The Internet plays a pivotal role in our daily lives, from work to entertainment and from shopping to paying utility bills. Ever wondered how the world is literally connected with the World Wide Web, both in spirit and physical sense. The physical connection is achieved through a UTP cable, also known as Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable. This twisted pair of cabling offers a steady network tailor-made for data transfer and telephony.
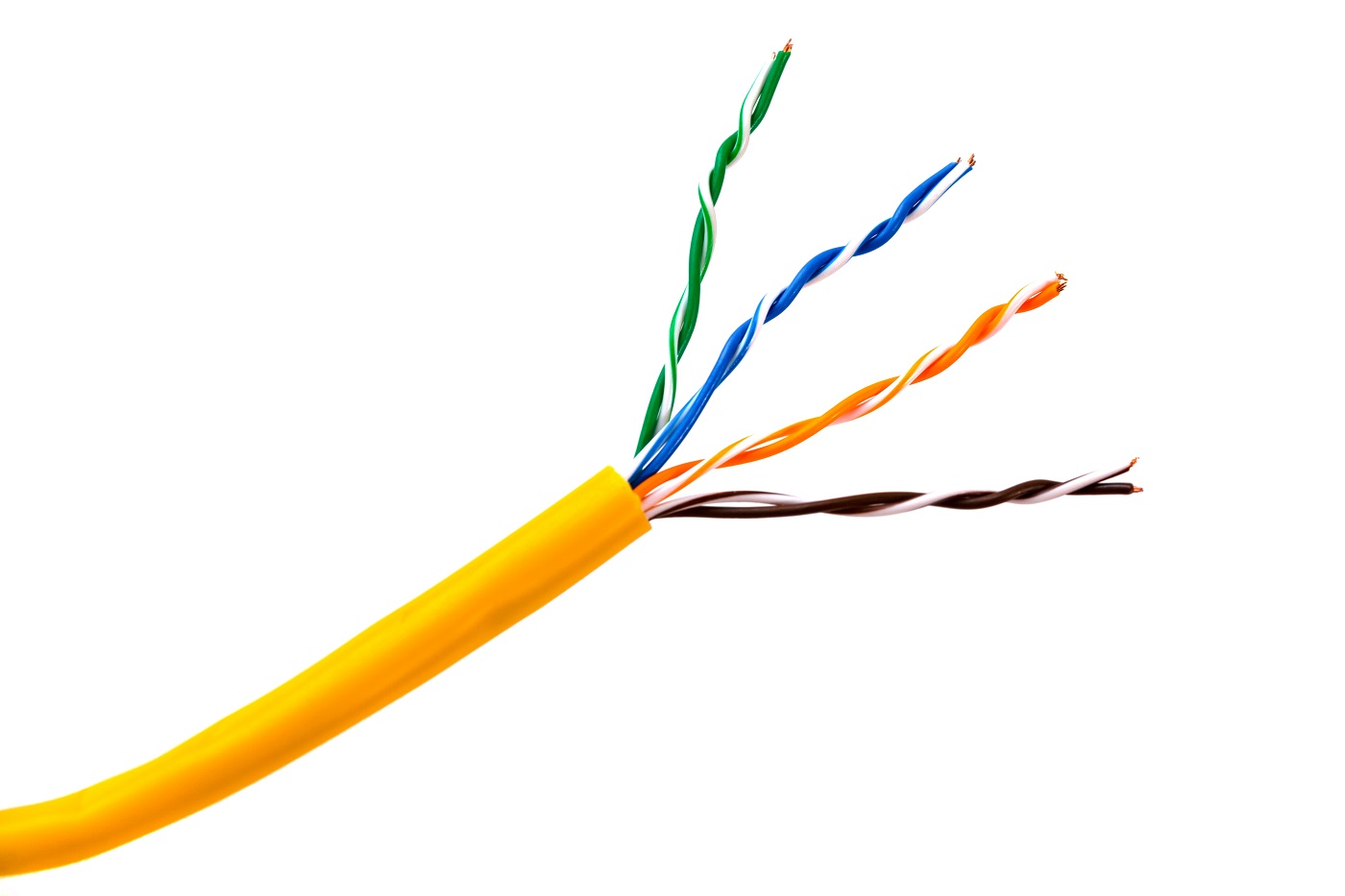
A standard UTP cable consists of a 100-ohm copper cable made with 2 – 1800 unshielded twisted pairs shielded by an outer jacket. As they have no metallic shield, the cable diameter is reduced but cannot avoid electrical interference. The twisting in these cables boosts immunity to EMI and electrical noise. In the mantle of an unshielded twisted pair cable, there are 8 separate wires twisted in 4 pairs. A connector is placed at the end of these cables, usually known as RJ45 plugs.
