone to signal loss and interference, optical fibers are made of glass or plastic and can transmit data over much longer distances without loss of signal quality.
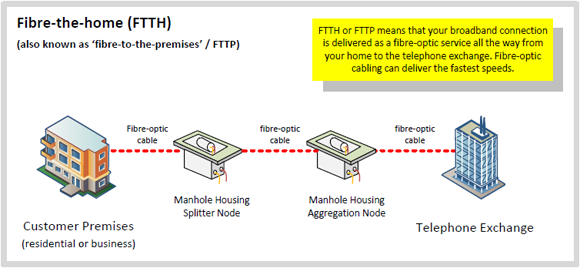
Fig 1: FTTH broadband basic architecture
Image credit: thinkbroadband.com
Contents
- 1 Advantages of FTTH broadband connectivity
- 2 Increased speed and bandwidth
- 3 Improved reliability
- 4 Greater flexibility
- 5 Enhanced security
- 6 Future-proofing
- 7 Cost-effective
- 8 Factors driving fiber to the home success
- 9 Typical elements of fiber to the home
- 10 The evolution of fiber to the home
- 11 What are the challenges facing the widespread adoption of FTTH broadband?
- 12 How is FTTH broadband being used in real-world industry applications?
- 13 The future of fiber to the home
- 14 Conclusion
- 15 FAQs
Advantages of FTTH broadband connectivity
Contents [hide]
- 1 Advantages of FTTH broadband connectivity
- 2 Increased speed and bandwidth
- 3 Improved reliability
- 4 Greater flexibility
- 5 Enhanced security
- 6 Future-proofing
- 7 Cost-effective
- 8 Factors driving fiber to the home success
- 9 Typical elements of fiber to the home
- 10 The evolution of fiber to the home
- 11 What are the challenges facing the widespread adoption of FTTH broadband?
- 12 How is FTTH broadband being used in real-world industry applications?
- 13 The future of fiber to the home
- 14 Conclusion
- 15 FAQs
The benefits of FTTH broadband are clear. It offers faster speeds and more reliable connections than traditional broadband technologies. According to a study by RVA LLC Market Research & Consulting, fiber broadband now reaches over 60.5 million households in the United States, showing a 12% increase in 2021 alone. According to a study, it was found that fiber broadband is now available to 43% of households in the United States and 60% of households in Canada. The study revealed that major providers such as Verizon, AT&T, Lumen, and the best five cable MSOs had built 72% of the overall fiber broadband access, while Tier 2 regional operators like Frontier, Windstream, TDS and Consolidated accounted for 10% of the growth. But how exactly is it revolutionizing internet connectivity? Let’s take a closer look.
Increased speed and bandwidth
One of the most obvious benefits of FTTH broadband is its increased speed and bandwidth. With speeds of up to 100 Gbps, FTTH broadband is significantly faster than traditional broadband technologies such as DSL and cable. This means that users can stream high-definition videos, play online games, and work remotely with much less lag.
Improved reliability
Another major benefit of FTTH broadband is its improved reliability. Because optical fibers are not affected by electromagnetic interference, they are less prone to signal loss and outages. This means that users can enjoy a more consistent and reliable internet connection.
Greater flexibility
FTTH broadband also offers greater flexibility for users. With its increased speed and bandwidth, it can support multiple devices and users at the same time. This makes it ideal for households with multiple people working from home or for small businesses that need to connect multiple devices to the internet.
Enhanced security
FTTH broadband also provides enhanced security for users. Because optical fibers are difficult to tap into, they offer a higher level of security than traditional broadband technologies. This makes them an attractive option for businesses and individuals who need to transmit sensitive data over the internet.
Future-proofing
Perhaps most importantly, FTTH broadband is future-proof. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see an even greater demand for faster and more reliable internet connections. With its increased speed and bandwidth, FTTH broadband is well-equipped to meet these demands.
Cost-effective
FTTH broadband is also more cost effective than traditional broadband technologies. Because optical fibers are more durable and require less maintenance, they can offer a lower total cost of ownership over time. Additionally, FTTH broadband is less prone to outages and service interruptions, which can save users money in the long run.
Factors driving fiber to the home success
One key factor driving FTTH broadband’s success is the increased demand for faster and more reliable internet connections. With more and more people working remotely, streaming videos, and playing online games, the need for faster and more reliable internet connections has never been greater. Additionally, the future-proof nature of FTTH broadband makes it an attractive option for both individuals and businesses.

Fig 2: The rise in global FTTH/B subscriptions between 2017-2021
Image credit: prysmiangroup.com
Typical elements of fiber to the home
The typical elements of FTTH broadband include an optical network terminal (ONT), an optical line terminal (OLT), and optical fibers. The ONT is the device that connects to users’ homes and converts the optical signal into an electrical signal that devices like computers and routers can use. The OLT is the device that connects the ONT to the internet service provider’s network. The optical fibers are the medium that carries the optical signal between the ONT and the OLT.
