
We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- What is 5G
- What is it capable of
- 5G vs earlier generations
- How 5G exceeds 4G – 4G vs 5G
- 5G in India
- 5G uses
- STL and 5G technology
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following 5G FAQs:
- What will 5G do?
- Which countries have 5G? 5G network countries?
- Who developed 5G?
- Will 5G kill WiFi?
- What underlying technologies make up 5G?
- How and when will 5G affect the global economy?
- What does 5G mean for consumers?
- How do cities use 5G?
- 5G speed – How fast is 5G?
- How does 5G work?
- Does 5G change my home internet service?
- Do I need a new phone with 5G technology to work?
Contents
What is 5G all about?
5G is the next buzzword in the field of wireless technology networking. Simply said, it is wireless technology’s fifth generation. The fifth generation of technology is expected to be bigger, faster, and better. 5G architecture is based on a considerably higher next-generation technology plane, with the goal of connecting everything and everyone – people, buildings, cities, sensors, smartphones, robots, and drones. As compared to the existing wireless technology, it will have higher data rates, reduced latency, higher capacity system, energy savings and cost reductions. It will bring new capabilities and create opportunities for society and business. Here is some of the excited chatter about 5G:
“Connected cars will shape the future of individual mobility, and next-generation mobile networks will take car‑to‑x connectivity to a new level.” – Alfons Pfaller, Head of Infotainment Development, AUDI AG
“The adoption of 5G will be even faster than what we saw on 4G, which was already fairly fast,” said Ignacio Contreras, Qualcomm’s director of marketing
“5G will be the post-smartphone era,” said Robert J. Topol, Intel’s general manager for 5G business and technology. “Phones are the first place to launch because [they’re] such an anchor in our lives from a connectivity standpoint.”
“5G is one of those heralds, along with artificial intelligence, of this coming data age,” said Steve Koenig, senior director of market research for the Consumer Technology Association.
What is 5G capable of?
Imagine living in a world where people, gadgets, buildings, and infrastructure talk to each other. In this world, doctors can conduct surgeries from thousands of miles away; cars drive on their own; buildings, factories and cities can interact with you; and you can shop and watch live sports events in VR!
Now open your eyes, because we’re not talking about a sci-fi movie here. Rather, this is what our world will become thanks to 5G – hyper-connected, secure and experiential on an unimaginable scale.
Fascinating, right?
What makes 5G different?
So far, with technologies like 4G, we have mostly imagined connectivity as human-to-human, or human to the internet. But, with 5G, that will no longer be enough.
The next natural evolution of connectivity is to not only connect everyday machines and devices to humans but machines to other machines. In fact, the entire promise behind 5G lies in connecting our entire environment with each other! With the number of connected devices globally set to triple by 2030 to 25.4 billion, terms like Internet of Things (IoT), Virtual Reality (VR), and Artificial Intelligence will no longer be just fanciful connotations of what will happen in the future. All these amazing experiences will be unlocked on the back of 5G.
- Enhanced mobile broadband (EMBB) – Faster data rates, wider network coverage areas, enhanced ultra-HD video streaming
- Ultra-reliable, low latency communication (URLLC) – Increased communication speed and quality in critical functions such as robots and drones
Massive machine-type communication (MMTC) – Automatic generation, processing and transmission of data between machines with almost zero human intervention
Differences between the previous generations of mobile networks and 5G
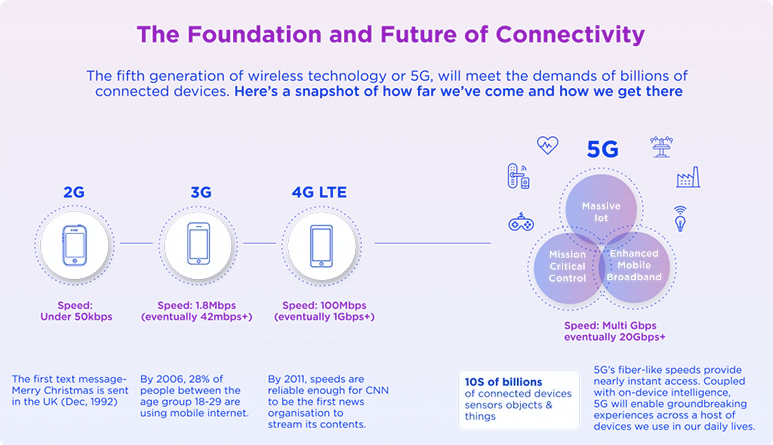
Let us chart out the journey of various generations of wireless technology to fully understand the phenomena of the fifth generation:
1G, or the first generation of mobile networks, was established in the 1970s and 1980s and carried only speech data. They were transmitted unencrypted across radio waves. Japan pioneered the 1G revolution. The disadvantages of 1G were low coverage and sound quality, lack of system interoperability, and unencrypted voice.
