Nations run on pillared infrastructures, and we’re not just talking about the physical ones. Various departments work in unison to keep the engines of a country running. Departments dealing with critical infrastructure like water systems, power grids, and transportation networks are vital cogs that need uninterrupted connectivity using a fibre optic network
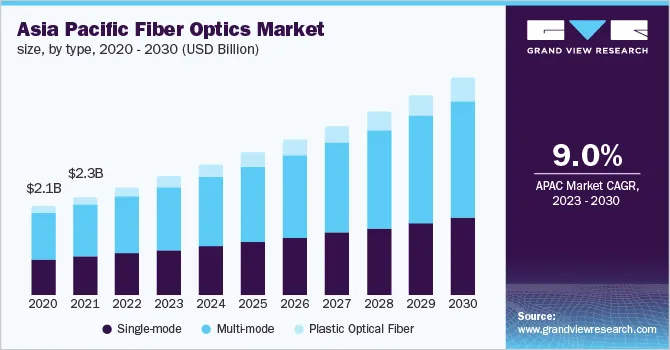
Fig 1: The growing APAC fiber optics market
Image credit: grandviewresearch.com
Nations run on pillared infrastructures, and we’re not just talking about the physical ones. Various departments work in unison to keep the engines of a country running. Departments dealing with critical infrastructure like water systems, power grids, and transportation networks are vital cogs that need uninterrupted connectivity using a fibre optic network.
Contents
- 1 Why are optical fibers considered an excellent option for critical infrastructure?
- 2 Security: The Primary Focus of Fibre Optics for Critical Infrastructure
- 3 Why are optical fiber networks more reliable for critical infrastructure systems?
- 4 Challenges in maintaining the security and reliability of fibre optic networks
- 5 What does the future hold?
- 6 FAQs
Why are optical fibers considered an excellent option for critical infrastructure?
For these critical infrastructures to ensure smooth functioning, seamless communication is the key to handling the large volumes of data produced daily. And fibre optics have emerged as the most reliable option for running critical infrastructure.
With critical infrastructure systems handling vast amounts of data using a network of smart devices and modern systems, faster communication networks are required, like 5G. And such advanced technology requires a robust 5G fiber backhaul network.
Security: The Primary Focus of Fibre Optics for Critical Infrastructure
Hackers are evolving with each passing day, and they see critical infrastructure systems as gold mines of exploitable data.
Without a secure communication network, critical infrastructure systems can collapse if malicious actors get a hold of the vulnerabilities. A fibre optic network is more secure than traditional communication technologies, with the following key differentiators:
- Data transmission using light – Pulses of light carry data in a fiber optic network, and they are harder to intercept than electrical signals carried by copper wires or wireless signals transmitted by satellites.
- Difficult to tamper with – Cable-based communication systems can be tampered with easily with a simple splice. However, gaining access to the data being carried inside optical fibres is much more challenging with the splicing process requiring exceptional expertise, fortifying your data security further.
- Easy to detect intrusions – Another exceptional security feature of using 5G fiber backhaul networks is that they allow for quick identification of compromised/tampered with cables.
Why are optical fiber networks more reliable for critical infrastructure systems?
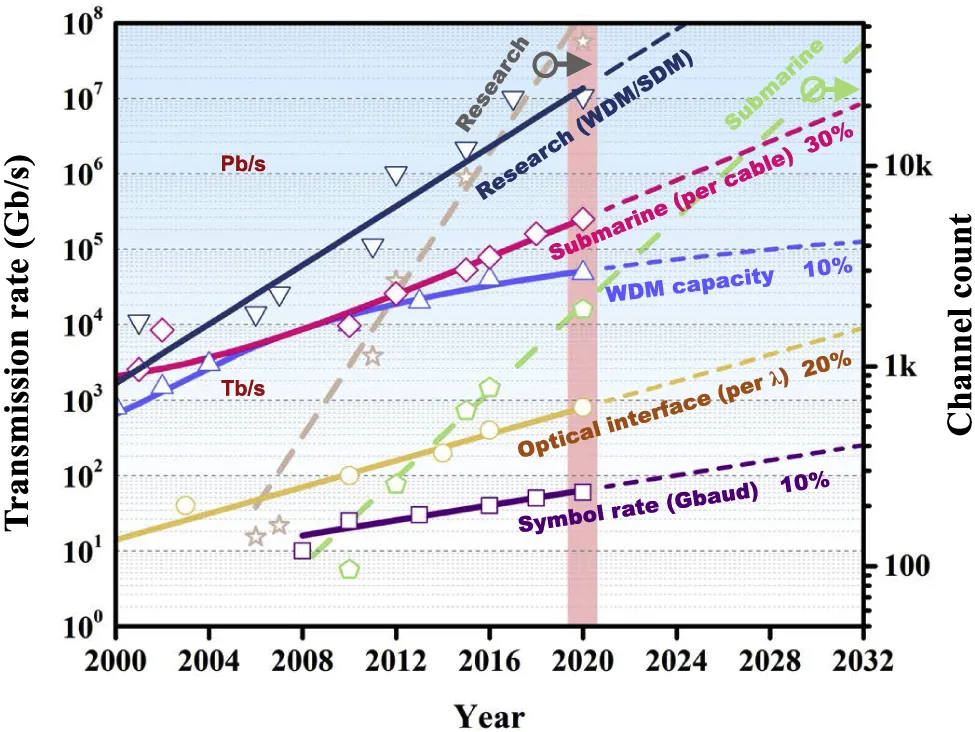
Fig 2: Fibre optic transmission capacity
Image credit: degruyter.com
Today’s critical infrastructure systems require a large amount of bandwidth to cater to hundreds of gigabits of data traffic and an exploding number of devices on the network. To ensure uninterrupted connectivity and high-speed data transfer speeds, building an efficient 5G fiber backhaul network is critical.
