In today’s digital age, businesses increasingly use cloud computing for innovation and scalability. Cloud migration, the process of moving applications and data to the cloud, is crucial for this transformation.
Fig 1: Banner
Image source: bluepiit.com
Cloud migration can’t be put on hold anymore. The global cloud computing market, valued at $445.3 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $947.3 billion by 2026, showcasing remarkable growth. This translates to an increase of more than $500 billion within five years.
Managed services play a crucial role in simplifying the complexities of cloud migration. Our blog explores the best practices for successful cloud migration with managed services. We cover assessing infrastructure, selecting the right cloud platform, and designing a robust migration plan.
Exploring Best Practices: Achieving Successful Cloud Migration with Managed Services
Contents
- 0.1 1. Foster conviction and alignment among senior leaders
- 0.2 2. Establish accountable leaders and train your teams
- 0.3 3. Build a Migration Plan
- 0.4 4. Observe application performance
- 0.5 5. Licensing and Migration Cost
- 0.6 6. Validate cloud security
- 0.7 7. Network Management
- 0.8 8. Enhancing Migration Efficiency: Overcoming Delays and Optimizing Speed
- 1 Conclusion
- 2 FAQs
1. Foster conviction and alignment among senior leaders
Cloud migration goes beyond technology; it is a comprehensive digital transformation that can modernize your entire organization, unlocking new efficiencies and capabilities to drive innovation across all business departments. However, successful migration requires a strong commitment from leadership. To ensure buy-in, establish clear goals that resonate with all stakeholders. Set timelines, benchmarks, and effective progress measurement mechanisms to keep the team informed. You can achieve the desired results by avoiding delays, implementing timely solutions, and staying focused without making false starts or losing momentum.
2. Establish accountable leaders and train your teams
Your team must be committed, skilled, and ready to embrace new working methods for successful top-down goals. Fortunately, most techies love the cloud, as it offers learning opportunities, innovation, and faster digital transformation. However, some may resist change, hindering progress or derailing plans.
Communicate the non-negotiable nature of the cloud journey, backed up by executive sponsorship and transformative results, to ensure buy-in. Address concerns about transitioning roles and highlight the opportunities in the cloud-led world.
Overcome hurdles by appointing accountable leaders passionate about cloud transformation. They will keep their teams focused on business goals, measure progress, and report to senior management. Train your teams to acquire cloud understanding and capabilities to navigate the hybrid environment effectively.
3. Build a Migration Plan
The 5 R’s, namely Rehost, Refactor/Re-architect, Revise/Replatform, Rebuild, and Replace/Repurchase, form a set of strategies for cloud migration. Each approach offers organizations different options to consider when transitioning their applications to the cloud.
Rehosting, also known as lift and shift, involves migrating applications to the cloud without making significant changes to the underlying architecture. It provides a quick and efficient migration process but may not fully leverage cloud-native capabilities. This approach is suitable for enterprises aiming for a timely transition from on-premises to the cloud.
Refactoring or re-architecting involves rewriting applications to optimize them for the cloud environment. This method allows businesses to take advantage of cloud-native features and improve performance. It requires more resources but enables scalability and automation.
Revise/Replatform involves revising applications to take advantage of specific cloud provider infrastructure features. It requires upfront investments and may involve modifying the existing codebase before applying other migration strategies.
Rebuilding entails rebuilding applications from scratch, utilizing cloud-native features and cutting-edge capabilities. This approach maximizes the benefits of the cloud platform but requires a significant time and financial commitment.
Replace or repurchase involves replacing legacy systems with equivalent or similar functionality offered by Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions. This method can streamline the migration process, especially when legacy applications are not compatible with the cloud.
It is important to carefully assess each approach in relation to specific business requirements, considering factors such as time, resources, scalability, and compatibility, to determine the most suitable strategy for a successful cloud migration.
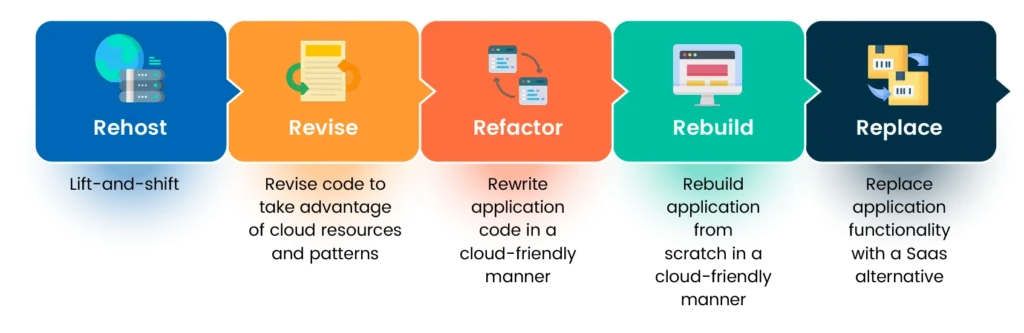
Fig 2: 5R strategy
Image source: qentelli.com
4. Observe application performance
Utilizing tools to monitor the essential resources (such as CPU, disk, network, and storage) that drive your applications, regardless of whether they are hosted on-premises or in the cloud, provides valuable insights into the overall health of your underlying system. However, these tools may not offer visibility into application state, responsiveness, or potential errors.