The term “2G” first appeared in the 1990s. The communications were digital and encrypted. Data of higher quality could be shared. Text, photo, and multimedia communications could be sent. This resulted in a revolution in telecommunications. Mobile cell towers appeared, and consumers and companies quickly adopted them. Smartphones were invented.
3G was constructed in the early 2000s. Because online connectivity was standardized in this age, people could access data from anywhere in the world. This was four times quicker than two gigabits per second. 3G enhanced data transfer capabilities as well as video conferencing, video streaming, and voice quality. This generation’s characteristics were included in the launch of Blackberry. iPhones were introduced in 2007, and 3G technology made smartphones a necessity rather than a luxury item.
4G: Apple, Google, and Facebook were instrumental in the introduction of 4G technology. Consumers now have access to high-quality video streaming thanks to 4G technology. Currently, the most widely utilised technology, 4G technology, provides high-definition videos, conferencing, and gaming services. Switching from 2G to 3G was as simple as swapping sim cards. However, a change in mobile devices is required for 4G.
5G: We are at the cusp of the 5th generation revolution. This generation promises higher speed, reduced latency, energy savings and higher capacity systems. The superior connectivity offered by 5G aspires to equal access to the network regardless of location or social status in society. 5G offers the possibility of innovations such as remote surgeries, telemedicine, self-driving cars, smart cities, smart buildings and smart factories, virtual reality experience while gaming, shopping and viewing sporting events. It looks to expand wireless services from the internet to the Internet of Things and communication sectors.
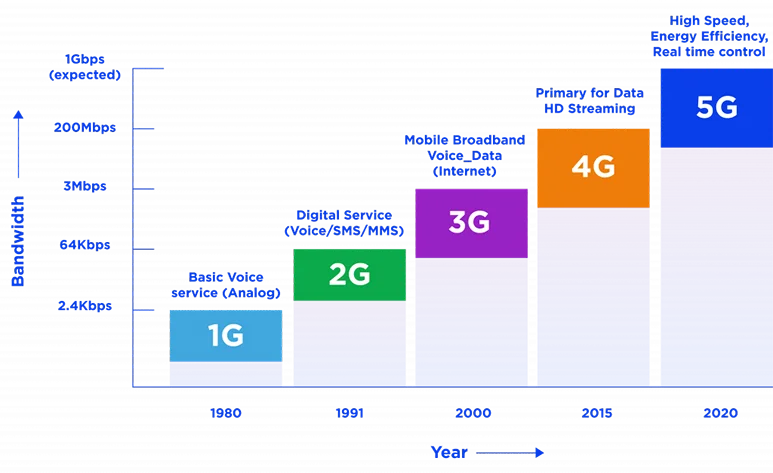
How is 5G better than 4G?
For starters, think of 5G as not the natural evolution of 4G but a new, more advanced technology itself.
