Cloud technology has become popular in India. Especially during Covid, when people worked remotely, its popularity grew exponentially. Moreover, high-speed internet has become more accessible; The 5G introduction will further increase the popularity of remote work and
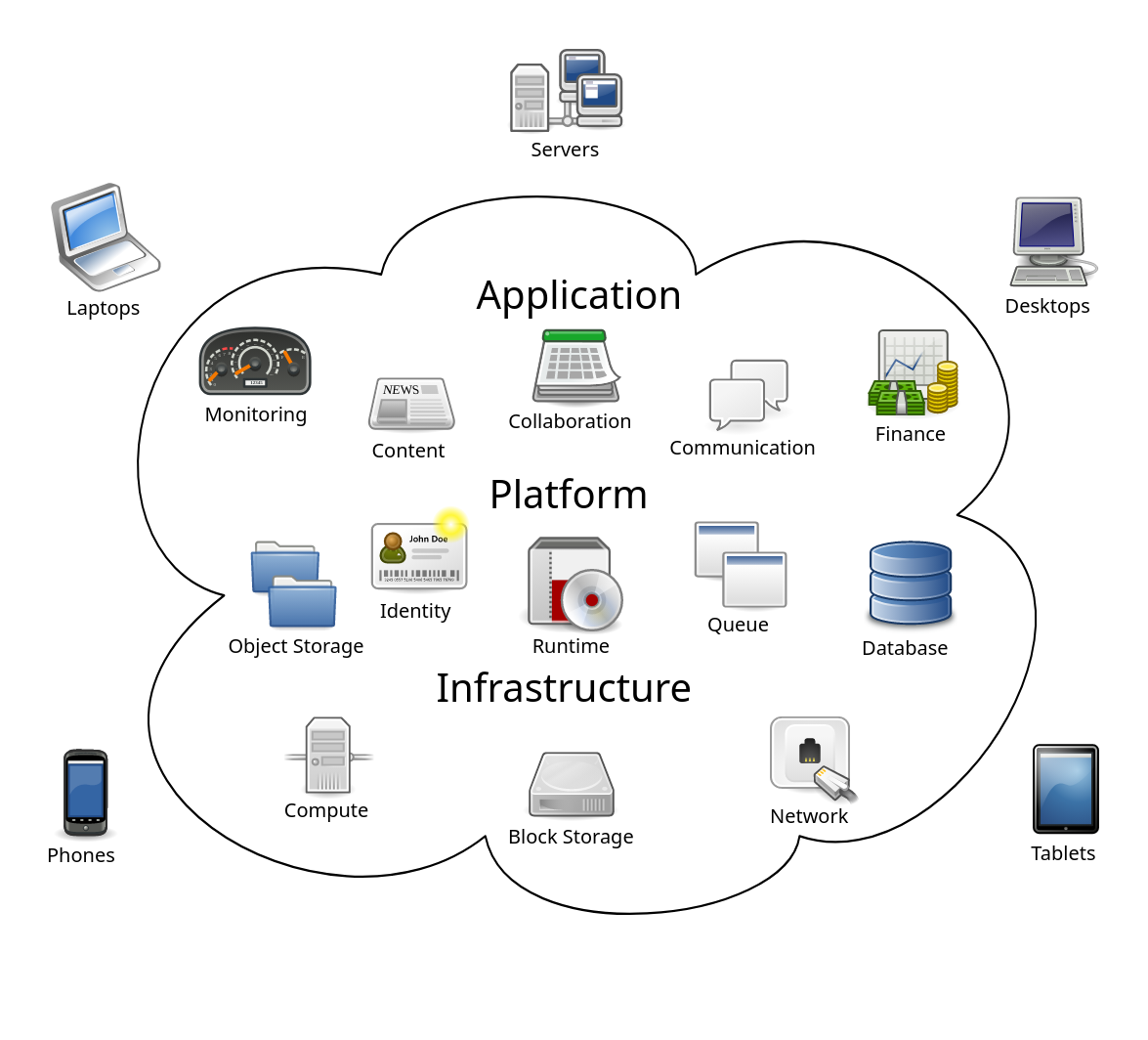
In this article, you can explore various points regarding India’s cloud infrastructure.
Contents
Why Do We Need Cloud Computing?