Here are the main areas where fiber optics score highly on reliability when it comes to critical infrastructure systems:
1. High data transmission capacity – Single-mode and multimode optical fibers are extremely effective at carrying incredible amounts of data, from short-range data transmission to many kilometers with speeds of up to 160 Gbit/s.
2. Low latency – One of the most critical requirements of 5G networks is low latency. Previous generations of communication technology were simply not able to cope with large data volumes and maintain their low latency levels. However, with a network built on fiber optics, the latency levels have been brought significantly down to enable near real-time critical operations.
3. Lower attenuation – Signal loss due to various factors is the most common issue faced by copper-based cable networks. On the other hand, a fibre optic network delivers better performance with much lower attenuation levels.
Challenges in maintaining the security and reliability of fibre optic networks
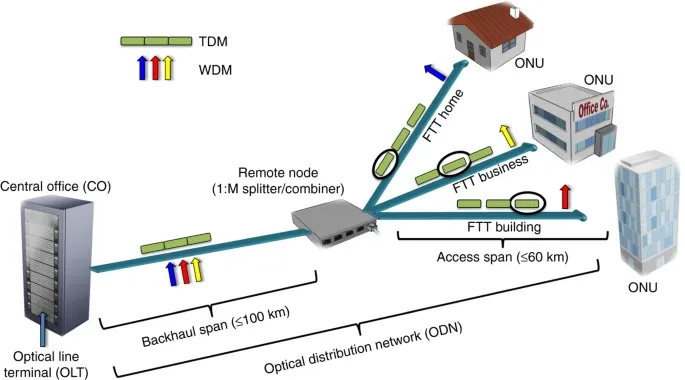
Fig 3: General schematic of a typical optical access network
Image credit: nature.com
Although optical fibers are increasingly being deployed by businesses and critical infrastructure organizations, some challenges are impeding the adoption of fiber optic networks.
Network Security
Despite their high levels of security, optical fibers are still vulnerable. Therefore, sophisticated security measures like encryption and intrusion detection systems are recommended to protect the 5G fiber backhaul network.
Physical Security
Vandalism and theft pose a significant risk to an optical fiber network. Such events can cause physical damage, disrupting the network’s functionality. Measures must be taken to prevent such incidents from happening.
What does the future hold?
Taking into account the various promises and challenges presented by fiber optic networks, one can say that it’s critical for critical infrastructure systems to seek the help of market leaders in fiber optics to ensure that their 5G fiber backhaul networks are prepared to deal with future challenges and demands.
STL is leading the charge when it comes to expanding the level of fiberization to cater to the modern-day data needs of critical infrastructure. Speak to our experts to see how we can help you prepare for the future of connectivity.
To know more about STL’s optical interconnect products, click here.
FAQs
1. Why do critical infrastructure systems need fiber connectivity?
Since modern systems of education, healthcare, government operations, power, and water systems, etc., work with vast amounts of data, they need an optical fiber network to cater to the high computational demands.
2. How do fiber networks prevent external interference?
Optical fiber networks use light pulses for data transmission inside fibres made of glass, making them immune to external interference. Moreover, hacking the network by splicing the cables is extremely challenging.
3. What are the different challenges faced in the fiber network rollout and maintenance?
Incidents of specialized hacking, physical incidents like theft and vandalism, and natural disasters like earthquakes and floods can hinder the adoption of fiber optic networks.