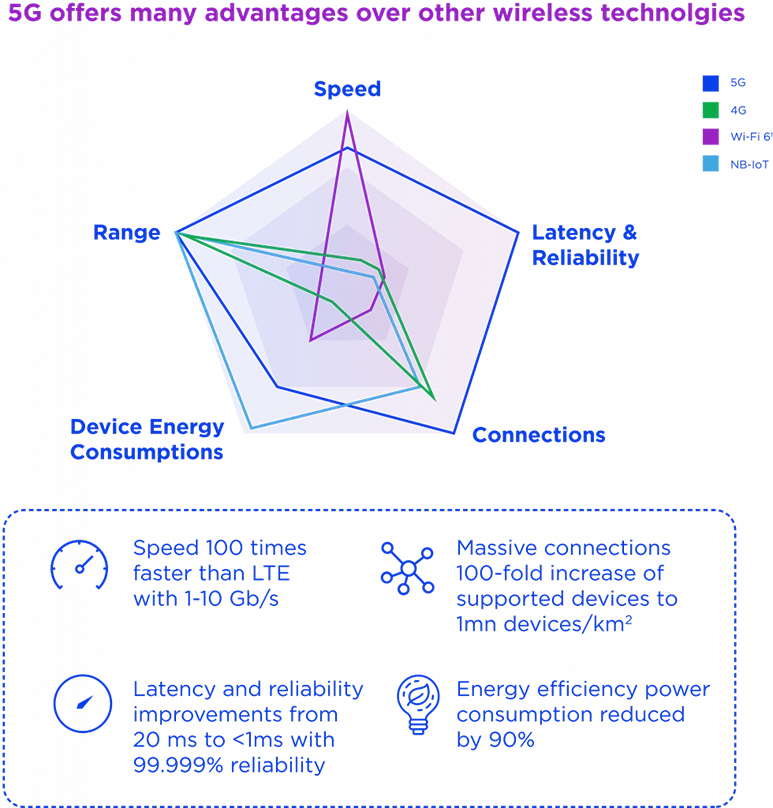
While earlier generations used cell towers to transmit signals, 5G will use small cell technology. This means that carriers will deploy high band 5G smalls cells in multiple locations. Additionally, as part of its OFDM coding, 5G technology is built to use 100 to 800 MHz channels instead of 4G’s 20 MHz. Remember, the higher the channels, the more the download speed. Thus, 5G is 20 times faster than the previous generation, has much lower latency and tremendously improved reliability. It allows a higher number of users to connect simultaneously, while lower latency will ensure greater download speed.
| 4G | 5G | |
| Bandwidth | 200mbps | 1gbps |
| Download Speed | 1gbps | 10gbps |
| Latency | 60-90ms | 1ms |
| Base Station | Cell towers |
Small cells |
| OFDM Coding | 20MHZ channels | 100-800 MHZ channels |
5G in India
Owing to increased mobile and broadband penetration, India is already in the midst of a digital revolution. But once the future of 5G in India comes to fruition, it will spearhead this revolution and transform the productivity, experiences and aspirations of a billion people in a blink of an eye.
Today, “When is 5G coming to India?” and “Is 5G already in India?” are two of the most pressing queries that all knowledgeable Indians have. Although the central government envisioned a viable, robust 5G network in India by 2018, insufficient spectrum availability, exorbitant spectrum pricing, poor test case development, insufficient back-haul capacity, low reach of optical fibre across the country, and delays in planning have pushed the date to the second half of 2021.
Despite all these issues, the number of 5G-connected devices in India is forecasted to be around 350 million by 2026, as per Ericsson. This means that the nation is ready to embrace the next-gen technology soon, with companies involved in 5G in India such as telecom giants like Airtel and Jio ready to commercially roll out 5G by October 2021.
At present, all industry stakeholders in the country, including 5G infrastructure companies in India, are actively involved in readying the necessary 5G-compliant ecosystem in wake of the roll-out. The Department of Telecom is focused on R&D around PPP projects, testbeds, pilot roll-outs and standards formulation. They are also working with TRAI and other stakeholders on a Spectrum Management Framework while encouraging collaborations between start-ups and ICT companies. Simultaneously, Indian telcos and OEMs are conducting 5G deployment feasibility studies. Indian IT sector has come up with its own set of solutions and 5G applications to support this new era of connectivity. In terms of fibre penetration to enhance 5G reach and distance, India plans to increase fibre backbone to 2.5 million km by 2022, with 300,000 km of fibre planned under the BharatNet programme for rural areas.
So, how will 5G change India?
The answer is simple: kickstarting the Industrial Revolution 4.0 to bring us technologically on par with global leaders like China, Japan, the US and Western Europe. As the industry develops hundreds of 5G use cases, many of the applications like IoT, smart cities and automation will enable us to transform the country’s manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, education, IT, work and living infrastructure. Reasonably, many emerging companies to benefit from 5G in India will belong to these domains, further contributing to the economy. Indeed, there is a strong belief amongst the nation’s leaders and visionaries that 5G will be the catalyst in pushing India to become a $1 trillion economy by 2025.