- We need cloud computing when it becomes impractical to invest in upfront equipment. For example, startups need a robust and secure infrastructure but lack funding. In such a situation, a pay-as-you-go cloud infrastructure model becomes more feasible. Furthermore, people have started to show more interest in remote work, especially when they found that it increased their productivity because cloud technology eliminates travelling.
- Cloud computing is greener; service providers can use high-quality, long-lasting infrastructure to provide a work environment that individuals may not afford. That means you don’t have to buy a new laptop every few years because of a faulty motherboard if you use a cloud workstation.
- Finally, the most significant advantage of cloud computing is the reduced responsibility for infrastructure security and maintenance. You don’t have to worry about tiresome upgrades and the physical safety of the devices; the infrastructure maintenance comes under the service provider’s package. You might be able to upgrade or downgrade your plan according to the responsibility you are willing to take.
Cloud Investment in India
People want to invest more in cloud computing because of its increased scalability, security, maintenance, and cost predictability. Cloud technology investments accelerated in India during the pandemic. According to Business Standard, an international research firm estimates the CAGR of the Indian cloud market to be 23.1% by 2025 and may grow to USD 13 billion.
SaaS holds the most interest among the different models of cloud computing in India because of its low skill bar and least responsibility, as estimated by IDC. And micro, small, and medium companies contribute most to the SaaS economy.
The big three cloud service providers, Azure, AWS, and GCP, continue their investments in India. According to Business Standard, AWS may invest around USD 4.4 billion by 2030. Microsoft has planned to create its largest Indian data centre. These investments by major corporations point to the accelerated growth of the Indian cloud market.
Cloud Skills in India
Global Skills Report (GSR) by Coursera states India’s technology skills have become 46% from 38% and the top six globally. This report uses 100 million learners as the sample space and shows business, technology, and data science statistics. And it further states that cloud technology is the most robust technology skill, with a proficiency of 74%.
The NASSCOM report says that India will need around 20 lakh cloud experts by 2025 as cloud skills will become highly crucial. The future of cloud computing in India holds the following as the most in-demand skills:
- Cloud Deployment and Migration: Industries will continue to migrate towards the cloud, requiring several efficient employees to make it possible.
- Cloud Security: Increased cloud use demands robust security; India will need more cloud security professionals to ensure the cloud infrastructure remains hacker-proof.
- Coding and DBMS: As more cloud users grow, the requirement for coding and database management skills will also increase.
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: You need clouds with high processing powers to run AI/ML models, making it a crucial cloud skill.
