Edge AI amalgamates two emerging technologies of today’s digital transformation era — Edge Computing and Artificial Intelligence (AI). As part of this, AI applications are deployed either directly on devices or on the servers closer to the devices. Therefore, it is called edge AI.
AI computation takes place at the network’s edge, close to the actual location of data instead of a data centre or a cloud computing server. In times when the Internet can reach the remotest corners of the world, we cannot limit the edge of a network to any location. Therefore, the location can be a factory or even a retail store. We are completely surrounded by devices like smartphones, automatic machines and even traffic signals.
Contents
Importance of Edge AI
Path-breaking developments in the field of AI, ever-increasing adoption of IoT devices as well as the power of edge computing have all joined forces together to unleash the true potential of edge AI. This automatically opens the door to new opportunities which we couldn’t imagine previously — driving automatic cars on highways, smart farming and even enabling real-time, accurate diagnosis.
Businesses today do understand the need to bring the devices closer to the customers and fulfil their needs. This is the primary reason why Edge AI market is all set to witness high growth in the near future. At present, maximum job functions in organisations worldwide have the capability to leverage edge AI. As a matter of fact, edge AI applications are prepared to enhance our daily lives whether at home, at work or in transit.
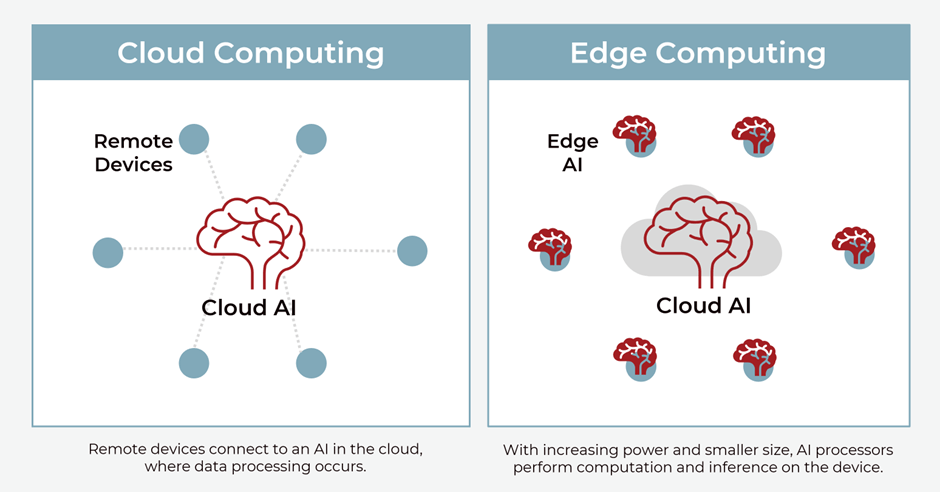
Edge AI vs. Cloud AI
Data is the fuel that keeps the engine of businesses running in today’s times. Various technology applications generate ~2.5quintillion bytes of data every single day. Therefore, the million-dollar question is: ‘Where and how can the data be processed?’ This is exactly where Cloud AI and Edge AI step in. Using AI with machine learning (ML) helps deploy both these architectures for data processing. Below are the differences between cloud and edge AI:
- Latency: It measures a network’s responsiveness, that is, the time difference between request initiation and response. Cloud AI is not efficient enough for applications that require real-time responses such as self-driving cars.
- Connectivity: Continuous connectivity and real-time processing are essential for safety-critical applications which edge AI offers. Automated vehicles or smart homes need to be connected 24X7 because even the slightest delay can lead to unexpected consequences.
- Processing capacity: The processing capacity of the cloud is more than edge devices. It is also difficult to replace or upgrade edge devices.
- Security: Due to on-site storage of data, edge AI devices help provide better privacy and security. Unlike cloud AI, edge AI avoids to and fro between the source and receiver as the information is available locally. Therefore, edge AI better suits the requirements of authentication devices.
- Energy utilisation: Edge devices need more energy. However, with the cloud, there are negligible or no energy consumption limitations.
Regardless of the differences between edge and cloud AI, the two technologies complement each other and do not create a roadblock in each other’s paths.
How does Edge AI technology work?
In Edge AI, a portion of data stored is taken out of the principal data centre and moved closer to the data source. Here, machine learning (ML) algorithms are utilised for data processing and analysis within the area in which the data is generated — which could be a smart city, shopfloor, or a retail store. Internet connectivity is not essential for process completion; real-time decision making takes place in milliseconds.