Where is 5G being used | Industry Applications | Real Life Examples
5G technology is truly all-inclusive. Here are some of the industries where 5G technology is being used to revolutionize things:
- Smart cities and smart buildings: With IoT (Internet of Things) sensors being able to monitor and collect data on air quality, energy usage, traffic patterns for cities, civic authorities will be able to manoeuvre operations effectively. Emergency vehicles will connect to destinations unhindered, smart buildings will have disruption-free basic amenities and connected buildings will make remote working the norm!
- Manufacturing sector: Artificial intelligence will analyse vast volumes of data being collected in order to automate human procedures such as quality control, standardisation, precision checking, and so on. End-to-end automation via the IoT (Industrial Internet of Things) will enable smart firms to employ robots for dangerous/repetitive tasks.
- Farming sector, environment: Connected devices will transform data on weather conditions, crop health, chemical levels, pest presence, allowing proper labour allocation, cost and waste reduction and yield. Environmental monitoring, both flora and fauna, and restoring ecological balance in accessible areas will be a reality.
- Healthcare, telemedicine: Remote diagnosis and surgeries will become common, while medical device implants will capture and transmit health data to specialists with ease, making early detection of diseases possible.
- The automobile sector, transportation: Self-driving vehicles that can communicate in real-time with other nearby vehicles and fixed roadway infrastructures will be possible.
- Virtual reality, entertainment, live event experiences: Virtual Reality will become more viable, enabling remote working from global locations, or an authentic live sports stadium experience at home. Virtual shopping in different cities of the world will emerge while downloading offline entertainment will be redundant.
How is STL Transforming the 5G scope?
STL has been ready for the 5G technology revolution. In July 2020, Sterlite Technology Limited mentioned that it would be investing in 5G architecture to develop the Make in India ecosystem. The investment would be in the form of hardware, software and people recruitment. 5G India is what STL is working towards.
“We are seeing the current telecom infrastructure evolving to a new digital network architecture – virtual, converged, disaggregated, and close to the Edge”, said Anand Agarwal, Group CEO, STL. He added that STL is positioned with its 5G ecosystem and digital network integration capabilities to deliver next-generation digital networks for its customers globally.
Looking at the future, STL is among the chief Indian companies involved in 5G technology and has set up end to end 5G ecosystem with its strong portfolio of optical fibres and wireless technology. STL has also emerged as one of the major 5G cable companies in India with plans to invest ₹300 crores for augmenting optical fibre capacity across India and Europe from 18 to 33 million km. At STL, we have also invested in a one-of-a-kind end-to-end development of fully programmable, open and disaggregated Open RAN 5G-NR and Private LTE solutions that leverage real-time intelligence and Edge Convergence Orchestration to deliver enhanced network performance. Our portfolio of 5G-enabled wireless solutions for citizen networks, telcos, enterprises and governments include small cells, outdoor multi-band radio and Open RAN standards complaint WiFi-6 solutions. These antennas and radio equipment stand to greatly boost speed and connectivity in dense areas. Our products for telcos also include machine learning and AI-enabled RAN Intelligent Controller, Orchestration and VNF solutions!
FAQs
- What will 5G do?
5G technology will create a connected, secure world through connectivity. People, gadgets, buildings, infrastructure will be talking to each other through this next-generation technology. Possibility of remote surgeries, telemedicine, self-driving cars, smart cities and smart factories, virtual reality experience while gaming, shopping and viewing sporting events is what 5G is built to do.
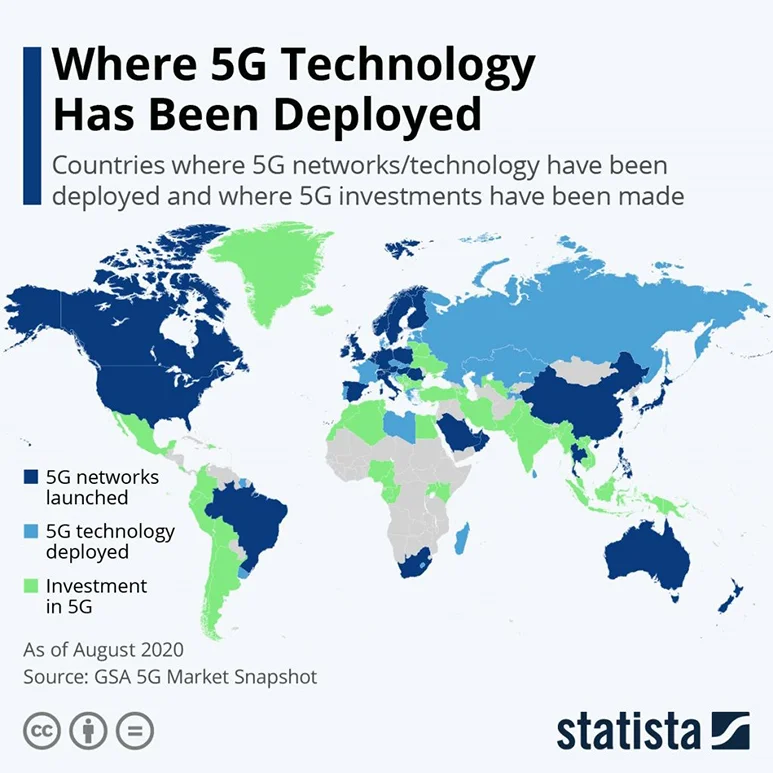
- Which countries have 5G? 5G network countries?