Benefits of Cloud Computing During Covid
Cloud computing has benefitted the most during the Covid. The lockdown has forced people to sit in their homes. The only way employees could work was through a remote connection; this compelled companies to improve the infrastructure of remote login. And the most feasible and quick way to establish a remote work environment was through cloud technology.
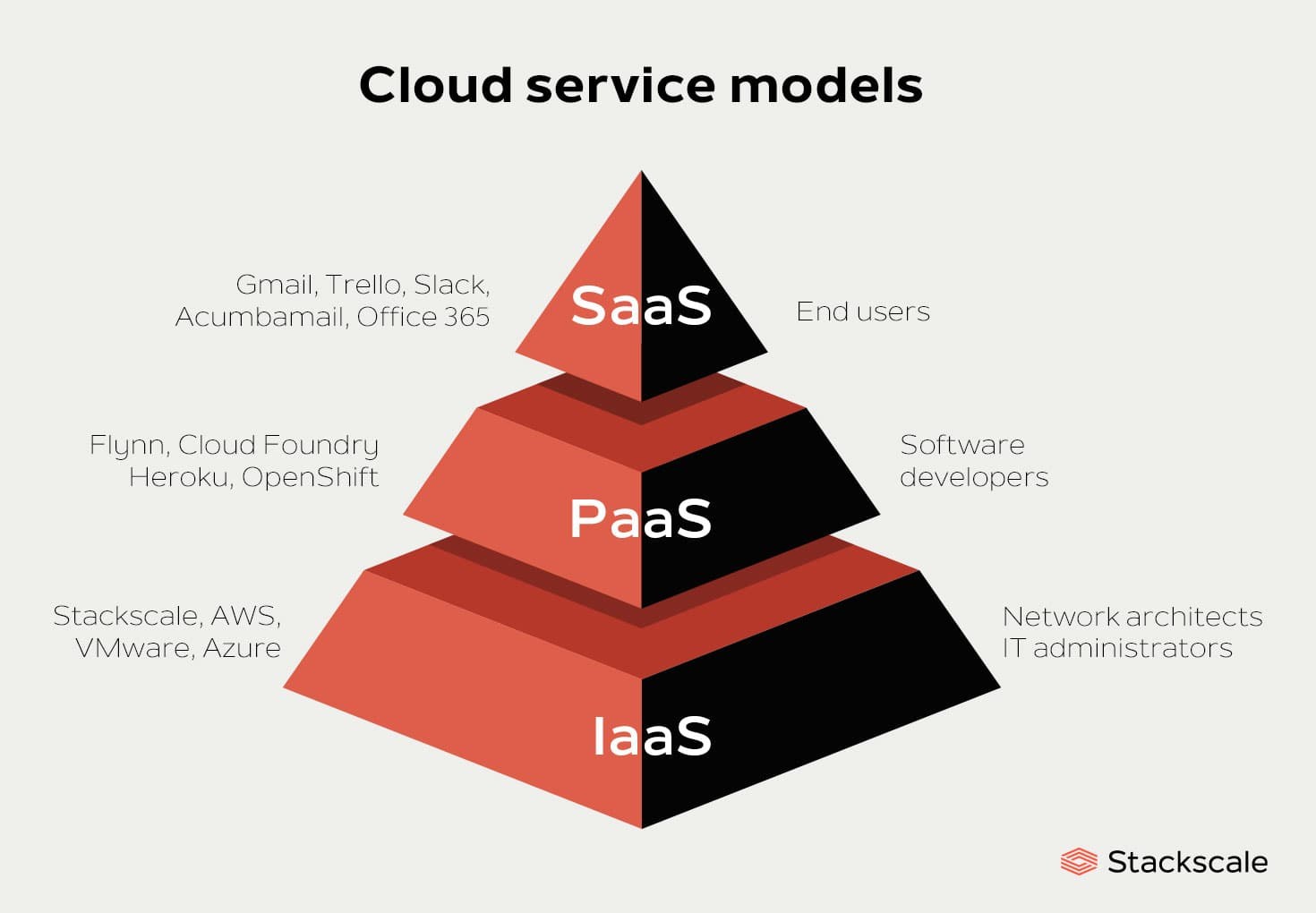
Cloud computing enabled companies to subscribe pay-as-you-go model from cloud service providers. These providers may be SaaS, PaaS, or IaaS; companies only have to pay for what they have used in a specific month. This feature reduces the companies’ burden of planning and implementing an infrastructure robust enough for remote work. Moreover, the most popular service, SaaS, eliminates the responsibility of infrastructure security.
Even after the lockdown, this situation made it feasible for asymptomatic Covid positive patients to work from their homes. Further, even healthy people found these facilities helpful as they could reduce travel time, which required various formalities.
Various government facilities during COVID used cloud technology. As a result, the government could provide reliable services, including Cowin, Arogya Setu, MyGov Saathi, etc., only through cloud computing facilities.
India’s Robust Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Cloud technology cannot be stopped as India strides towards a new technological future. Cloud provides an agile and accessible environment for computing. Moreover, its powerful serverless architecture can offer robust digital infrastructure capable of implementing AI/ML and Big Data models; the serverless architecture ensures that developers do not have to worry about maintaining the infrastructure.
A robust cloud infrastructure can attract innovation and provide employment opportunities. With many companies boasting a digital-first architecture, India is facing demands for various jobs, including cloud developer, cloud security engineer, front-end developer, etc.; in 2021, India had 379 000 cloud job openings, according to NASSCOM. This situation points to a functioning and robust infrastructure in India.
However, the demand for employees is around 8-10 times higher than the available candidates. That means you need comprehensive upskilling, reskilling, and training programs to ensure the cloud skills meet the infrastructure demands.
Indian cloud computing infrastructure has contributions from various private entities, including GCP, Azure, and AWS. In addition, GI Cloud (MeghRaj), the National and state service Delivery Gateways, AIRAWAT (Cloud-based AI platform), and TechSaksha are some Indian initiatives backing up the Indian cloud infrastructure.
The Scope of Cloud Computing in India
In conclusion, the cloud computing industry has tremendous scope in India. It is also crucial for the country’s further development in the twenty-first century. Currently, the infrastructure is improving rapidly, and the need for cloud computing experts is growing. So by comprehensive upskilling, reskilling, and education, India can fill the cloud skill gaps and become a USD 5 trillion economy.