Contents
- 1 Workings of a UTP Cable
- 2 Functions of a UTP Cable
- 3 Different Categories of UTP cable
- 4 UTP Cable Specifications & Performance
- 5 Solid Conductor UTP Cable and Stranded Conductor UTP Cable
- 6 Applications of a UTP Cable
- 7 FAQ
- 7.1 Why is the UTP cable is Unshielded?
- 7.2 How to connect a UTP cable?
- 7.3 What is the difference between UTP & STP Cable?
- 7.4 Which UTP cable is most commonly used?
- 7.5 What is UTP cable commonly used for?
- 7.6 Why is UTP popular in LAN technology?
- 7.7 How does UTP cable transmit data?
- 7.8 How many twists per inch is Cat6?
- 7.9 Which category cat of UTP cabling is the fastest?
- 7.10 Difference b/w shielded twisted pair cable and unshielded twisted pair cable?
- 7.11 What connector is used for twisted pair cable?
Workings of a UTP Cable
Inside a shield twisted pair cable, there are 4 twisted pairs of copper wires surrounded by a protective plastic cover. The greater the number of pairs corresponds to more bandwidth. The two individual copper cables in a single pair are twisted around each other, and later other pairs of such wires are twisted together. It is done to minimize cross talk and electromagnetic interference as they can reduce network performance in the long run.
Each twisted pair of cabling in the UTP cable is color-coded for easy identification. In North America, each wire in a twisted pair is identified by one of 5 colors: blue, orange, green, brown, or slate (gray). Then this copper wire is paired with a different wire from the other color group made up of white, red, black, yellow, or violet. Usually, one copper wire in a twisted pair is solid-colored, and the second one is striped with the color of its mate. Ex: A solid blue colored copper cable is paired with a white and blue striped copper cable. It will make it easy to identify and match them. Alexander Graham Bell invented this twisted pair of cabling in 1881.
Functions of a UTP Cable
The main functions of a UTP cable are listed below:
- The shield twisted pair cable is used in network LAN connections, connecting computers with target devices such as printers, modems, etc. It is advised not to use them in places where there is large electrical interference since they don’t have any metal shields.
- UTP cables are used for transferring audio signals in surveillance and security systems on NVR (network video recorders), DVR (Digital video recorders), and HVR (hybrid video recorder) components.
- Unshielded twisted pair cable is extensively used in horizontal & backbone cabling subsystems.
- UTP cables are used as ethernet cables and telephone wires for short to medium distances to transfer data and audio signals
- Unshielded twisted pair cable is also excellent for data transfer at low speeds and requires no grounding.
- They are used for signal transfer in automation and control systems.
- They are used for dumb terminal connections to mainframe computers.
- They are less expensive and hence can be used as patch cables.
- UTP cables are used in gigabit media converters, fiber media converters, and fiber optic switches
Different Categories of UTP cable
- CAT 1 Cables are usually used for telephone wiring. It transfers up to 1MBPS of data.
- CAT2 Cables are the second-lowest grade UTP cables used for supporting digital voice and data communication. It transfers up to 4 MBPS of data.
- CAT 3 Cables are third-grade unshielded twisted pair cables used for Token Ring and 10BASE-T Ethernet applications. It transfers up to 10 MBPS of data.
- CAT 4 Cables have four pairs of UTP copper cables used for Token ring networks. It transfers up to 16 MBPS of data.
- CAT 5 cables are used in structured cabling for Ethernet, Token ring, and Fast Ethernet connections. It transfers up to 100 MBPS data.
