Traditional Radio Access Networks will present difficulties in establishing a 5G infrastructure. As a result, telcos will have to modernize their RANs by upgrading them using vRANs and O-RANs. vRANs means virtual RAN, where the RAN uses virtual components, and O-RAN refers to the Open RAN alliance that aims to reduce vendor lockdown by transforming to an open architecture.
Contents
D-RAN, vRAN, and O-RAN
D-RAN is the traditional Radio Access Network setup where every cell site has a Remote Radio Unit and a BaseBand Unit running on proprietary hardware. The need for proprietary hardware results in vendor-lockin and is a bottleneck for technical advancement.
vRAN aims to reduce its bottleneck by virtualizing and running the RAN hardware on commercial servers. This way, telcos can avoid vendor lock-in for their BBUs. However, the RAN depends on proprietary interfaces and hardware for radio transmission.
O-RAN alliance further eliminates the need for proprietary devices. Its goal is to create an SW/HW disaggregated environment where multiple vendors can build devices using open architecture.
Why does 5G create the necessity to Modernize RANs?
5G needs a lot more antennas, so telcos must invest more. But current RANs running on proprietary hardware make this investment unfeasible. Moreover, the service providers need to place the application closer to the end user, but traditional RANs need more space and a higher power supply to make this possible.
The 5G infrastructure requires a lot more services lacking in the previous generation. And installing these services inter proprietary hardware will present complications, leading to inefficiencies and bugs.
Because of the increased capital and operational expenses, industries might have to use inconsistent designs. This error may be severely inefficient for launching their services for 5G because of operational errors.
5G connects more devices, increasing exposure. That means hackers get more attack surfaces to compromise the network. However, including countermeasures in a traditional RAN architecture will introduce latency because of the higher processing power required.
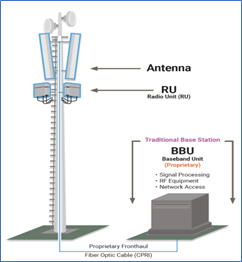
Source: Traditional RAN
The goal of The Modernized RAN architecture
- Telecos will get a common platform to run their RAN and non-RAN functions. This platform will enable them to deploy 5G services alongside RAN; their services will be closer to the customer, enabling higher efficiency.
- Only a competent vRAN architecture can fulfill the latency requirement of the 5G infrastructure.
- A modernized RAN platform will have automation capabilities. Industries will have the power to automate repeating mundane tasks to improve efficiency.
- The open disaggregated architecture of the modern RAN will enable higher talent in the support team as multiple vendors will pool in their staff.
- Modernized RAN architecture is necessary for improving security as AI will be essential and require a higher-performing environment.
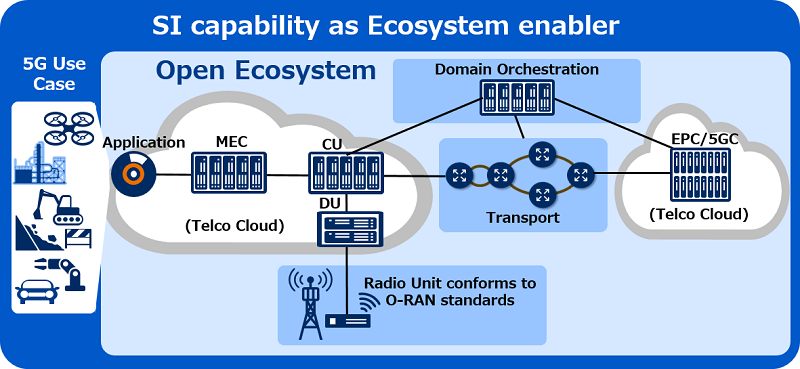
Source: Open RAN Ecosystem
The RAN Market
Industries are investing much in RAN modernization, substantiated by the market growth:
- The market research estimates RAN services market revenue to be 44.78 billion by 2026.
- The rising demand for mobile broadband services and more dense networks are causing the surge in the market; the Asia-pacific region is the leading in this growth.
- The small cells may contribute to 43% of the total RAN services market in 2023.
- An increase in IoT devices worldwide is another driving factor for RAN market growth; by 2030, 500 IoT devices will get connected.
In conclusion, the current RAN architecture will fail to accommodate emerging networking technologies, especially 5G. Therefore, traditional RANs become unfeasible if you use them for deploying 5G architecture. Moreover, the extensive network size possible with 5G requires a robust security solution that needs AI assistance. And AI requires higher processing power, causing lags in a traditional RAN. These points make the modernization of RAN architecture necessary.