It is beneficial to collect and analyze this data in your current infrastructure configuration and compare it with the post-migration cloud environment to gain a comprehensive understanding of the new state. Combining observations of system-level resources with application performance monitoring can effectively identify instances of over- or under-provisioning in your new setup.
5. Licensing and Migration Cost
Managing licenses and migration costs is a critical aspect of cloud migration. It involves overseeing operating system licenses, application server licenses, and licenses for third-party tools. It is important to validate whether licenses can be transferred or converted into cloud-based licenses. Cloud providers often include operating system licenses in the instance cost, but some may offer options to apply for Windows licenses at the host level. License management for third-party tools is an area that is continuously evolving and being refined. When considering licenses, one can choose between bringing their own license (BYOL) or opting for a pay-per-use model. It is essential to evaluate the costs associated with migration tools, including any expenses related to third-party tools.
6. Validate cloud security
According to 81% of survey respondents, ensuring strong cloud security throughout the migration process is of utmost importance. Leveraging machine data, including analytics and machine learning, plays a vital role in detecting vulnerabilities. Furthermore, analyzing unprocessed log data uncovers security violations and identifies gaps, enabling prompt resolution in the existing environment while carrying over the necessary measures to the cloud.
7. Network Management
To ensure a smooth migration, planning the entire cloud architecture in advance and allocating resources to their respective subnets is essential. The cloud enables the creation of virtual private networks and subnets with specific IP addresses, facilitating routing between them. Legacy application components should retain their original IP addresses for uninterrupted functionality. To achieve seamless migration and communication, resources should be mapped to the same domain name, and clear instructions should be provided to stakeholders to prevent confusion.
Figure 3: Steps for Cloud Migration Strategy
Image source: linkedin.com
8. Enhancing Migration Efficiency: Overcoming Delays and Optimizing Speed
Choose the right migration pattern to prevent stalls and slowdowns in the migration process. Overcoming common stalls requires addressing anti-patterns. Continuous executive buy-in wastes time. Migrating everything at once causes challenges and delays benefits. Gradually moving to a cloud-native architecture helps overcome this. Pursuing non-convergent goals leads to ineffective results. Alignment among teams is essential for a successful migration, addressing specific problems, and achieving desired outcomes.
Conclusion
Successful cloud migration is a crucial step for businesses seeking innovation and scalability in today’s digital landscape. By following best practices and leveraging the expertise of managed service providers like STL Global Services, organizations can navigate the complexities of cloud migration with confidence. From fostering leadership alignment and training teams to building a robust migration plan and ensuring security and network management, businesses can unlock the full potential of the cloud. Embrace these best practices and embark on a transformative cloud journey to drive innovation and future-proof your organization.
FAQs
The 5 R’s – Rehost, Refactor/Re-architect, Revise/Replatform, Rebuild, and Replace/Repurchase – are strategies for cloud migration. Rehost involves quick migration without architectural changes; Refactor/Re-architect optimizes applications for the cloud; Revise/Replatform adapts applications to leverage cloud infrastructure; Rebuild involves rebuilding applications from scratch; and Replace/Repurchase replaces legacy systems with SaaS solutions. Assessing factors like time, resources, scalability, and compatibility is crucial to determining the most suitable strategy for successful cloud migration.
Transitioning to a DevOps operating model in a cloud-first world allows enterprises to maximize the business impact of their applications. Developers are freed from platform governance concerns by having a central team handle the configuration and integration of platform services. This enables faster application migration and optimization by utilizing standardized, self-service enterprise capabilities.
Follow these steps for a successful cloud migration:
● Appoint a dedicated migration manager who will oversee the entire migration process, make informed decisions, and ensure effective coordination among all stakeholders.
● Develop a comprehensive plan that encompasses account structure, security measures, and governance policies aligned with the desired migration key performance indicators (KPIs).
● Evaluate and choose the most suitable migration strategy from the options available, such as the “6 R’s” (Rehost, Refactor, Revise, Rebuild, Replace, or Retire), considering the specific needs and requirements of the applications being migrated.
● Assess the various cloud deployment options, including public, private, and hybrid cloud, and select the one that best aligns with your organization’s objectives and considerations, such as data privacy, control, and scalability.
● Thoroughly calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for the migration project, taking into account both the initial migration expenses and the ongoing operational fees associated with the chosen cloud solution.
By following these steps, organizations can navigate the cloud migration process more effectively and increase their chances of a successful and smooth transition.
Monitoring and governance ensure efficient cloud migration by examining the environment, correlating components, and optimizing performance. By capturing application, system, network, and audit logs, organizations can visualize enhancement areas and reduce infrastructure costs through right-sizing. Effective monitoring and governance maximize benefits and minimize risks in the migrated environment.
What is a cloud-managed service?
Cloud Managed Service is the outsourcing of various IT operations and tasks to a third-party service provider, for cloud-based infrastructure management and maintenance, including monitoring, optimization, security, backup, and technical support of cloud resources, such as servers, databases, storage, networking, and applications.
What are the benefits of partnering with a managed cloud service provider?
– Cost Savings
– Updated network infrastructure along with evolving technology
– Enables faster disaster recovery with minimal downtime.