- CAT 5e cables are very popular and used in Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and Fast Ethernet connections. It transfers up to 1 GBPS data.
- CAT 6 cables are high-grade UTP cables used for Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Ethernet (55m) connections. It transfers up to 10 GBPS data.
- CAT 6a cables are also used for Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Ethernet (55m). It transfers up to 10 GBPS data.
- CAT 7 cables are top graded UTP cables used for Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Ethernet (100m). It transfers nearly 10 GBPS data.
UTP Cable Specifications & Performance
| UTP Cable Category | Grade | Business Application | Frequency Range |
| CAT 1 Cables | voice grade | Only telephone networks voice-grade Not suitable for data transmissions- | 750 kHz |
| CAT 2 Cables | voice grade | telephone networks voice-grade, mainframe computers IBM dumb-terminal connections | 1 MHz |
| CAT 3 Cables | data grade | voice-grade telephone networks, 4Mbps Token Ring, 10Mbps Ethernet 100BaseT4 Fast Ethernet, and 100 VG Any LAN | 16 MHz |
| CAT 4 Cables | data grade | 16Mbps Token Ring networks | 20 MHz |
| CAT 5 Cables | data grade | 100BastTX Fast Ethernet, OC-3 ATM networks, and SONET | 100 MHz |
| CAT 5e Cables | data grade | Gigabit (1000Mbps) Ethernet | 100 MHz |
| CAT 6 Cables | data grade | Gigabit (1000Mbps) Ethernet | 250 MHz |
| CAT 6a Cables | data grade | Gigabit (1000Mbps) & 10 Gigabit Ethernet | 500 MHz |
| CAT 7 Cables | Data grade | 1 Gbps or higher Ethernet-based computer networks | 600 MHZ |
Solid Conductor UTP Cable and Stranded Conductor UTP Cable
Solid Conductor UTP Cable
As the name suggests, Solid Conductor unshielded twisted pair cables have a single, solid conducting copper cable as the conductor. They are physically stronger and much easier to work with.
Solid Conductor twisted pair cabling have lower susceptibility and DC resistance to higher frequency effects due to their larger diameters. These properties enable these UTP cables to support longer distance transmission runs and higher data rates when compared to stranded type UTP cables.
Stranded Conductor UTP Cable
Stranded Conductor UTP Cables are usually preferred as patch cables in work areas and telecommunication rooms. In addition, they have commonly used twisted pair cabling in most network connections. When you look at the cross-section of a Stranded Conductor UTP Cable, you will find that each individual copper conductor is made up of a bunch of smaller size wire strands. These are arranged in such a way that several wires, usually in the range of 6-18, surround a single wire at the center of the bundle. The outer wires are arranged around a single wire through the process of stranding. They together form a single copper conductor with a diameter similar to a solid conductor UTP cable.
Applications of a UTP Cable
The different applications of UTP cables are,
- Used in LAN networks and Telephone connections
- Used in Ethernet connections from the slow speed to high-speed data transfers
- Used in connecting printers and modems to computer
- Used in Token Ring and 10BASE-T Ethernet applications
- Used in OC-3 ATM networks and SONET applications
- Used in IBM dumb-terminal connections to mainframe computers
FAQ
Why is the UTP cable is Unshielded?
The advantages of not shielding UTP cable. They are,
- Without shielding, the UTP cable becomes smaller in diameter and hence easy to install and takes up less space than STP cables
- UTP cables become less expensive as they don’t need a metal cover similar to STP cables
- These twisted pair cablings don’t need any grounding to work effectively
- The design is made for countering crosstalk, RFI, and EMI
- Almost every networking architecture use UTP cables
- They are excellent to be used as patch cables
- For home and office use, UTP is better than STP as they have less electrical interference.