As of August 2020, 38 countries have 5G networks deployed. A quick review of the infographics from Statista will give us an idea:
- Who developed 5G?
Development of 5G cannot be attributed to a single person or company. It is really a collaboration between various parts of the world. The important thing is to have a uniform standard for the proper development of 5G technology. The standards for 5G technology was set by 3GPP in mid-2018. 3GPP is a conglomerate of 7 regional organizations.
- Will 5G kill WiFi?
As of now, 5G technology is not built to cross out WiFi. 5G could provide an alternate in places having sketchy WiFi. It is better if WiFi and 5G work in tandem with each other and develop better versions to achieve the goal of strong connectivity.
- What underlying technologies make up 5G?
5G technology is based on OFDM. OFDM means the process of coding digital data on different bandwidths and frequencies. Along with OFDM, 5G technology also uses 5G NR air interface.
- How and when will 5G affect the global economy?
According to a report by Huawei, 5G technology could add $1.5 trillion by 2030, across key industries.
STL mentioned that 5G technologies solutions could add $200 billion in benefits.
- What does 5G mean for consumers?
With 5G technology, a faster mobile internet connection is just the beginning, for consumers. A stronger, secure connection at greater speed and lower latency will help the consumer with many more devices being connected with this next-generation technology. Self-driving cars, smart homes, virtual reality experience while gaming, shopping and viewing sporting events, tele-medicines and remote health monitoring are what the consumers can look forward to with 5G.
- How do cities use 5G?
IoT (Internet of Things) sensors will monitor and collect data on air quality, energy usage, traffic patterns for cities. This will help civic authorities to effectively manoeuvre their operations. Emergency vehicles like ambulances, fire engines, police cars will be able to connect with their destination unhindered. Smart buildings will be able to supply basic amenities without disruptions and would become hub spots for the working population. These are the benefits of smart cities using 5G technology. Millions of devices will be connected to help collect data and operate based on demand and supply. Some of the sectors which will be truly automated ad connected for cities is below.
- 5G speed – How fast is 5G?
The 5G speed is 20 times faster than the previous generation, has much lower latency and tremendously improved reliability. Theoretically, 5G download speed is set to achieve 10gbps over 1gbps for 4G technology.
- How does 5G work?
5G uses cell sites that divide the area into sectors and send data through radio waves. This principle is similar to earlier networks. Each cell site should be connected to a network, and the type of network 5G uses is OFDM. This enables the 5G radio waves to get better speed through more efficient coding.
- Does 5G change my home internet service?
5G is a wireless solution. The Internet needs cables that connect to modems which then connects to the home internet. At present, it seems that 5G and home internet will probably run in tandem together. 5G will not be able to replace internet services totally in the immediate future as it has its own settling it parameters.
Wireless 5G reception might not be similar in various local geographies – urban and rural. The 5G wireless services might be costlier at the beginning for individuals. Moreover, not all gadgets are yet 5G compliant, hence might not run if the fifth generation is fully encompassed.
- Do I need a new phone with 5G technology to work?
The simple answer is that you will need a 5G compliant phone to access a 5G technology network. However, one need not discard the old phone yet. 5G technology works distinctly on top of the 4G technology. If your phone is working on 4G, it will continue to do so. 5G will not replace 4G wireless technology soon and your 4G technology-enabled phone will continue to work.















1 Comment
Aditya
November 18, 2020Very informative and well written! Covers all aspects of 5G!