The output of the process (which could be real-time predictions, forecasts, or business insights) that takes place at the edge is sent to the principal data centre. In this manner, Edge AI takes data closest to the user’s touch points, be it a computer, an Edge server or IoT device. For example, when a user communicates something to Alexa or Google, voice recording is sent to Edge network which is further sent to text through AI and a response is processed accordingly.
Pros & Cons of Edge AI
Like any other technology, edge AI too has its pros and cons that every user must weigh in before opting for it. Let us bifurcate and understand both:
Pros
- Increased responsiveness: Unlike any device that waits for data collection, processing and sending it back, local data processing with edge AI enables quicker decision-making and is action oriented.
- Bandwidth reduction: Edge AI processes data locally thereby reducing the quantity of data sent through the Internet. This helps save Internet bandwidth as well.
- Privacy enhancement: Edge AI ensures that the data is not compromised. It helps data owners exercise greater control over data in terms of what is being shared with whom. Processing and storage of data in edge networks allows filtering unnecessary, extraneous, and redundant data. Therefore, only critical data is sent further to the cloud.
Cons
- Cost and storage – Creation of storage capacity leads to an increase in cost component at the local level. Moreover, traditional IT infrastructure is also upgraded or replaced to manage edge devices. This again involves cost.
- Data loss – During implementation, edge AI systems must be carefully planned to avoid loss of data. Majority edge devices discard irrelevant data. However, if relevant data is discarded by mistake, it leads to unnecessary losses and inconsistent analysis.
Edge AI: Why now?
At present, business value is getting created on the edge. Nothing but edge AI helps convert raw data into actionable insights in a cost-effective and efficient manner. As perGartner’s prediction, by 2025, the creation and processing of 75% data owned by enterprises will take place outside data centres or cloud. Moreover,ABI Research forecasts that 43% AI tasks shall take place on edge devices by 2023. The increasing closeness of intelligence to machines (where data gets created) drives the efficiency of demanding AIoT systems. This reduces possibilities of failure and improves cost and latency. Greater power and capacity, faster access to extensive networks, and presence of smarter machines has helped open the doors to life-changing AI opportunities in the future.
Edge AI use cases
As one of the most powerful technology forces in today’s times, AI is all set to revolutionise the biggest industries worldwide. Be it transportation, healthcare, manufacturing or finance, edge AI is driving everything around such as:
- Intelligent forecast: In the energy sector, edge AI helps combine weather patterns, historical data, and other details to develop complex simulations that facilitate generation, distribution as well as management of energy resources.
- Predictive maintenance: Edge AI detects anomalies quickly and predicts the time for failure of a machine. Installation of sensors on equipment helps inform the management beforehand. This reduces cost downtime as the issue at hand is addressed early on.
- AI-powered healthcare instruments: AI-enabled medical devices will increase the efficiency of precise medical tasks such as thermal screening, remote monitoring, disease prediction and inventory management.
- Virtual assistants: Retailers aim to improve a customer’s digital experience by introducing voice orders. With voice ordering, it is easier to search for products, ask for related information and place online orders using intelligent mobile devices.
The future of edge technology
Edge technology has arrived. With processors becoming powerful, availability of cheaper storage, and improvement in network access, edge technology presents many dynamic opportunities across industries in the future. Edge AI is all set to bask in the glory of advanced networks such as satellite mesh and 5G. Moreover, the ever-increasing use of IoT devices and availability of infrastructure for Machine Learning helps enterprises leverage AI. It also provides additional benefits such as access to real-time insights, cost reduction, and increased privacy. No aspect of our lives shall remain insulated against the influence of edge AI. It has the power to improve climate, enhance our health, reduce road rage and what not.
The future of edge AI has a dark side too. Edge solutions will need several vendors, which increases complexity. Any new smart device, network connection, and even a server is vulnerable to attack from hackers. In addition, edge technology is also prone to sustainability issues due to increase in the quantity of hardware leading to higher energy consumption, more heat and electronic wastage.
FAQs
- What is the advantage of edge AI?
Edge AI helps in bringing computing capabilities closer to the device, the place where IoT and sensors are located. This facilitates AI applications in running deep learning (DL) and machine learning (ML) algorithms.
- Is edge computing the same as AI?
Edge computing and AI are both future technologies that have become buzzwords in the recent past. However, considering them together is better — edge computing is an enabler that helps AI deliver performance and reduce costs, likewise, AI is an important use case for edge computing.
- What is edge AI hardware?
It is a group of many devices utilised to drive & process AI-based devices and robots. These gadgets coordinate and manage AI gadgets by processing information in the hardware.