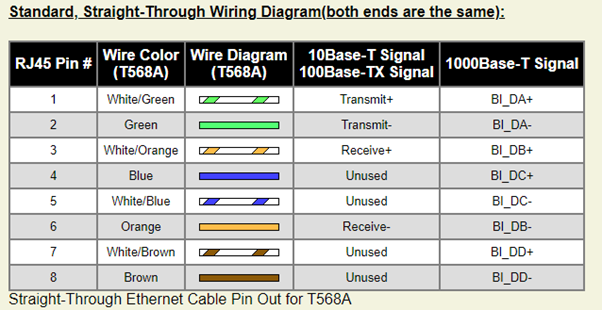
How to connect a UTP cable?
- Strip off or remove approximately 2″ of the ethernet cable sheath.
- Untwist the UTP cable pairs, but don’t untwist them beyond what you have exposed.
- Align the wires as per the diagram below.
- Insert the copper wires into the RJ45 plug and ensure each wire is completely inserted into the front of the RJ45 plug and in the right order.
- Verify the copper wires are in the right order and ensure the cables extend to the front of the RJ45 plug, and make decent contact with the metal connections in the RJ45 plug.
- Repeat for the 2nd RJ45 plug.
What is the difference between UTP & STP Cable?
| Parameters | UTP Cable | STP cable |
| Structure | These cables have twisted pairs of copper wires | These cables have twisted pair of copper wires enclosed in a metal foil |
| Form | Unshielded twisted pair cable | Shielded twisted pair cable |
| Cost | Relatively cheaper than STP cables | More expensive than UTP cables |
| Electrical Interference and Noise | Prone to Electrical Interference and Noise | Less prone to Electrical Interference and Noise |
| Data transfer speed | Supports slower speed | Supports higher speed |
| Grounding | Not necessary | Necessary |
| Target locations | Homes and Offices | Airports and factories |
Which UTP cable is most commonly used?
Stranded Conductor UTP Cable is the most commonly used unshielded twisted pair cable in most network connections. The advantages it offers are,
- The flexibility is much better than solid conductor UTP cables
- These have better shelf life than solid types and have good resistance against wear & tear, and vibrations
- They can be used as patch cables
- The scratching and nicking effects cause less damage to Stranded Conductor UTP Cable.
- For increased flexibility, we can add more copper wire strands which are not possible in solid-type.
What is UTP cable commonly used for?
UTP cables are commonly used as telephone wired and ethernet cables in telephone connections and LAN (Local Area Networks). It is used to transfer audio signals and electronic data. These are also used in horizontal and backbone cabling subsystems.
Why is UTP popular in LAN technology?
The main reasons UTP cables are popular in LAN technology are,
- It is less expensive when compared to STP cables
- Installation is quick and easy
- As the twisted-pair cabling size is less, a lot of space is saved
- It is unaffected by grounding issues
- It can counter RFI, crosstalk, and EMI
- It works very well even at lesser data speed
How does UTP cable transmit data?
The data sent over an unshielded twisted pair cable is converted into binary code consisting of 0s and 1s. The device that transmits data will send the current along the cable at two different voltages, 0 and 5 volts. On the other hand, the device receiving the data will interpret these voltages as binary codes and then reconvert them to the original format.
How many twists per inch is Cat6?
While CAT 5E cables have 1.5 to 2 twists per cm, CAT6 cables are wound more tightly with 2 or more twists per cm. To reduce crosstalk, the twist rates are varied in most UTP cables.
Which category cat of UTP cabling is the fastest?
Currently, CAT 6 cables are the fastest among all the UTP cable types used in Gigabit (1000Mbps) & 10 Gigabit Ethernet connections and 500 MHZ frequency range.
Difference b/w shielded twisted pair cable and unshielded twisted pair cable?
| Unshielded twisted pair cable | Shielded twisted pair cable |
| These are twisted pairs of copper wires | These cables have twisted pair of copper wires covered by a metal foil |
| Grounding cable is not required | Grounding cable is required |
| Less expensive | Costlier than UTP cables |
| Less maintenance and repair needed | Less maintenance and repair needed |
| Noise is higher | Noise is less |
| attenuation is high | attenuation is low |
| Works well with low data speed | Works well with high data speed |
What connector is used for twisted pair cable?
The standard connector configuration used for unshielded twisted pair cable is the RJ-45 connector. RJ is an acronym for Registered Jack which means that the connector follows standards set by telephone companies.