The evolution of fiber to the home
FTTH broadband has come a long way in a relatively short period of time. Initially, it was only used in select areas and primarily for high-end business and government applications. However, as the demand for faster and more reliable internet connections has grown, so too has the adoption of FTTH broadband. Today, it is increasingly being deployed in residential areas, and many internet service providers now offer FTTH broadband as a standard service.
What are the challenges facing the widespread adoption of FTTH broadband?

Certainly, one of the main challenges facing the widespread adoption of FTTH broadband is the cost of deployment. Installing optical fibers requires significant infrastructure and can be quite expensive, especially in areas with difficult terrain or a dispersed population. For example, the cost of running optical fibers to every home in rural areas can be cost-prohibitive for internet service providers. Additionally, the cost of digging up streets and laying the infrastructure can be substantial in densely populated urban areas.
Another challenge is the lack of standardization in the industry. With different internet service providers using different equipment and technology, it can be difficult to ensure compatibility between different FTTH broadband systems. This can make it difficult for customers to switch providers and can also hinder the development of new technologies that rely on FTTH broadband.
Regulatory and legal challenges can also be a barrier to deployment. In some areas, there may be restrictions on where internet service providers can lay fiber optic cables, or there may be disputes over who is responsible for maintaining the infrastructure. Additionally, there may be issues with gaining access to private property or with obtaining the necessary permits and approvals to lay the infrastructure.
Lastly, there is a lack of awareness and education about the benefits of FTTH broadband among the general public. While more people are becoming aware of the benefits of FTTH broadband, many still do not understand the technology or its benefits, making it difficult for internet service providers to gain support for their deployment efforts.
In conclusion, while FTTH broadband offers many benefits, the cost of deployment, lack of standardization, regulatory and legal challenges, and lack of awareness and education are some of the main challenges facing its widespread adoption. However, as the demand for faster and more reliable internet connections continues to grow, it is likely that these challenges will be overcome, and we will see a wider deployment of FTTH broadband in the future.
How is FTTH broadband being used in real-world industry applications?
A wide range of industries and companies around the world are using FTTH broadband. In the telecommunications industry, it is being used to connect homes and businesses to the internet. In the healthcare industry, it is being used to connect hospitals and clinics to remote medical experts for consultations. In the education industry, it is being used to connect schools and universities to online resources and remote learning platforms.
The future of fiber to the home
The future of FTTH broadband looks bright. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even faster speeds and more advanced capabilities. For example, some experts predict that we will see the emergence of “smart homes” in which all household devices are connected to the internet and can be controlled remotely. FTTH broadband will play a crucial role in making this a reality. Additionally, it will continue to be a key enabler for deploying new technologies such as 5G and IoT.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fiber-to-the-home broadband is revolutionizing internet connectivity by providing faster speeds, more reliable connections, greater flexibility, enhanced security, and future-proofing. It is an important technology that will continue to play a crucial role in our digital lives. Its benefits are clear, and as the demand for faster and more reliable internet connections continues to grow, we can expect to see even more widespread adoption of FTTH broadband in the years to come.
Learn more about STL’s FTTx Access Network Solutions, click here.
FAQs
1. What is fiber to the home broadband?
Fiber-to-the-home broadband is a specifically designed fiber network solution for residential deployments. Within the FTTH network, the fibers are directly connected to the buildings or individual homes. It is installed and used from a central point, which is linked directly to the individual’s property.
2. How does fiber to the home broadband differ from traditional broadband technologies?
The major difference between the traditional broadband and the FTTH broadband is mostly measured in terms of the speed. The fiber connection has an enhanced potential of being much faster in order to transmit data and information. In addition to that, fiber optic connections have bigger bandwidth than the traditional options, and are evidently more secure as well.
3. What are the benefits of fiber to the home broadband?
The sole understanding of people about FTTH broadband is that it offers high connection speeds for seamless use of internet and associated services. But FTTH broadband offers ample other benefits as well, for the end consumers. Some of them include:
- Faster speed and increased bandwidth
- Enhanced reliability
- Greater flexibility
- Increased network performance
- Cost-effective
4. What are the typical elements of fiber to the home broadband?
FTTH broadband has some typical operational elements such as:
- Optical line terminal (OLT)
- Optical network terminal (ONT)
- Optical fibers.
ONT is the device that is responsible for connecting to the individual homes. Following that, it will convert the optical signals to electrical signals, for the routers or computers to use. OLT is responsible for connecting ONT to the internet service provider’s network. Finally, the optical fiber is the bridge that carries the optical signals within ONT and OLT.
5. What are the challenges facing the widespread adoption of fiber to home broadband?
Some of the challenges that is hindering the seamless deployment of FTTH broadband on a wide scale are:
- Increased cost of deployment
- Evident lack of proper standardization within the industry
- Legal and regulatory challenges halt the major deployment project
- Lacking awareness or education among people towards the benefits of FTTH.















